
How can the formation of sigma and pi bonds be explained?
Answer
547.5k+ views
Hint: The orbital overlapping decides the type of bond formation. There are hydrocarbons which are saturated and unsaturated. The saturated compounds have only one type of bond which is sigma bond while the unsaturated have two types of bonds sigma as well as pi bonds. There are unsaturated compounds which are having more than one pi bond.
Complete step-by-step answer:The formation of bond can take place either by giving or taking up the electrons or by sharing them. The sharing of electrons by which the chain size increases is called a property of catenation. Carbon is the most popular atom to show catenation properties. After that we have silicon. The catenation property of carbon gives rise to two types of bond formation which are sigma and pi bonds.
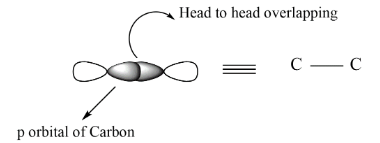
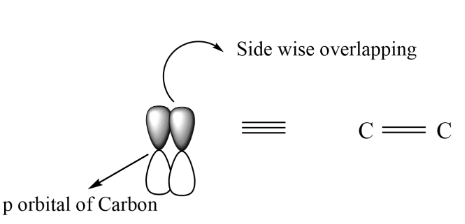
In case of sigma bond there is head to head overlapping between the orbitals by which the bond formed is termed as sigma bond and represented as, $C - C$ . On the other hand, when the side wise overlapping takes place, it is termed as pi bond and can be represented as, $C = C$
If we see the overlapping of the orbital , these can be explained by the formation of sigma and pi bonds.
Note: In any compound the pi bond can be detected by using alkaline \[KMn{O_4}\] solution this solution changes color if there is a double or triple bond. In double bond there is only one pi bond while in case of triple bond two pi bonds are present which are shown above are perpendicular to each other. In place of alkaline \[KMn{O_4}\] bromine water is also used.
Complete step-by-step answer:The formation of bond can take place either by giving or taking up the electrons or by sharing them. The sharing of electrons by which the chain size increases is called a property of catenation. Carbon is the most popular atom to show catenation properties. After that we have silicon. The catenation property of carbon gives rise to two types of bond formation which are sigma and pi bonds.
In case of sigma bond there is head to head overlapping between the orbitals by which the bond formed is termed as sigma bond and represented as, $C - C$ . On the other hand, when the side wise overlapping takes place, it is termed as pi bond and can be represented as, $C = C$
If we see the overlapping of the orbital , these can be explained by the formation of sigma and pi bonds.


Note: In any compound the pi bond can be detected by using alkaline \[KMn{O_4}\] solution this solution changes color if there is a double or triple bond. In double bond there is only one pi bond while in case of triple bond two pi bonds are present which are shown above are perpendicular to each other. In place of alkaline \[KMn{O_4}\] bromine water is also used.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




