
Formation of real image using a biconvex lens is shown below:
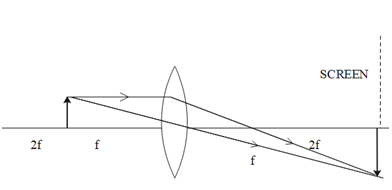
If the whole set up is immersed in water without disturbing the object and the screen position, what will one observe on the screen?
(A) Image disappears
(B) No change
(C) Erect real image
(D) Magnified image

Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint To find out what will appear in the screen, we need to apply the Lens maker’s formula. We have to find out what will happen for the focal length of the lens, and thus, from there we will get to know what will happen to the image.
Formula used In this solution we will be using the following formula,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {{u_{rel}} - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right)$
Where, the focal length of the lens be $f$,
the object distance be $u$, the image distance be $v$,
$\Rightarrow {\mu _{rel}}$ be the relative refractive index of the lens to that of the refractive index of the medium and
${R_1}$ and ${R_2}$ be the radius of curvature of the lens on two sides.
Complete step by step answer
Let us consider the focal length of the lens be $f$, the object distance be $u$, the image distance be $v$, ${\mu _{rel}}$ be the relative refractive index of the lens to that of the refractive index of the medium.
Then, from the lens maker’s formula we can write as,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {{u_{rel}} - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right)$
Here, when we immerse the apparatus in water without changing the object and screen positions, if the relative refractive index changes, the focal length of the lens also changes.
This reflects in the change in object and image distance. But, as we are not changing the object distance, the image distance gets influenced by the change in focal length.
Thus, the image's distance changes.
Since, we did not change the distance from the screen also, so we cannot get the image reflection on the screen. Thus, the image disappears.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note
The limitations of lens maker’s formula includes,
-The lens needs to be thin. This is because the separation between the two refracting surfaces will also be small.
-The medium on either side of the lens needs to be the same.
Formula used In this solution we will be using the following formula,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {{u_{rel}} - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right)$
Where, the focal length of the lens be $f$,
the object distance be $u$, the image distance be $v$,
$\Rightarrow {\mu _{rel}}$ be the relative refractive index of the lens to that of the refractive index of the medium and
${R_1}$ and ${R_2}$ be the radius of curvature of the lens on two sides.
Complete step by step answer
Let us consider the focal length of the lens be $f$, the object distance be $u$, the image distance be $v$, ${\mu _{rel}}$ be the relative refractive index of the lens to that of the refractive index of the medium.
Then, from the lens maker’s formula we can write as,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {{u_{rel}} - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right)$
Here, when we immerse the apparatus in water without changing the object and screen positions, if the relative refractive index changes, the focal length of the lens also changes.
This reflects in the change in object and image distance. But, as we are not changing the object distance, the image distance gets influenced by the change in focal length.
Thus, the image's distance changes.
Since, we did not change the distance from the screen also, so we cannot get the image reflection on the screen. Thus, the image disappears.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note
The limitations of lens maker’s formula includes,
-The lens needs to be thin. This is because the separation between the two refracting surfaces will also be small.
-The medium on either side of the lens needs to be the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




