
Formation of primary spermatocyte/oocyte from a spermatogonium/ oogonium requires
(a)Mitosis
(b)Meiosis I
(c)Meiosis II
(d)Growth
Answer
584.1k+ views
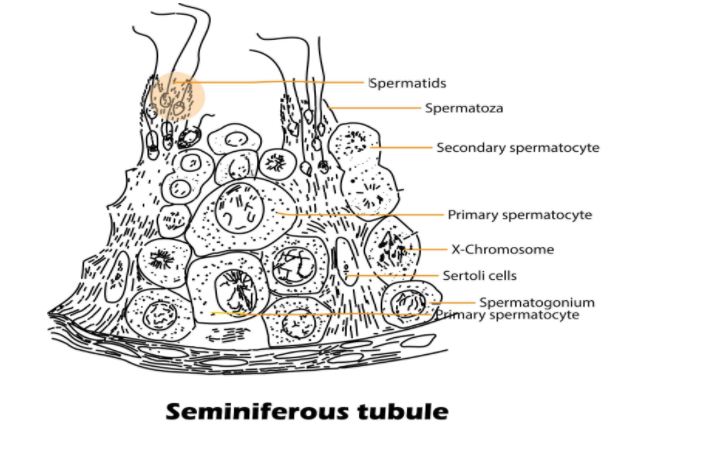
Hint: In humans, the seminiferous tubules are located within the male testes. The Sertoli cells are surrounded by spermatogenic cells on the epithelial interior, these cells and stem cells (or spermatogonia) exteriorly make up the seminiferous tubules.
Complete answer:
The spermatogonia (singular Spermatogonium) are an undifferentiated male germ cell and are present on the inside wall of seminiferous tubules. It multiplies by mitotic division and increases in numbers and is diploid and contains 46 chromosomes. A spermatogonium undergoes spermatogenesis to form mature spermatozoa. There are three types of spermatogonia:
Type A (dark)- they are cells with dark nuclei and are reserve spermatogonial stem cells. They don’t usually go through mitosis.
Type A (pale)- they are cells with pale nuclei and are the spermatogonial stem cells. They undergo active mitosis to produce Type B cells.
Type B cells- they grow to become primary spermatocytes. They accumulate large amounts of nutrient and chromatin material and increase in size.
Primary spermatocytes are diploid (2N) cells and after completing the first meiotic divisions lead to the formation of two equal, haploid cells called secondary spermatocytes. These contain half the number of chromosomes and thereby give rise to male gamete-sperm.
So, the correct answer is ‘Growth’.
Note: Sertoli cells are nurse cells that create a hematotesticular barrier and give nourishment to the spermatozoa. The sperm heads become embedded in these cells after the process of spermiogenesis. They are finally released from the seminiferous tubules by a process called spermiation.
Complete answer:
The spermatogonia (singular Spermatogonium) are an undifferentiated male germ cell and are present on the inside wall of seminiferous tubules. It multiplies by mitotic division and increases in numbers and is diploid and contains 46 chromosomes. A spermatogonium undergoes spermatogenesis to form mature spermatozoa. There are three types of spermatogonia:
Type A (dark)- they are cells with dark nuclei and are reserve spermatogonial stem cells. They don’t usually go through mitosis.
Type A (pale)- they are cells with pale nuclei and are the spermatogonial stem cells. They undergo active mitosis to produce Type B cells.
Type B cells- they grow to become primary spermatocytes. They accumulate large amounts of nutrient and chromatin material and increase in size.
Primary spermatocytes are diploid (2N) cells and after completing the first meiotic divisions lead to the formation of two equal, haploid cells called secondary spermatocytes. These contain half the number of chromosomes and thereby give rise to male gamete-sperm.
So, the correct answer is ‘Growth’.
Note: Sertoli cells are nurse cells that create a hematotesticular barrier and give nourishment to the spermatozoa. The sperm heads become embedded in these cells after the process of spermiogenesis. They are finally released from the seminiferous tubules by a process called spermiation.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




