
For the reaction: ${{N}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}(g)\to {{N}_{2}}{{O}_{4}}(g)+\dfrac{1}{2}{{O}_{2}}(g)$, the initial pressure is $114mm$ and after $20$ seconds, the pressure of the reaction mixture becomes $133mm$. Then the average rate of reaction will be:
A. $1.9\text{ atm }{{\text{S}}^{-1}}$
B. $8.75\times {{10}^{-3}}\text{ atm }{{\text{S}}^{-1}}$
C. $2.5\times {{10}^{-3}}\text{ atm }{{\text{S}}^{-1}}$
D. $\text{6}\text{.65 atm }{{\text{S}}^{-1}}$
Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: You can apply the simple formula for finding the average rate of the reaction by dividing the change in pressure and change in time in the reaction. Already the initial pressure, total pressure and change in time is given. So, now you can find the change in pressure from the reaction given.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that,
The reaction involved is:
${{N}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}(g)\to {{N}_{2}}{{O}_{4}}(g)+\dfrac{1}{2}{{O}_{2}}(g)$
The initial pressure for the reaction at time $0$ second is given as $114mm$.
The total pressure of the reaction mixture after $20$ seconds is given as $133mm$.
So, the change in time of the reaction is $(20-0)=20$ seconds.
Let’s consider the change in pressure as $\alpha $.
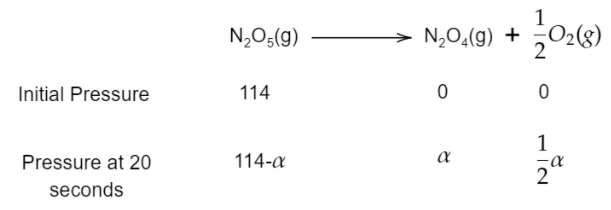
The initial pressure (at zero second) of ${{N}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}$, ${{N}_{2}}{{O}_{4}}$ and ${{O}_{2}}$ will be $114mm$, $0mm$ and $0mm$.
The pressure at $20$ seconds for ${{N}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}$, ${{N}_{2}}{{O}_{4}}$ and ${{O}_{2}}$ will be $114-\alpha $, $\alpha $ and $\dfrac{\alpha }{2}$.
Therefore, the total pressure will be $114-\alpha +\alpha +\dfrac{\alpha }{2}=133mm$.
Then, $114+\dfrac{\alpha }{2}=133mm$
Thus, $\dfrac{\alpha }{2}=(133-114)mm=19mm$
So, $\alpha =19\times 2=38mm$
We know that one atmosphere equals to $760mm$.
So, converting $38mm$ to the atmosphere will be $\dfrac{38}{760}=0.05atm$.
Thus, the change in pressure will be $0.05atm$.
The average rate of the reaction can be calculated by using the formula of dividing the change in pressure to that of the change in time.
So, the average rate of the reaction will be
$rate=\dfrac{\text{change in pressure}}{\text{change in time}}=\dfrac{0.05atm}{20s}=2.5\times {{10}^{-3}}atm\text{ }{{\text{s}}^{-1}}$
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: While calculating keep in mind about the units. The rate of a chemical reaction determines the speed of the reaction at which it tends to proceed. It is generally expressed in terms of either the concentration of a product formed in a unit time or the concentration of a reactant consumed in a unit time.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that,
The reaction involved is:
${{N}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}(g)\to {{N}_{2}}{{O}_{4}}(g)+\dfrac{1}{2}{{O}_{2}}(g)$
The initial pressure for the reaction at time $0$ second is given as $114mm$.
The total pressure of the reaction mixture after $20$ seconds is given as $133mm$.
So, the change in time of the reaction is $(20-0)=20$ seconds.
Let’s consider the change in pressure as $\alpha $.
The initial pressure (at zero second) of ${{N}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}$, ${{N}_{2}}{{O}_{4}}$ and ${{O}_{2}}$ will be $114mm$, $0mm$ and $0mm$.
The pressure at $20$ seconds for ${{N}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}$, ${{N}_{2}}{{O}_{4}}$ and ${{O}_{2}}$ will be $114-\alpha $, $\alpha $ and $\dfrac{\alpha }{2}$.

Therefore, the total pressure will be $114-\alpha +\alpha +\dfrac{\alpha }{2}=133mm$.
Then, $114+\dfrac{\alpha }{2}=133mm$
Thus, $\dfrac{\alpha }{2}=(133-114)mm=19mm$
So, $\alpha =19\times 2=38mm$
We know that one atmosphere equals to $760mm$.
So, converting $38mm$ to the atmosphere will be $\dfrac{38}{760}=0.05atm$.
Thus, the change in pressure will be $0.05atm$.
The average rate of the reaction can be calculated by using the formula of dividing the change in pressure to that of the change in time.
So, the average rate of the reaction will be
$rate=\dfrac{\text{change in pressure}}{\text{change in time}}=\dfrac{0.05atm}{20s}=2.5\times {{10}^{-3}}atm\text{ }{{\text{s}}^{-1}}$
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: While calculating keep in mind about the units. The rate of a chemical reaction determines the speed of the reaction at which it tends to proceed. It is generally expressed in terms of either the concentration of a product formed in a unit time or the concentration of a reactant consumed in a unit time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




