
For the reaction $C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}+HOCl\to A$. Product A is
A.

B.
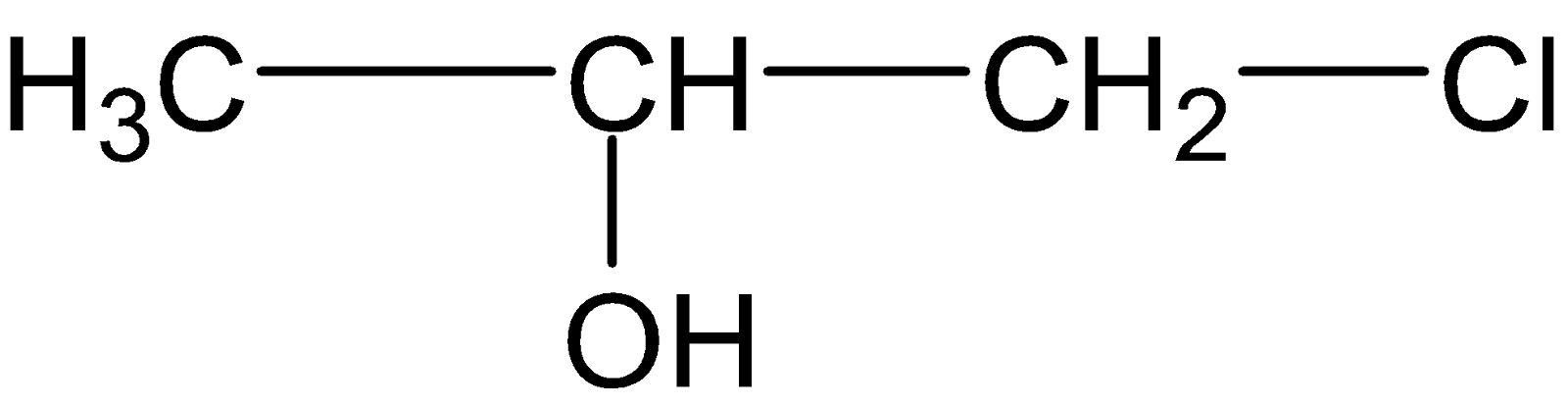
C.
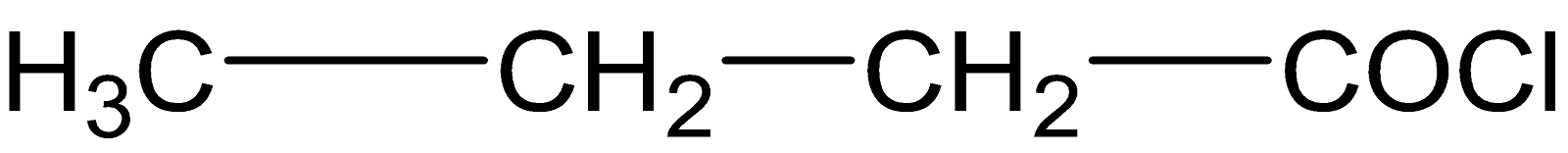
D.
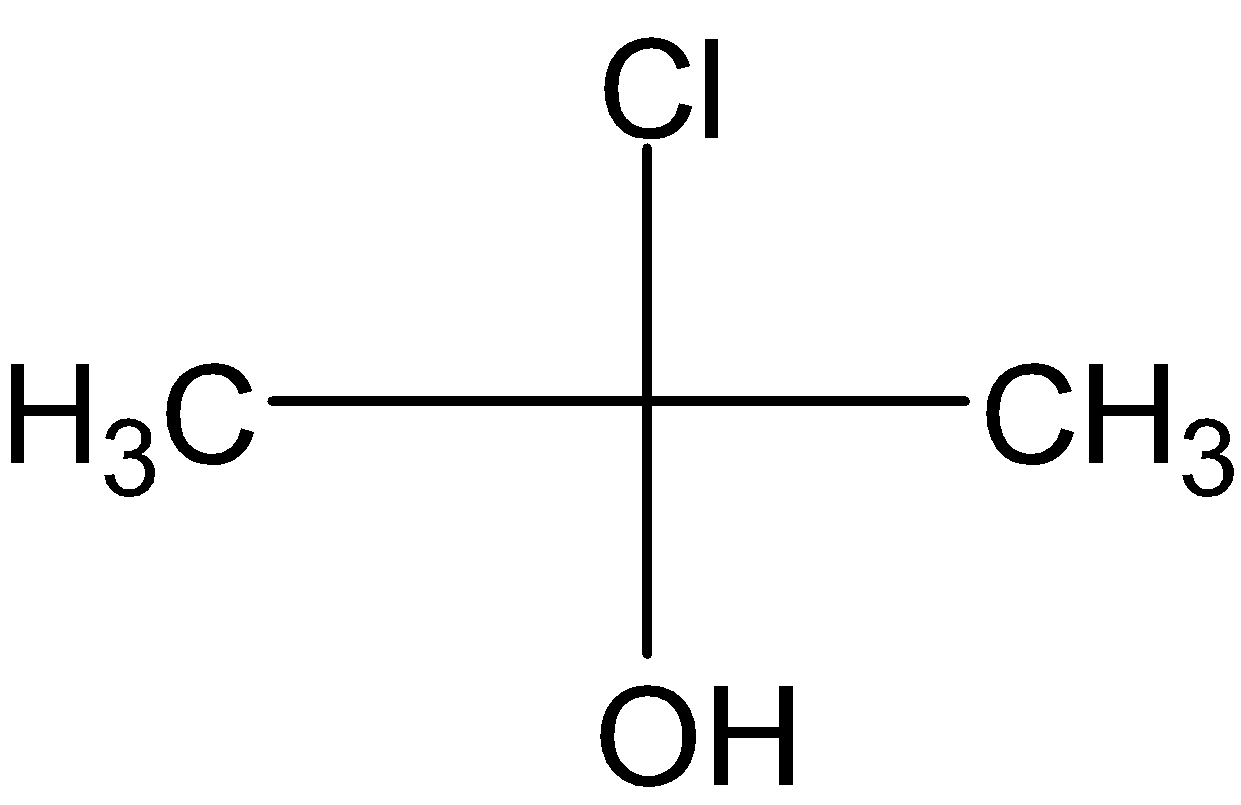


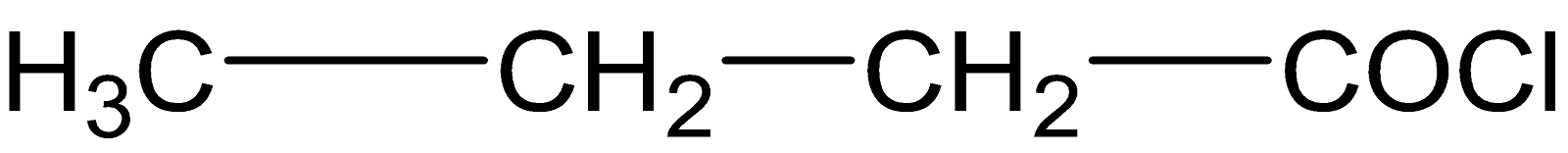

Answer
355.8k+ views
Hint: When we add any polar compound to an asymmetric alkene the negative part of the polar compound is attached to the carbon having less hydrogen. Here we also have asymmetric alkene and a polar hypochlorous compound, $HOCl$. Now the negative part $H{{O}^{-}}$ goes to the asymmetric carbon having less number of hydrogen atoms across the double bond.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Propene $C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$ reacts with hypochlorous acid and forms an additional product. This additional reaction follows Markovnikov’s rule. According to Markovnikov’s rule protic acid or hydrogen, the halide is added to an asymmetric alkene, and the hydrogen from protic acid is attached to the carbon with a higher number of hydrogens. Thereby the halide group gets attached to the higher number of alkyl substituents.
As oxygen is more electronegative than chlorine hence negative charge resides in the oxygen of the hydroxyl group and the positive charge resides in chlorine.
The first step consists of the formation of a cyclic intermediate between the double bond of alkene and electrophilic $C{{l}^{+}}$ ion. Here the electrophile polarises the double bond and is added to one of the carbon atoms. Thereby the other carbon atom bears a positive charge forming carbocation.
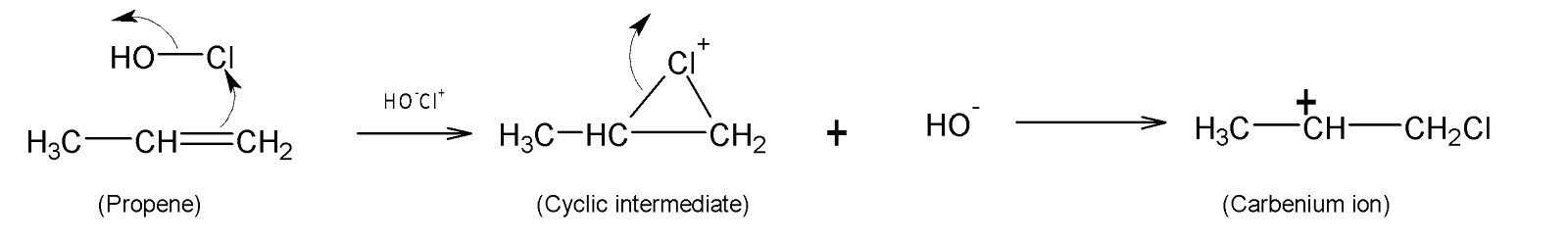
In the next step, the remaining $H{{O}^{-}}$ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic positive carbon centre. Hence a compound named halohydrin is formed as a final product.
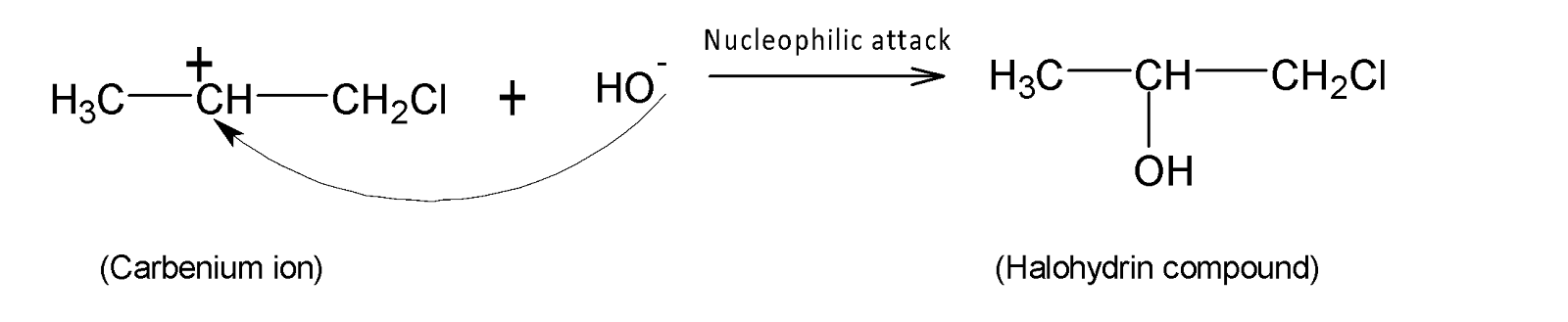
Therefore propene reacts with hypochlorous acid to form a halohydrin compound (B).
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: Anti-Markovnikov rule states that hydrogen atom from protic acid is attached to the carbon atom with less number of the hydrogen atom of asymmetric alkene and the negative part gets attached to the carbon with a higher number of hydrogen atoms. This rule is applicable for alkenes or alkynes but the Anti-Markovnikov rule is applied in presence of organic peroxide $(R-O-O-R)$.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Propene $C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$ reacts with hypochlorous acid and forms an additional product. This additional reaction follows Markovnikov’s rule. According to Markovnikov’s rule protic acid or hydrogen, the halide is added to an asymmetric alkene, and the hydrogen from protic acid is attached to the carbon with a higher number of hydrogens. Thereby the halide group gets attached to the higher number of alkyl substituents.
As oxygen is more electronegative than chlorine hence negative charge resides in the oxygen of the hydroxyl group and the positive charge resides in chlorine.
The first step consists of the formation of a cyclic intermediate between the double bond of alkene and electrophilic $C{{l}^{+}}$ ion. Here the electrophile polarises the double bond and is added to one of the carbon atoms. Thereby the other carbon atom bears a positive charge forming carbocation.

In the next step, the remaining $H{{O}^{-}}$ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic positive carbon centre. Hence a compound named halohydrin is formed as a final product.

Therefore propene reacts with hypochlorous acid to form a halohydrin compound (B).
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: Anti-Markovnikov rule states that hydrogen atom from protic acid is attached to the carbon atom with less number of the hydrogen atom of asymmetric alkene and the negative part gets attached to the carbon with a higher number of hydrogen atoms. This rule is applicable for alkenes or alkynes but the Anti-Markovnikov rule is applied in presence of organic peroxide $(R-O-O-R)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the factors of 100 class 7 maths CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE




