
For the given figure the direction of electric field at point A will be (Given that AB=BC=CA)
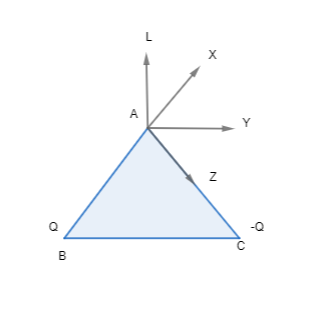
A.Towards AL
B.Towards AY
C.Towards AX
D.Towards AZ

Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: Study about the electric field at a distance r due to a point charge. Find the direction and the value of the field at point A due to both the charges. Then take the components and cancel the opposite and equal terms. The final value and direction will be given by the vector sum of the remaining components.
Formula used:
$E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{q}{{{r}^{2}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
The electric field due to a point charge q at a distance r is given by,
$E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{q}{{{r}^{2}}}$
Where, ${{\varepsilon }_{0}}$ is the permittivity of free space
$\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}=8.98\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-2}}\approx 9\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-2}}$
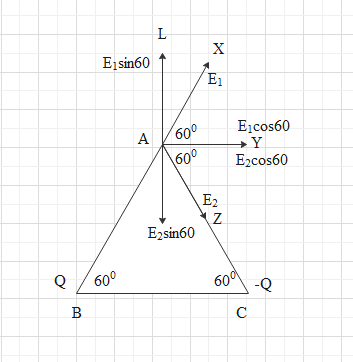
Electric field at point A due to the point charge Q at point B is
${{E}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{Q}{A{{B}^{2}}}$ , which will be along AX
Electric field at point A due to the point charge -Q at point C is
${{E}_{2}}=-\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{Q}{A{{C}^{2}}}$ , which will be along AZ
Now, ${{E}_{1}}$ will make an angle of ${{60}^{0}}$with AY
Taking the components of ${{E}_{1}}$,
Along AY ${{E}_{1}}\cos {{60}^{0}}$
Along AL ${{E}_{1}}\sin {{60}^{o}}$
${{E}_{2}}$ will make an angle of ${{60}^{0}}$with AY
Taking the components of ${{E}_{2}}$,
Along AY ${{E}_{2}}\cos {{60}^{0}}$
Along negative direction of AL ${{E}_{2}}\sin {{60}^{0}}$
Now along AL and opposite to AL we have the same field. So, it will cancel out each other.
So, we have the total field along AY direction.
The correct option is (B)
Note: Superposition of electric charge tells us that if there is more than one charge then each charge will contribute individually to the electric field. The total electric field will be the vector sum of all the fields.
Formula used:
$E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{q}{{{r}^{2}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
The electric field due to a point charge q at a distance r is given by,
$E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{q}{{{r}^{2}}}$
Where, ${{\varepsilon }_{0}}$ is the permittivity of free space
$\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}=8.98\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-2}}\approx 9\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-2}}$

Electric field at point A due to the point charge Q at point B is
${{E}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{Q}{A{{B}^{2}}}$ , which will be along AX
Electric field at point A due to the point charge -Q at point C is
${{E}_{2}}=-\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{Q}{A{{C}^{2}}}$ , which will be along AZ
Now, ${{E}_{1}}$ will make an angle of ${{60}^{0}}$with AY
Taking the components of ${{E}_{1}}$,
Along AY ${{E}_{1}}\cos {{60}^{0}}$
Along AL ${{E}_{1}}\sin {{60}^{o}}$
${{E}_{2}}$ will make an angle of ${{60}^{0}}$with AY
Taking the components of ${{E}_{2}}$,
Along AY ${{E}_{2}}\cos {{60}^{0}}$
Along negative direction of AL ${{E}_{2}}\sin {{60}^{0}}$
Now along AL and opposite to AL we have the same field. So, it will cancel out each other.
So, we have the total field along AY direction.
The correct option is (B)
Note: Superposition of electric charge tells us that if there is more than one charge then each charge will contribute individually to the electric field. The total electric field will be the vector sum of all the fields.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




