
For the given electric voltage signal dc value is:
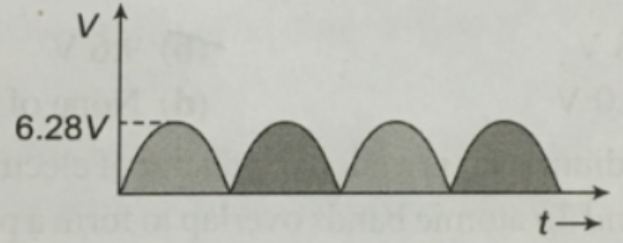
(A) 4.26V
(B) 3.14V
(C) 4V
(D) 0V

Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint:As the waves are sinusoidal waves and each wave area is \[\pi \]so the output dc is twice the given voltage divided by\[\pi \].
Formula Used:
\[{{V}_{dc}}={{V}_{ac}}=\dfrac{2{{V}_{0}}}{\pi }\]
Here,
\[{{V}_{dc}}=\]The required dc voltage.
\[{{V}_{ac}}=\]The ac voltage which is equal to the dc voltage.
\[{{V}_{0}}=\]The given voltage.
\[\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}=3.14\]
Complete step by step answer:
We have,
\[{{V}_{0}}=6.28\,V\]
Putting this value in the formula we get:
\[\begin{gathered}
& {{V}_{dc}}={{V}_{ac}}=\dfrac{2{{V}_{0}}}{\pi } \\
& {{V}_{dc}}=\dfrac{2\times 6.28}{\pi } \\
\end{gathered}\]
Putting \[\pi =3.14\]
\[\begin{gathered}
& {{V}_{dc}}=\dfrac{2\times 6.28}{\pi } \\
& {{V}_{dc}}=\dfrac{2\times 6.28}{3.14} \\
& {{V}_{dc}}=2\times 2 \\
& {{V}_{dc}}=4\,V \\
\end{gathered}\]
Hence the required dc voltage is\[4\,V\].
For this question option C is the correct answer.
Note:Note:
An electrical signal is a voltage or current which conveys information, usually it means a voltage. The term can be used for any voltage or current in a circuit. The frequency is an important property is the number of cycles per second. The diagram shows a half sine wave but the properties apply to any signal with a constantly repeating shape. Some of the properties of a sine wave are: Amplitude is the maximum voltage reached by the signal. It is measured in volts, V. Peak voltage is another name for amplitude.Peak-peak voltage is twice the peak voltage (amplitude). When reading an oscilloscope trace it is usual to measure peak-peak voltage.Time period is the time taken for the signal to complete one cycle. It is measured in seconds (s) but time periods tend to be short so milliseconds (ms) and microseconds (µs) are often used.
1ms = 0.001s and 1µs = 0.000001s.
Frequency is the number of cycles per second. It is measured in hertz (Hz), but frequencies tend to be high so kilohertz (kHz) and megahertz (MHz) are often used.
1kHz = 1000Hz and 1MHz = 1000000Hz.
Formula Used:
\[{{V}_{dc}}={{V}_{ac}}=\dfrac{2{{V}_{0}}}{\pi }\]
Here,
\[{{V}_{dc}}=\]The required dc voltage.
\[{{V}_{ac}}=\]The ac voltage which is equal to the dc voltage.
\[{{V}_{0}}=\]The given voltage.
\[\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}=3.14\]
Complete step by step answer:
We have,
\[{{V}_{0}}=6.28\,V\]
Putting this value in the formula we get:
\[\begin{gathered}
& {{V}_{dc}}={{V}_{ac}}=\dfrac{2{{V}_{0}}}{\pi } \\
& {{V}_{dc}}=\dfrac{2\times 6.28}{\pi } \\
\end{gathered}\]
Putting \[\pi =3.14\]
\[\begin{gathered}
& {{V}_{dc}}=\dfrac{2\times 6.28}{\pi } \\
& {{V}_{dc}}=\dfrac{2\times 6.28}{3.14} \\
& {{V}_{dc}}=2\times 2 \\
& {{V}_{dc}}=4\,V \\
\end{gathered}\]
Hence the required dc voltage is\[4\,V\].
For this question option C is the correct answer.
Note:Note:
An electrical signal is a voltage or current which conveys information, usually it means a voltage. The term can be used for any voltage or current in a circuit. The frequency is an important property is the number of cycles per second. The diagram shows a half sine wave but the properties apply to any signal with a constantly repeating shape. Some of the properties of a sine wave are: Amplitude is the maximum voltage reached by the signal. It is measured in volts, V. Peak voltage is another name for amplitude.Peak-peak voltage is twice the peak voltage (amplitude). When reading an oscilloscope trace it is usual to measure peak-peak voltage.Time period is the time taken for the signal to complete one cycle. It is measured in seconds (s) but time periods tend to be short so milliseconds (ms) and microseconds (µs) are often used.
1ms = 0.001s and 1µs = 0.000001s.
Frequency is the number of cycles per second. It is measured in hertz (Hz), but frequencies tend to be high so kilohertz (kHz) and megahertz (MHz) are often used.
1kHz = 1000Hz and 1MHz = 1000000Hz.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




