
For the given compounds:
A) Tetracyanoethylene
B) Carbon dioxide
C) Benzene
D) \[1,3 - \] Butadiene
Ratio of $\sigma $ and $\pi $ -bonds is in order:
1.A = B > C < D
2.A = B > D < C
3.A = B = C D
4.D > C > B = A
Answer
563.7k+ views
Hint:We have to know that the single bonds means sigma bonds. Sigma $\left( \sigma \right)$ bonds are not very strong bonds. Double bonds are strong bonds and they are the pi $\left( \pi \right)$ bonds. It is difficult to break this bond. The ratio should always be written on reduced form. When we write ratios in reduced form then, we have more clarity. With the help of this method it is easy to find out the ratio of various compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
To count the bonds all one needs to know are the following rules of chemistry:
Single bond is $1\sigma $ bond.
Double bond is when there is one sigma $\left( \sigma \right)$ and one pi $\left( \pi \right)$ bond.
Triple bond is when there is one sigma $\left( \sigma \right)$ and two pi $\left( \pi \right)$ bonds.
A.We can draw the structure of Tetracyanoethylene as,
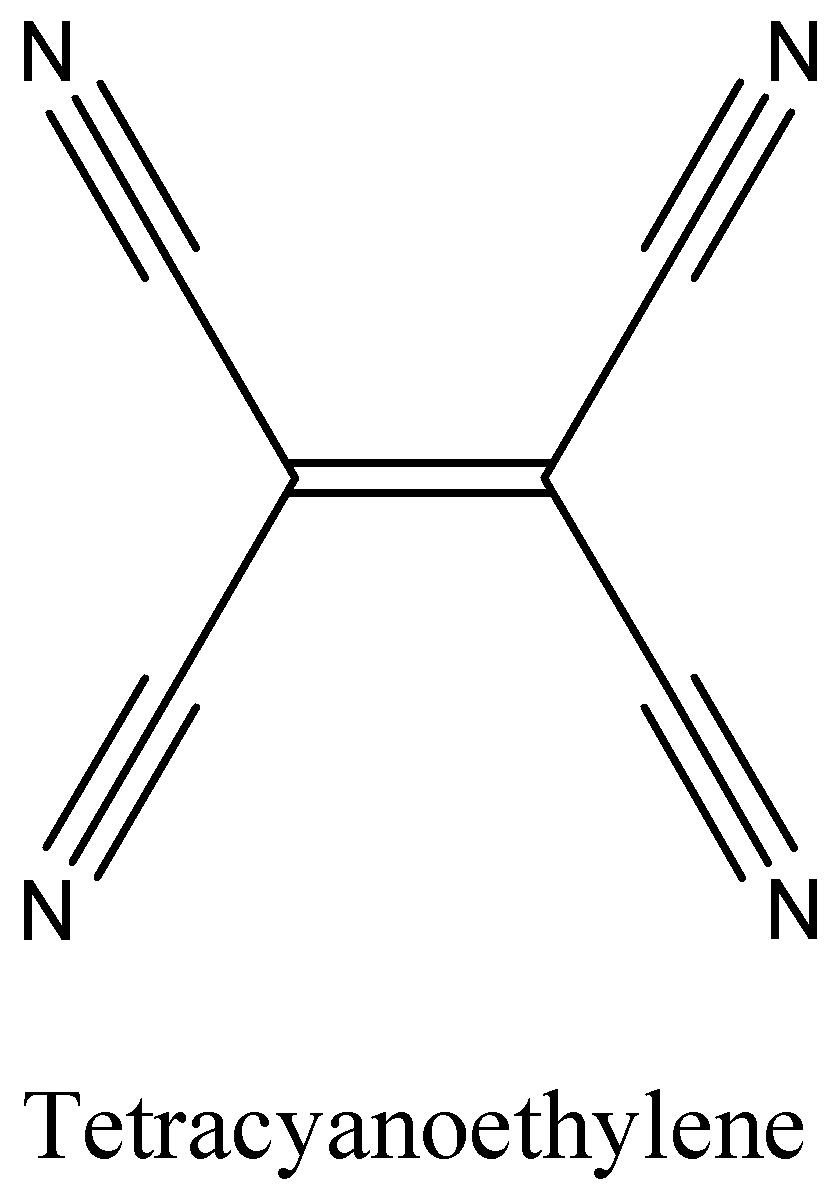
The above diagram clearly shows it has $9\pi $ bonds and $9\sigma $ bonds.
(B) We can draw the structure of Carbon dioxide as,
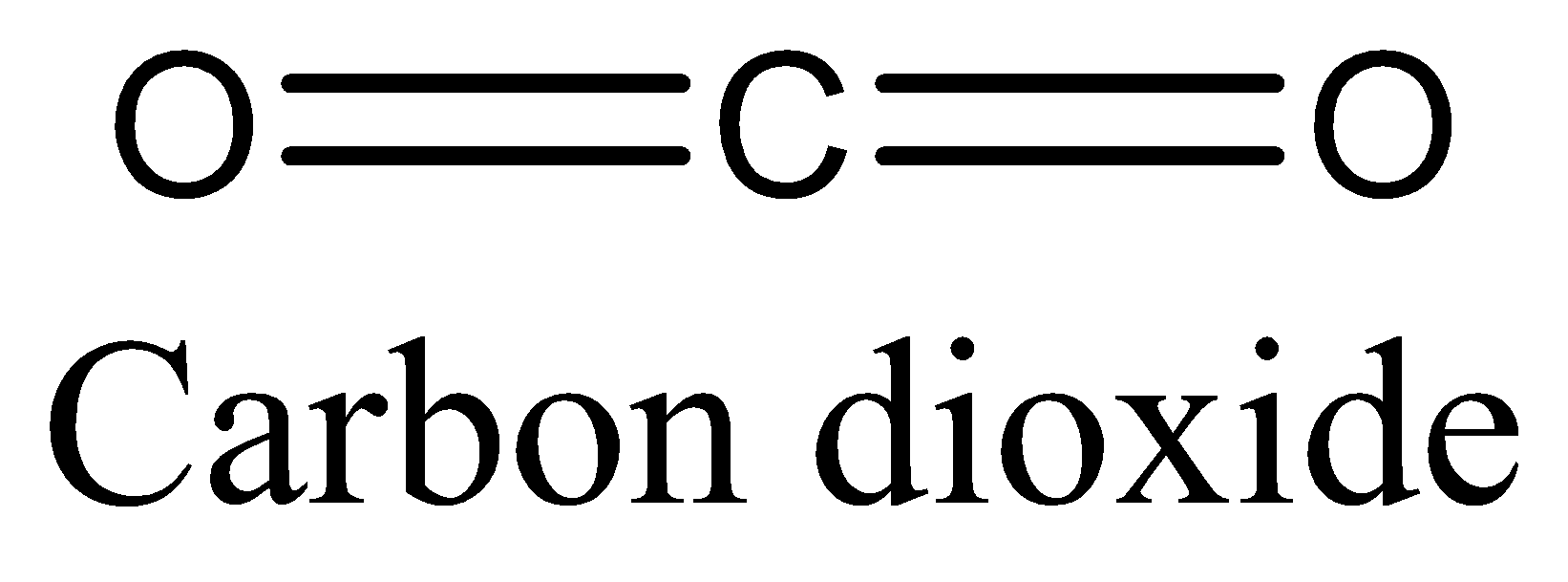
The above diagram clearly shows that carbon dioxide has $2\pi $ bonds and $2\sigma $ bonds.
(C) Now we can draw the structure of Benzene as,
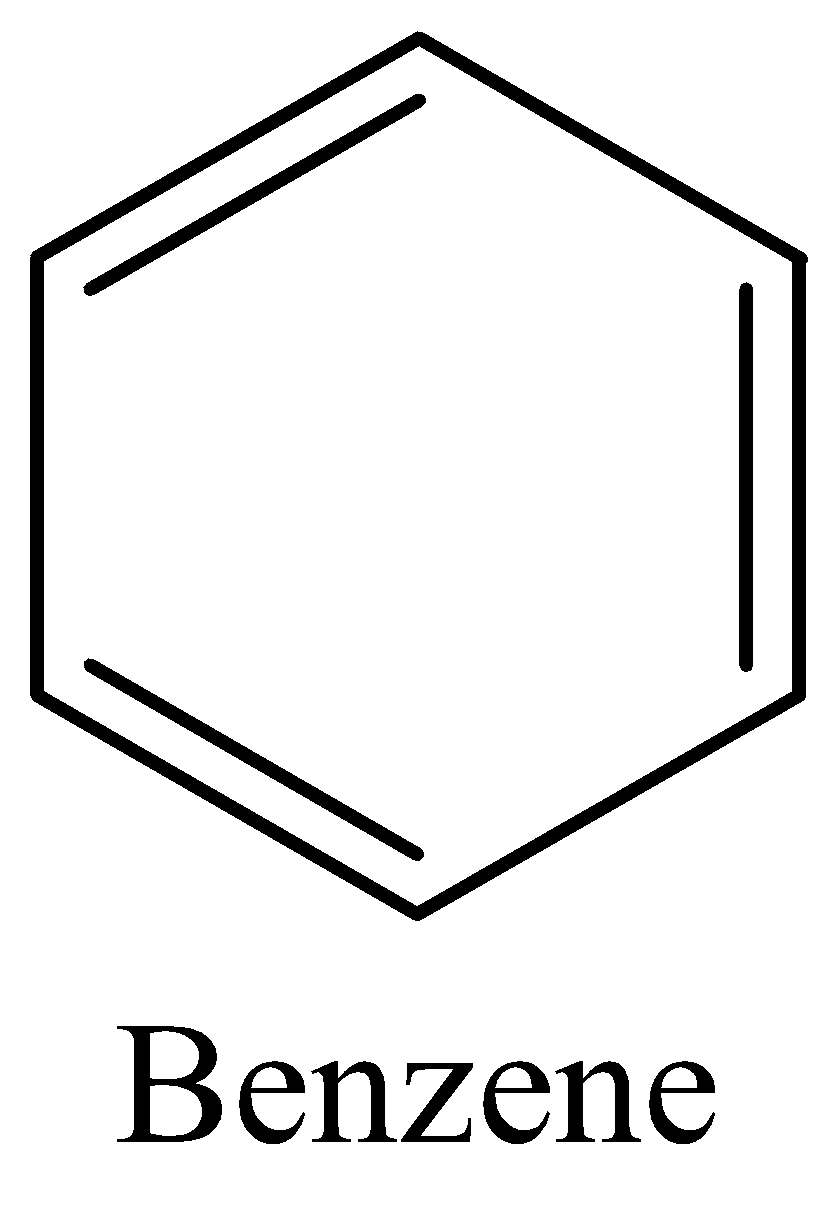
The above diagram clearly shows that the carbon dioxide has $3\pi $ bonds and $12\sigma $ bonds.
(D) Now we can draw the structure of 1,3-Butadiene as,
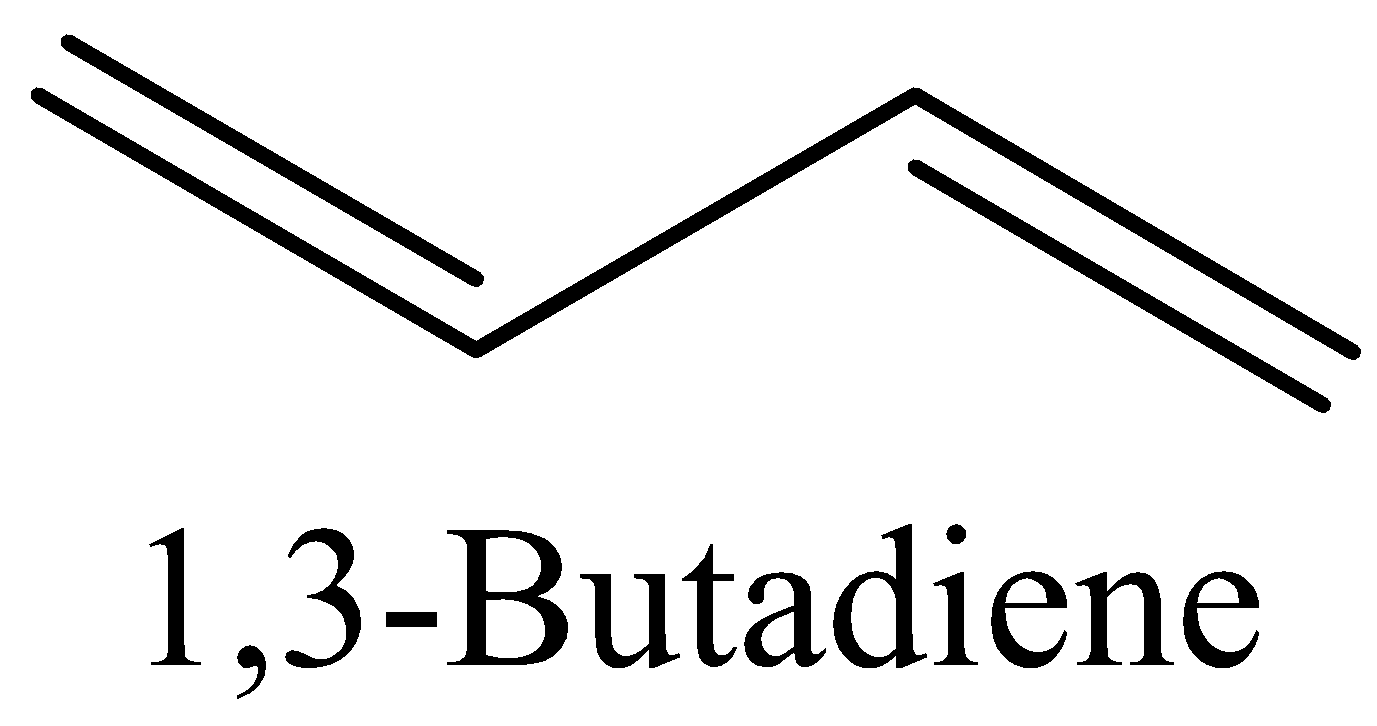
The above structure of 1,3-butadiene has $9\pi $ bonds and $2\sigma $ bonds.
From the above discussion we can conclude as,
In 1,3-Butadiene the ratio is \[9:2\]
In benzene the ratio is \[12:3\] which is \[4:1\]
In Carbon dioxide the ratio is \[2:2\] which is \[1:1\]
In Tetracyanoethylene the ratio is $9:9$ which is \[1:1\]
Thus, D>C>B=A.
From this information we can conclude that Tetracyanoethylene and Carbon dioxide have the same ratio and benzene’s ratio is more than them. \[1,3\]-Butadiene has the highest ratio.
So option 4 is correct for the given question.
Note:
We also remember that benzene is a compound which is a cyclic compound. It has alternate double and single bonds. Carbon dioxide has a carbon attached to two different oxygen. Tetracyanoethylene is colourless in nature and it is also important in organic chemistry. 1,3-Butadiene is a colourless gas which can be easily condensed into liquid state.
Complete step by step answer:
To count the bonds all one needs to know are the following rules of chemistry:
Single bond is $1\sigma $ bond.
Double bond is when there is one sigma $\left( \sigma \right)$ and one pi $\left( \pi \right)$ bond.
Triple bond is when there is one sigma $\left( \sigma \right)$ and two pi $\left( \pi \right)$ bonds.
A.We can draw the structure of Tetracyanoethylene as,

The above diagram clearly shows it has $9\pi $ bonds and $9\sigma $ bonds.
(B) We can draw the structure of Carbon dioxide as,
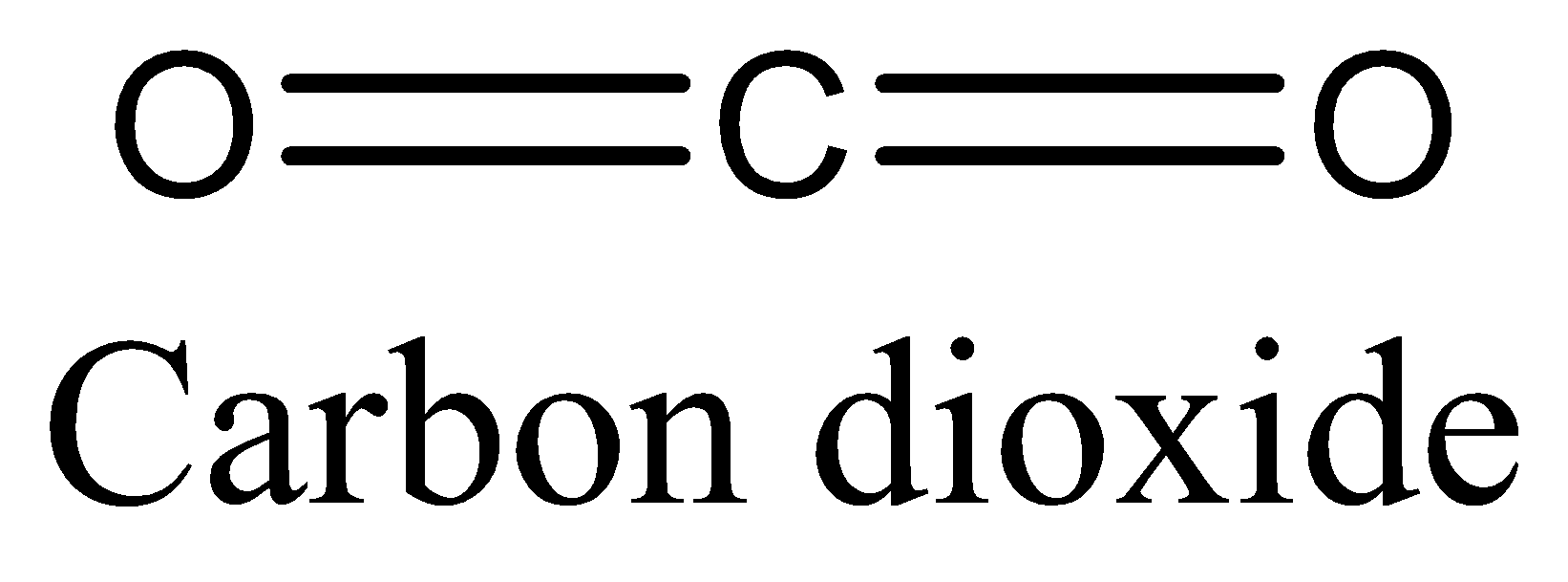
The above diagram clearly shows that carbon dioxide has $2\pi $ bonds and $2\sigma $ bonds.
(C) Now we can draw the structure of Benzene as,

The above diagram clearly shows that the carbon dioxide has $3\pi $ bonds and $12\sigma $ bonds.
(D) Now we can draw the structure of 1,3-Butadiene as,

The above structure of 1,3-butadiene has $9\pi $ bonds and $2\sigma $ bonds.
From the above discussion we can conclude as,
In 1,3-Butadiene the ratio is \[9:2\]
In benzene the ratio is \[12:3\] which is \[4:1\]
In Carbon dioxide the ratio is \[2:2\] which is \[1:1\]
In Tetracyanoethylene the ratio is $9:9$ which is \[1:1\]
Thus, D>C>B=A.
From this information we can conclude that Tetracyanoethylene and Carbon dioxide have the same ratio and benzene’s ratio is more than them. \[1,3\]-Butadiene has the highest ratio.
So option 4 is correct for the given question.
Note:
We also remember that benzene is a compound which is a cyclic compound. It has alternate double and single bonds. Carbon dioxide has a carbon attached to two different oxygen. Tetracyanoethylene is colourless in nature and it is also important in organic chemistry. 1,3-Butadiene is a colourless gas which can be easily condensed into liquid state.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




