
For the coordination complex ion ${\left[ {Co{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}$
(i) Give the IUPAC name of the complex ion.
(ii) What is the oxidation number of cobalt in the complex ion.
(iii) State the type of hybridisation of the complex ion.
(iv) State the magnetic behaviour of the complex ion.
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: The complex given is coordination complex hence while the IUPAC name should be written by using the rules accordingly. While calculating the oxidation number one needs to also consider the charge on the complex. Hybridization and magnetic behaviour can be decided based on the electronic configuration.
Complete step by step answer:
1) First of all let's write the electronic configuration of the coordination complex ion ${\left[ {Co{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}$ as by rules, there six amine groups are present in the coordination ion which is written first while writing the IUPAC name. The cobalt is the central metal and its oxidation state is written in the bracket in roman numbers.
Hence, the IUPAC name for the coordination complex ion ${\left[ {Co{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}$ is Hexammine cobalt(III) ion.
2) The oxidation number of cobalt in the complex ion is as below,
$x + 6 \times (0) = + 3$
$x = + 3$
Where the ${\text{x}}$ denotes the oxidation state of cobalt. As the molecule $N{H_3}$ contributes the zero electrons in the total oxidation state its net contribution will be zero. The ${\text{ + 3}}$ is the charge which is present on the complex. Therefore, the oxidation state of the cobalt is ${\text{ + 3}}$.
3) Now to get the hybridization of the complex let's first write the electronic configuration of the complex.
Electronic configuration of the Cobalt$C{o^{3 + }} = \left[ {Ar} \right]3{d^6}4{s^0}$
It means that there are six electrons present in the d-orbital of which two electrons are paired and the other four are unpaired.
As the coordination complex ion ${\left[ {Co{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}$ is a high spin complex all the unpaired electrons will get paired with each other in the d-orbital. Hence, now the d-orbital has six electrons which are paired and other empty. The representation is shown in the following diagram,
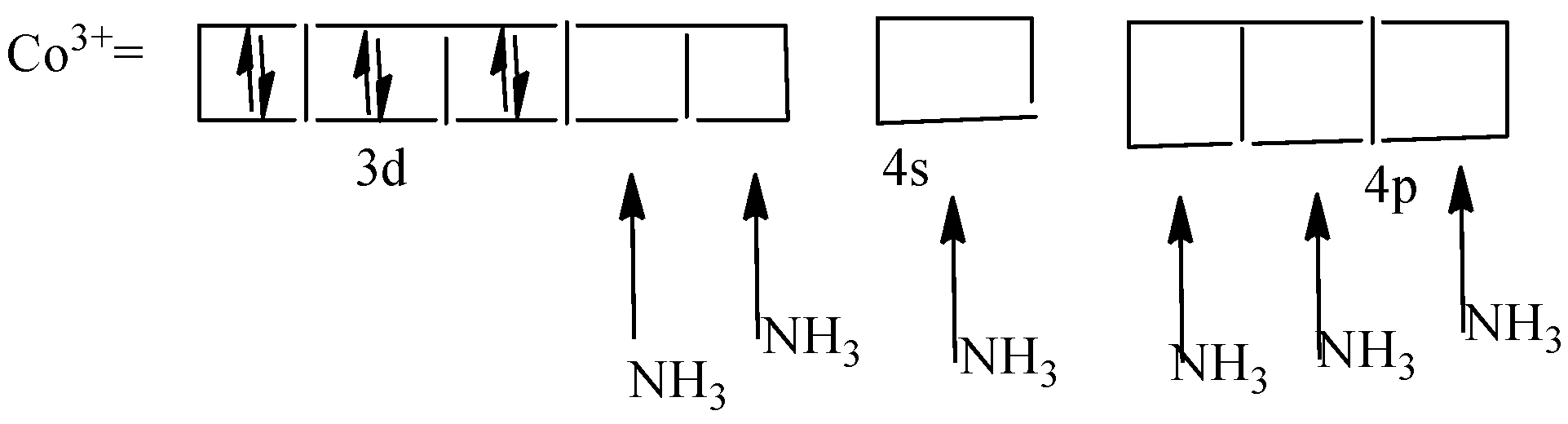
The $N{H_3}$ ligand will form a bond with the empty spaces in the orbital and forms six bonds. Therefore, hybridization will be ${d^2}s{p^3}$.
4) As there are no unpaired electrons present in the complex we can say that the complex is diamagnetic in nature.
Note:
In the hybridization will be ${d^2}s{p^3}$ where two bonds are formed from the d-orbital, one from the s-orbital, and three from the p-orbital. The diamagnetic complex is resistant to undergo any change when an external magnetic field is applied. Always remember to consider the charge on the complex while calculating the oxidation state.
Complete step by step answer:
1) First of all let's write the electronic configuration of the coordination complex ion ${\left[ {Co{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}$ as by rules, there six amine groups are present in the coordination ion which is written first while writing the IUPAC name. The cobalt is the central metal and its oxidation state is written in the bracket in roman numbers.
Hence, the IUPAC name for the coordination complex ion ${\left[ {Co{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}$ is Hexammine cobalt(III) ion.
2) The oxidation number of cobalt in the complex ion is as below,
$x + 6 \times (0) = + 3$
$x = + 3$
Where the ${\text{x}}$ denotes the oxidation state of cobalt. As the molecule $N{H_3}$ contributes the zero electrons in the total oxidation state its net contribution will be zero. The ${\text{ + 3}}$ is the charge which is present on the complex. Therefore, the oxidation state of the cobalt is ${\text{ + 3}}$.
3) Now to get the hybridization of the complex let's first write the electronic configuration of the complex.
Electronic configuration of the Cobalt$C{o^{3 + }} = \left[ {Ar} \right]3{d^6}4{s^0}$
It means that there are six electrons present in the d-orbital of which two electrons are paired and the other four are unpaired.
As the coordination complex ion ${\left[ {Co{{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}$ is a high spin complex all the unpaired electrons will get paired with each other in the d-orbital. Hence, now the d-orbital has six electrons which are paired and other empty. The representation is shown in the following diagram,

The $N{H_3}$ ligand will form a bond with the empty spaces in the orbital and forms six bonds. Therefore, hybridization will be ${d^2}s{p^3}$.
4) As there are no unpaired electrons present in the complex we can say that the complex is diamagnetic in nature.
Note:
In the hybridization will be ${d^2}s{p^3}$ where two bonds are formed from the d-orbital, one from the s-orbital, and three from the p-orbital. The diamagnetic complex is resistant to undergo any change when an external magnetic field is applied. Always remember to consider the charge on the complex while calculating the oxidation state.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




