
For a series LCR circuit at resonance, the statement which is not true is:
(A) Peak energy stored by a capacitor = peak energy stored by an inductor
(B) Average power = apparent power
(C) Wattless current is zero
(D) Power factor is zero.
Answer
526.8k+ views
Hint: At resonance of an LCR circuit, the capacitive impedance of the circuit becomes equal to the inductive impedance. This means that they being out of phase cancel out each other. And the net impedance is due to resistance alone. We shall use this property of series LCR circuit at resonance to solve the above problem.
Complete answer:
We will check for all the options and see which of them are correct and which of them are incorrect. Also, a series LCR circuit can be understood with the help of the following diagram:
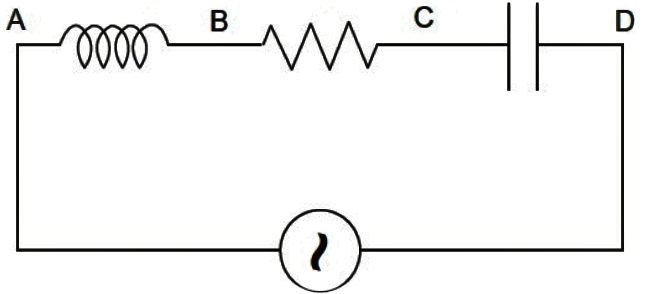
Here, the inductance is ‘L’, the resistance being ‘R’ and the capacitance being ‘C’ are shown as connected in series to an external voltage supply.
(A) Peak energy stored by a capacitor = peak energy stored by an inductor
The peak energy stored by a capacitor is: $\dfrac{1}{2}C{{V}^{2}}$
And, the peak energy stored by an inductor is: $\dfrac{1}{2}L{{I}^{2}}$
Also, at resonance, ${{X}_{C}}={{X}_{L}}$
Or, we can write:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\omega C}=\omega L \\
& \therefore C=\dfrac{1}{{{\omega }^{2}}L};L=\dfrac{1}{{{\omega }^{2}}C} \\
\end{align}$
On multiplying C with $\dfrac{1}{2}{{V}^{2}}$ and L with $\dfrac{1}{2}{{I}^{2}}$ , we get:
L.H.S. = $\dfrac{{{V}^{2}}}{2{{\omega }^{2}}L}$ and R.H.S. = $\dfrac{{{I}^{2}}}{2{{\omega }^{2}}C}$
On cross multiplying the terms in R.H.S. with L.H.S., we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}C{{V}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}L{{I}^{2}}$
Hence, option (A) is true.
(B) Average power = apparent power
Now, average power = ${{V}_{rms}}{{I}_{rms}}$
This is equal to $=I_{rms}^{2}R$
And, apparent power = ${{V}_{Z}}{{I}_{rms}}$
Since, at resonance, $Z=R$, that is net impedance is equal to resistance, therefore
Average power is equal to apparent power.
Hence. option (B) is also correct.
(C) Wattless current is zero
At the time of resonance, the potential difference across the capacitor-inductor is zero. This is because they store all the energy in the form of electric field and magnetic field respectively. Thus, the wattless current is also zero.
Hence, option (C) is also correct.
(D) Power factor is zero
Power factor ($\cos \phi $) is given by:
$\Rightarrow \cos \phi =\dfrac{Z}{R}$
At resonance, $Z=R$,
Therefore, Power factor equals to 1.
Hence, option (D) is the incorrect option.
Hence, the only option which is incorrect is option (D). So, option (D) is our answer.
Note:
We should remember all these options as important properties of an LCR circuit at resonance. It should also be noted that the question asked which of them was incorrect and not the correct choice. So, after solving such problems, we shouldn’t be hasty and first re-read the problem again and check what has been asked.
Complete answer:
We will check for all the options and see which of them are correct and which of them are incorrect. Also, a series LCR circuit can be understood with the help of the following diagram:

Here, the inductance is ‘L’, the resistance being ‘R’ and the capacitance being ‘C’ are shown as connected in series to an external voltage supply.
(A) Peak energy stored by a capacitor = peak energy stored by an inductor
The peak energy stored by a capacitor is: $\dfrac{1}{2}C{{V}^{2}}$
And, the peak energy stored by an inductor is: $\dfrac{1}{2}L{{I}^{2}}$
Also, at resonance, ${{X}_{C}}={{X}_{L}}$
Or, we can write:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\omega C}=\omega L \\
& \therefore C=\dfrac{1}{{{\omega }^{2}}L};L=\dfrac{1}{{{\omega }^{2}}C} \\
\end{align}$
On multiplying C with $\dfrac{1}{2}{{V}^{2}}$ and L with $\dfrac{1}{2}{{I}^{2}}$ , we get:
L.H.S. = $\dfrac{{{V}^{2}}}{2{{\omega }^{2}}L}$ and R.H.S. = $\dfrac{{{I}^{2}}}{2{{\omega }^{2}}C}$
On cross multiplying the terms in R.H.S. with L.H.S., we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}C{{V}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}L{{I}^{2}}$
Hence, option (A) is true.
(B) Average power = apparent power
Now, average power = ${{V}_{rms}}{{I}_{rms}}$
This is equal to $=I_{rms}^{2}R$
And, apparent power = ${{V}_{Z}}{{I}_{rms}}$
Since, at resonance, $Z=R$, that is net impedance is equal to resistance, therefore
Average power is equal to apparent power.
Hence. option (B) is also correct.
(C) Wattless current is zero
At the time of resonance, the potential difference across the capacitor-inductor is zero. This is because they store all the energy in the form of electric field and magnetic field respectively. Thus, the wattless current is also zero.
Hence, option (C) is also correct.
(D) Power factor is zero
Power factor ($\cos \phi $) is given by:
$\Rightarrow \cos \phi =\dfrac{Z}{R}$
At resonance, $Z=R$,
Therefore, Power factor equals to 1.
Hence, option (D) is the incorrect option.
Hence, the only option which is incorrect is option (D). So, option (D) is our answer.
Note:
We should remember all these options as important properties of an LCR circuit at resonance. It should also be noted that the question asked which of them was incorrect and not the correct choice. So, after solving such problems, we shouldn’t be hasty and first re-read the problem again and check what has been asked.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




