
For a light ray undergoing refraction, $\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}$=
A.) $\mu $
B.) 1
C.) 0
D.) None of these
Answer
555.9k+ views
Hint: Refraction occurs when Light travels through a medium (like Lens). For example, a ray of light passing through a Lens/Water changes its direction and hence Refraction occurs in case of a light passing from Air to Water or Air to lens or Water to lens. Refraction also follow some basic laws
Complete answer:
In Refraction, when a wave of light passes through a medium it changes its direction and this is known as Refraction. For example, a ray of light passing through a Lens/Water changes its direction and hence Refraction occurs in case of a light passing from Air to Water or Air to lens or Water to lens.
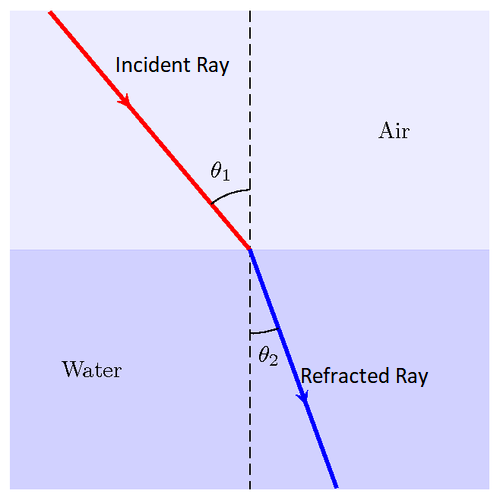
For Refraction We uses Snell’s Law ${{n}_{1}}\sin i={{n}_{2}}\sin r$…… Equation (1)
Where ${{n}_{1}}$ and ${{n}_{2}}$ are refractive index of medium
Or $\dfrac{{{n}_{2}}}{{{n}_{1}}}=\mu $
Equation (1) can be written as, $\dfrac{{{n}_{2}}}{{{n}_{1}}}=\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}$
Putting the value of $\dfrac{{{n}_{2}}}{{{n}_{1}}}=\mu $ we get,
$\mu =\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}$
Hence Option(A) $\mu =\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}$ is the correct answer.
Additional Information:
There is no ideally Reflecting or Refracting surface/medium, so we can say that whenever there is a Refraction, there must be a reflection and vice versa. When a light way gets Reflected some amount of it may get absorbed or Refracted and hence there is no Perfect reflection and same applies for refraction, Whenever There is a Refraction, some amount of Light get Reflected back and hence we can say there is no perfect or ideal refraction exists in this World.
Note:
Snell’s law states that the ratio of the refractive indices of two mediums is equal to the ratio of the sin of angle of the incident to the angle of refraction with respect to the normal. This law is very useful to describe the relationship between angle of incidence, angle of refraction and the refractive indices of two mediums.
Complete answer:
In Refraction, when a wave of light passes through a medium it changes its direction and this is known as Refraction. For example, a ray of light passing through a Lens/Water changes its direction and hence Refraction occurs in case of a light passing from Air to Water or Air to lens or Water to lens.

For Refraction We uses Snell’s Law ${{n}_{1}}\sin i={{n}_{2}}\sin r$…… Equation (1)
Where ${{n}_{1}}$ and ${{n}_{2}}$ are refractive index of medium
Or $\dfrac{{{n}_{2}}}{{{n}_{1}}}=\mu $
Equation (1) can be written as, $\dfrac{{{n}_{2}}}{{{n}_{1}}}=\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}$
Putting the value of $\dfrac{{{n}_{2}}}{{{n}_{1}}}=\mu $ we get,
$\mu =\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}$
Hence Option(A) $\mu =\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}$ is the correct answer.
Additional Information:
There is no ideally Reflecting or Refracting surface/medium, so we can say that whenever there is a Refraction, there must be a reflection and vice versa. When a light way gets Reflected some amount of it may get absorbed or Refracted and hence there is no Perfect reflection and same applies for refraction, Whenever There is a Refraction, some amount of Light get Reflected back and hence we can say there is no perfect or ideal refraction exists in this World.
Note:
Snell’s law states that the ratio of the refractive indices of two mediums is equal to the ratio of the sin of angle of the incident to the angle of refraction with respect to the normal. This law is very useful to describe the relationship between angle of incidence, angle of refraction and the refractive indices of two mediums.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




