
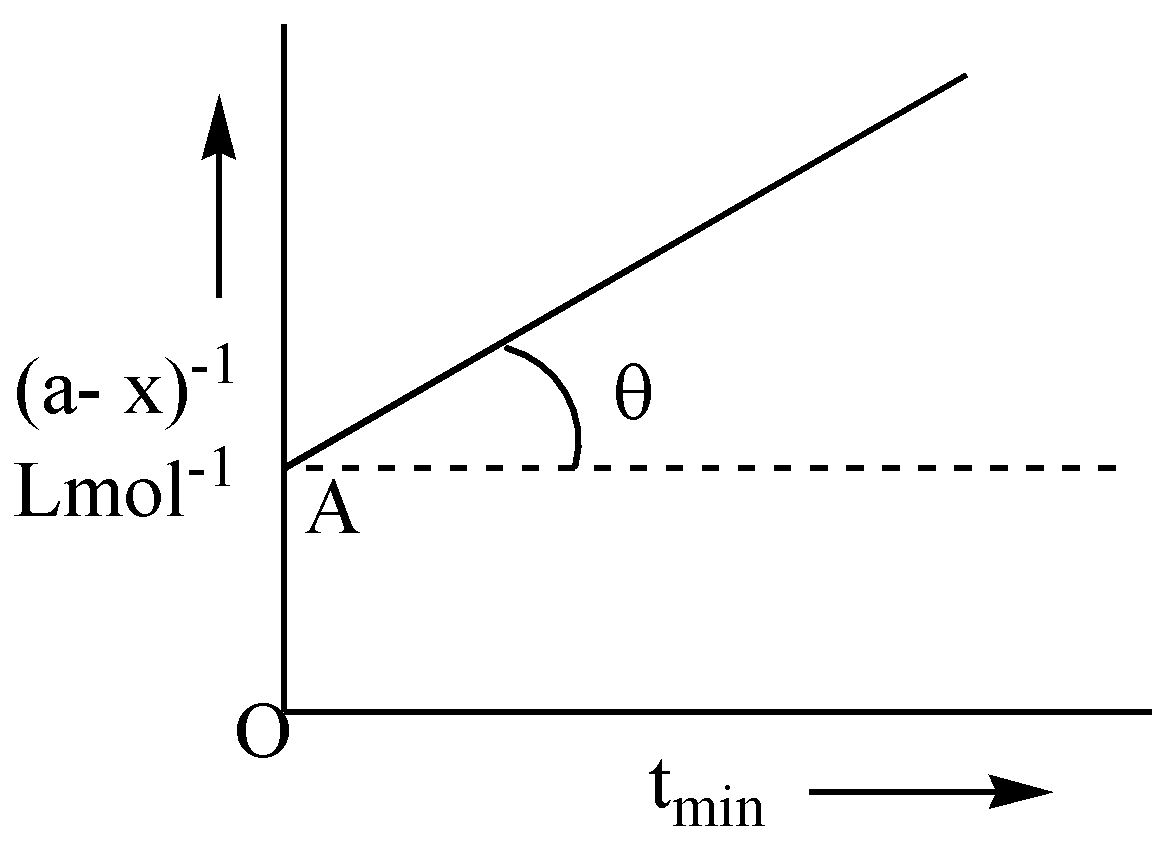
Following is the graph between ${\left( {a - x} \right)^{ - 1}}$ and time t for second order reaction. $\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {1/2} \right)$; $OA = 2Lmo{l^{ - 1}}$ , hence rate at the start of the reaction will be:
A. $1.25Lmo{l^{ - 1}}{\min ^{ - 1}}$
B. $0.5Lmo{l^{ - 1}}{\min ^{ - 1}}$
C. $0.125Lmo{l^{ - 1}}{\min ^{ - 1}}$
D. $1.25mol{L^{ - 1}}{\min ^{ - 1}}$

Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: We need to recall and understand the concept of second order reaction. The reaction order is a concept to study the reaction rate with respect to concentration of the reactants. There are a variety of rate laws used to determine the rate of a reaction but three commonly used are the zero order, first order and second order rate laws. We are to focus on the second order reaction rate law in order to solve the given question.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to know that for a reaction $xA \to yB$ the rate of the reaction is given by rate,
$r = k{\left[ A \right]^x}{\left[ B \right]^y}$ . The sum of these subscripts (x and y) gives the rate of the reaction. For a second order reaction, the sum of the subscripts is equal to two.
The integrated rate law equation for a second order reaction whose concentration of reactants at time 0 is ${\left[ R \right]_0}$ and at time t is ${\left[ R \right]_t}$ is given by
$\dfrac{1}{{{{[R]}_t}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{{[R]}_0}}} = kt$ ……………………(1)
We use this equation to solve the question.
Given,
At time 0, the concentration of the reactants = a and the concentration of the reactants at time $t = a - x$.
Using equation 1, we get $kt = (\dfrac{1}{{a - x}} = \dfrac{1}{a})$
Or, $\dfrac{1}{{a - x}} = kt + \dfrac{1}{a}$
The graph between (a-x)-1 and time t is a straight line whose equation is given by $y = mx + c$ where k is the slope $ = \tan \theta = 0.5$ and the intercept is $\dfrac{1}{a} = OA = 2$.
Therefore,
$A = \dfrac{1}{2} = 0.5$
Hence the rate of the reaction is $r = k{\left[ A \right]^2}$ (since it is a second order reaction, the subscript is equal to two)
Or, \[r = 0.5 \times {\left( {0.5} \right)^2} = 0.125mol{L^{ - 1}}mi{n^{ - 1}}\] .
Thus, the correct answer to the question is option C.
Note: It must be noted that the order of a reaction is the power dependence of rate on the concentration of all reactants. Plotting a graph where a straight line $\left( {y = mx + c} \right)$ corresponds to the equation where$y = \dfrac{1}{{\left[ R \right]}}$ , $x = t$ , $m = k$ , $c = \dfrac{1}{{{{\left[ R \right]}_0}}}$ . The order can be determined by the reaction concentrations only and not the product concentrations.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to know that for a reaction $xA \to yB$ the rate of the reaction is given by rate,
$r = k{\left[ A \right]^x}{\left[ B \right]^y}$ . The sum of these subscripts (x and y) gives the rate of the reaction. For a second order reaction, the sum of the subscripts is equal to two.
The integrated rate law equation for a second order reaction whose concentration of reactants at time 0 is ${\left[ R \right]_0}$ and at time t is ${\left[ R \right]_t}$ is given by
$\dfrac{1}{{{{[R]}_t}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{{[R]}_0}}} = kt$ ……………………(1)
We use this equation to solve the question.
Given,
At time 0, the concentration of the reactants = a and the concentration of the reactants at time $t = a - x$.
Using equation 1, we get $kt = (\dfrac{1}{{a - x}} = \dfrac{1}{a})$
Or, $\dfrac{1}{{a - x}} = kt + \dfrac{1}{a}$
The graph between (a-x)-1 and time t is a straight line whose equation is given by $y = mx + c$ where k is the slope $ = \tan \theta = 0.5$ and the intercept is $\dfrac{1}{a} = OA = 2$.
Therefore,
$A = \dfrac{1}{2} = 0.5$
Hence the rate of the reaction is $r = k{\left[ A \right]^2}$ (since it is a second order reaction, the subscript is equal to two)
Or, \[r = 0.5 \times {\left( {0.5} \right)^2} = 0.125mol{L^{ - 1}}mi{n^{ - 1}}\] .
Thus, the correct answer to the question is option C.
Note: It must be noted that the order of a reaction is the power dependence of rate on the concentration of all reactants. Plotting a graph where a straight line $\left( {y = mx + c} \right)$ corresponds to the equation where$y = \dfrac{1}{{\left[ R \right]}}$ , $x = t$ , $m = k$ , $c = \dfrac{1}{{{{\left[ R \right]}_0}}}$ . The order can be determined by the reaction concentrations only and not the product concentrations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




