
How can the following conversions be carried out?
Benzene to 4-bromonitrobenene.
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: Conversion of benzene to 4-bromonitrobenzene is a two-step process. Benzene converts to bromobenzene through a brominating catalyst. The brominated product is heated with mixed acid to get the required product.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that benzene is an organic compound with formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$. We can convert it to certain compounds by adding required reagents.
In the question, we have been asked to convert benzene to 4-bromonitrobenzene.
Now as we can understand from the name itself, 4-bromonitrobenzene contains bromine and nitro- groups as substituents in the benzene ring.
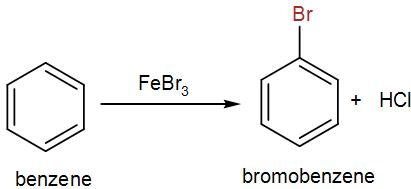
Now firstly, let us discuss the reagents for bromination of benzene. Bromine undergoes electrophilic substitution in presence of a catalyst to give us the brominated product. We use iron bromide here and the product is bromobenzene. We can write the reaction as-
Now, for nitration, we used mixed acid i.e. sulphuric acid and nitric acid. We heat bromobenzene with the mixed acid and we obtain three different nitrated products. One is the para-product which is the major product and the other is ortho-product and we also obtain a di-nitro product. We can write the reaction as-
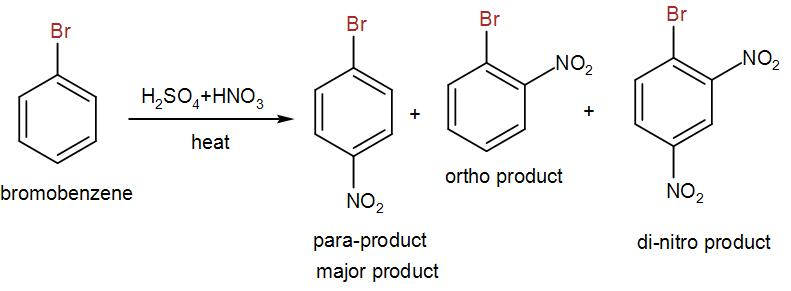
Here, the para-product us the 4-bromonitrobenzene.
Therefore, we can write the whole reaction of conversion of benzene to 4-bromonitrobenzene as-

Therefore, the above reaction is the required answer.
Note: Here, for the bromination of benzene we can either use aluminium (III) bromide or iron (III) bromide. Generally, we use iron (III) bromide because it is cheaper and readily available. We even use the chloride form of the same reagents for the chlorination of the aromatic benzene ring.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that benzene is an organic compound with formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$. We can convert it to certain compounds by adding required reagents.
In the question, we have been asked to convert benzene to 4-bromonitrobenzene.
Now as we can understand from the name itself, 4-bromonitrobenzene contains bromine and nitro- groups as substituents in the benzene ring.
Now firstly, let us discuss the reagents for bromination of benzene. Bromine undergoes electrophilic substitution in presence of a catalyst to give us the brominated product. We use iron bromide here and the product is bromobenzene. We can write the reaction as-

Now, for nitration, we used mixed acid i.e. sulphuric acid and nitric acid. We heat bromobenzene with the mixed acid and we obtain three different nitrated products. One is the para-product which is the major product and the other is ortho-product and we also obtain a di-nitro product. We can write the reaction as-

Here, the para-product us the 4-bromonitrobenzene.
Therefore, we can write the whole reaction of conversion of benzene to 4-bromonitrobenzene as-

Therefore, the above reaction is the required answer.
Note: Here, for the bromination of benzene we can either use aluminium (III) bromide or iron (III) bromide. Generally, we use iron (III) bromide because it is cheaper and readily available. We even use the chloride form of the same reagents for the chlorination of the aromatic benzene ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




