
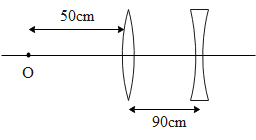
Focal length of a convex lens = 100cm and focal length of concave lens = -8cm.Find the magnification.

Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: The total magnification due to a system of lens is given by the product of magnification due to individual lenses. First we need to obtain the magnification produced due to the above individual lenses. Further accordingly we can determine the net magnification of the object placed at O.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
$m=\dfrac{v}{u}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let us say we have a lens and we place an object at a distance ‘u’ in front of the lens. If the focal length of the lens is given by ‘f’, then the position of the image ‘v’ produced by the lens is given by lens equation i.e.,
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
The magnification (m) produced by the same lens is given by
$m=\dfrac{v}{u}$
In the above question the object is placed at a distance of 50cm from the convex lens of focal length 100cm. Hence the position of the image is given by,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f} \\
& \because u=-50cm,\text{ }f=100cm \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{-50}=\dfrac{1}{100} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{100}-\dfrac{1}{50} \\
& \therefore v=-100cm \\
\end{align}$
Hence the magnification due to the convex lens is,
$\begin{align}
& {{m}_{1}}=\dfrac{v}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{1}}=\dfrac{-100}{-50}=\dfrac{100}{50} \\
& \therefore {{m}_{1}}=2 \\
\end{align}$
Since the image is formed in front of the convex lens at $100cm$ the position of the image ’x’ with respect to concave lens is,
$x=-90+\left( -100 \right)=-190cm$
This image would serve as an object for the concave lens. Hence from the above lens equation, the final image formed by the concave mirror is,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{1}{f} \\
& \because x=-190cm,\text{ }f=-8cm \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{-190}=\dfrac{1}{-8} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=-\dfrac{1}{8}-\dfrac{1}{190} \\
& \therefore v=-7.68cm \\
\end{align}$
Hence the magnification due to concave lens would be,
$\begin{align}
& {{m}_{2}}=\dfrac{v}{x} \\
& \therefore {{m}_{2}}=\dfrac{7.68}{190}=0.04 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the net magnification M of the above system of lens is,
$\begin{align}
& M={{m}_{1}}\times {{m}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow M=2\times 0.04 \\
& \therefore M=0.08 \\
\end{align}$
Hence the total linear magnification of the above lens is 0.08.
Note: The magnification is dimensionless quantity. When lenses are used in combination, the image formed by the preceding lens is used as an object by the next lens. Hence the net magnification is given by the product of magnification of individual lenses.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
$m=\dfrac{v}{u}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let us say we have a lens and we place an object at a distance ‘u’ in front of the lens. If the focal length of the lens is given by ‘f’, then the position of the image ‘v’ produced by the lens is given by lens equation i.e.,
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
The magnification (m) produced by the same lens is given by
$m=\dfrac{v}{u}$
In the above question the object is placed at a distance of 50cm from the convex lens of focal length 100cm. Hence the position of the image is given by,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f} \\
& \because u=-50cm,\text{ }f=100cm \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{-50}=\dfrac{1}{100} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{100}-\dfrac{1}{50} \\
& \therefore v=-100cm \\
\end{align}$
Hence the magnification due to the convex lens is,
$\begin{align}
& {{m}_{1}}=\dfrac{v}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{1}}=\dfrac{-100}{-50}=\dfrac{100}{50} \\
& \therefore {{m}_{1}}=2 \\
\end{align}$
Since the image is formed in front of the convex lens at $100cm$ the position of the image ’x’ with respect to concave lens is,
$x=-90+\left( -100 \right)=-190cm$
This image would serve as an object for the concave lens. Hence from the above lens equation, the final image formed by the concave mirror is,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{1}{f} \\
& \because x=-190cm,\text{ }f=-8cm \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{-190}=\dfrac{1}{-8} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=-\dfrac{1}{8}-\dfrac{1}{190} \\
& \therefore v=-7.68cm \\
\end{align}$
Hence the magnification due to concave lens would be,
$\begin{align}
& {{m}_{2}}=\dfrac{v}{x} \\
& \therefore {{m}_{2}}=\dfrac{7.68}{190}=0.04 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the net magnification M of the above system of lens is,
$\begin{align}
& M={{m}_{1}}\times {{m}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow M=2\times 0.04 \\
& \therefore M=0.08 \\
\end{align}$
Hence the total linear magnification of the above lens is 0.08.
Note: The magnification is dimensionless quantity. When lenses are used in combination, the image formed by the preceding lens is used as an object by the next lens. Hence the net magnification is given by the product of magnification of individual lenses.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




