
Fischer esterification is:
A.Nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction
B.Electrophilic substitution reaction
C.Electrophilic addition reaction
D.Free radical substitution reaction
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: when carboxylic acid and alcohol are refluxed in the presence of acid catalyst is called Fischer esterification. The acid catalyst acts as a dehydrating agent and increases the rate of the reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction between an organic acid $R - COOH$ and an alcohol $R - OH$ results in the formation of ester and this process is called esterification. The name of an ester is obtained from carboxylic acid, which takes part in the esterification reaction. Esterification process also occurs between alcohol and acid chloride.
A type of esterification, when carboxylic acid and an alcohol are refluxed in the presence of acid catalyst is called Fischer esterification. The acid catalyst acts as a dehydrating agent and increases the rate of the reaction.
We can write the general equation for Fischer Esterification as,
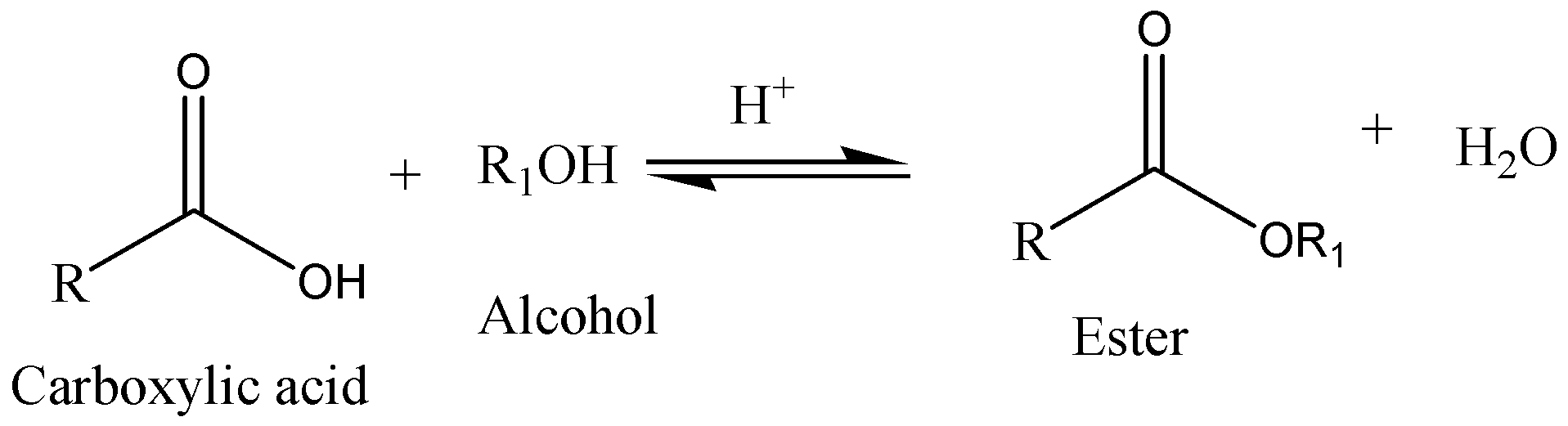
An example of nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction is Fischer esterification. It is based on the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon and the nucleophilicity of the alcohol. As electrophiles, the reactivity of carboxylic acid is less than the reactivity of esters. They have the tendency to deprotonate anions in dilute neutral solutions. Pure esters have a tendency to instinctively hydrolyze in water even though they are kinetically slow in the absence of catalysts. High yields of products aren’t favorable for Fischer esterification.
The mechanism of Fischer esterification involves in the following steps:
1.Transfer of proton from acid catalyst to the carbonyl oxygen raises the electrophilicity of carbonyl carbon.
2.Nucleophilic oxygen atom of the alcohol attacks the carbonyl carbon.
3.An activated complex is formed, when the proton is transferred from oxonium ion to a second molecule.
4.A new oxonium ion is formed by the protonation of one of the hydroxyl groups of the activated complex.
5.A molecule of water is lost from oxonium ion and deprotonation produces ester.
Therefore, the option (A) is correct.
Note:
We must know that several of the carboxylic acids are appropriate for Fischer esterification reaction, but alcohol used must be either primary (or) secondary. Usage of tertiary alcohols is liable to elimination. Some of commonly used catalyst in Fischer esterification process is,
Sulfuric acid
P-toluenesulfonic acid
Lewis acid like scandium (III) triflate
The major advantages of Fischer esterification is the use of simple reagents, and is thermodynamically-controlled.
The major disadvantages of Fischer esterification are its thermodynamic reversibility and the reaction rate is slow.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction between an organic acid $R - COOH$ and an alcohol $R - OH$ results in the formation of ester and this process is called esterification. The name of an ester is obtained from carboxylic acid, which takes part in the esterification reaction. Esterification process also occurs between alcohol and acid chloride.
A type of esterification, when carboxylic acid and an alcohol are refluxed in the presence of acid catalyst is called Fischer esterification. The acid catalyst acts as a dehydrating agent and increases the rate of the reaction.
We can write the general equation for Fischer Esterification as,

An example of nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction is Fischer esterification. It is based on the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon and the nucleophilicity of the alcohol. As electrophiles, the reactivity of carboxylic acid is less than the reactivity of esters. They have the tendency to deprotonate anions in dilute neutral solutions. Pure esters have a tendency to instinctively hydrolyze in water even though they are kinetically slow in the absence of catalysts. High yields of products aren’t favorable for Fischer esterification.
The mechanism of Fischer esterification involves in the following steps:
1.Transfer of proton from acid catalyst to the carbonyl oxygen raises the electrophilicity of carbonyl carbon.
2.Nucleophilic oxygen atom of the alcohol attacks the carbonyl carbon.
3.An activated complex is formed, when the proton is transferred from oxonium ion to a second molecule.
4.A new oxonium ion is formed by the protonation of one of the hydroxyl groups of the activated complex.
5.A molecule of water is lost from oxonium ion and deprotonation produces ester.
Therefore, the option (A) is correct.
Note:
We must know that several of the carboxylic acids are appropriate for Fischer esterification reaction, but alcohol used must be either primary (or) secondary. Usage of tertiary alcohols is liable to elimination. Some of commonly used catalyst in Fischer esterification process is,
Sulfuric acid
P-toluenesulfonic acid
Lewis acid like scandium (III) triflate
The major advantages of Fischer esterification is the use of simple reagents, and is thermodynamically-controlled.
The major disadvantages of Fischer esterification are its thermodynamic reversibility and the reaction rate is slow.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




