
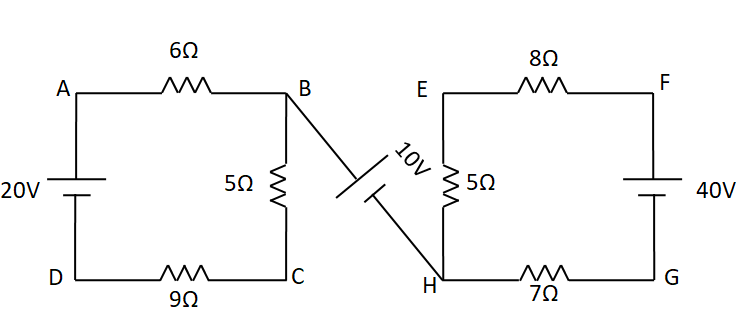
Find ${V_{CE}}$ and ${V_{AG}}$

Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint
To find this question, we need to use the KVL to find the currents in the given two meshes. Then, for finding the required potential difference, start from the initial point and choose any path to reach to the final path, while writing the potential gains or drops whichever comes in between.
Complete step by step answer
Let the currents in the two meshes be ${I_1}$ and ${I_2}$ respectively, as shown in the below circuit diagram.
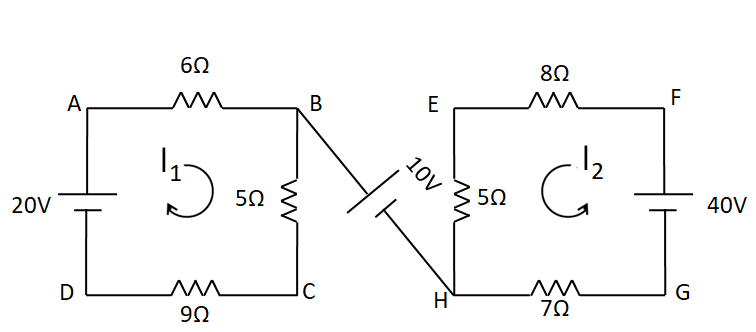
Applying KVL in the first loop ABCD, we have
$\Rightarrow 6{I_1} + 5{I_1} + 9{I_1} - 20 = 0$
$\Rightarrow 20{I_1} = 20$
Dividing both sides by $20$, we get
$\Rightarrow {I_1} = 1{\text{A}}$
Now, applying KVL in the second loop EFGH, we have
$\Rightarrow 8{I_2} + 5{I_2} + 7{I_2} - 40 = 0$
$\Rightarrow 20{I_2} = 40$
Dividing both sides by $20$, we get
$\Rightarrow {I_2} = 2{\text{A}}$
For ${V_{CE}}$, we travel along the path CBHE to get
$\Rightarrow {V_C} + 5{I_1} - 10 + 5{I_2} = {V_E}$
$\Rightarrow {V_C} + 5(1) - 10 + 5(2) = {V_E}$
On rearranging, we get
$\Rightarrow {V_C} - {V_E} = - 5{\text{V}}$
Or ${V_{CE}} = - 5{\text{V}}$
For ${V_{AG}}$, we travel along the path ABHG to get
$\Rightarrow {V_A} - 6{I_1} - 10 - 7{I_2} = {V_G}$
$\Rightarrow {V_A} - 6(1) - 10 - 7(2) = {V_G}$
On rearranging, we get
$\Rightarrow {V_A} - {V_G} = 30{\text{V}}$
Or ${V_{AG}} = 30{\text{V}}$
Hence, we have ${V_{CE}} = - 5{\text{V}}$ and ${V_{AG}} = 30{\text{V}}$.
Note
Before using the KVL, fix a sign convention of your choice. Do not confuse between the two sign conventions possible. We can use any sign convention of our choice. The choice of the sign convention does not affect the final answer.
-But while finding the potential difference between two points, there is no sign convention. As all the values of the currents are already found before this method is applied, so there is no need to think about any sign convention.
-We can choose any path between the initial point and the final point to find the potential difference. The potential difference between any two points in a circuit is not path dependent.
To find this question, we need to use the KVL to find the currents in the given two meshes. Then, for finding the required potential difference, start from the initial point and choose any path to reach to the final path, while writing the potential gains or drops whichever comes in between.
Complete step by step answer
Let the currents in the two meshes be ${I_1}$ and ${I_2}$ respectively, as shown in the below circuit diagram.

Applying KVL in the first loop ABCD, we have
$\Rightarrow 6{I_1} + 5{I_1} + 9{I_1} - 20 = 0$
$\Rightarrow 20{I_1} = 20$
Dividing both sides by $20$, we get
$\Rightarrow {I_1} = 1{\text{A}}$
Now, applying KVL in the second loop EFGH, we have
$\Rightarrow 8{I_2} + 5{I_2} + 7{I_2} - 40 = 0$
$\Rightarrow 20{I_2} = 40$
Dividing both sides by $20$, we get
$\Rightarrow {I_2} = 2{\text{A}}$
For ${V_{CE}}$, we travel along the path CBHE to get
$\Rightarrow {V_C} + 5{I_1} - 10 + 5{I_2} = {V_E}$
$\Rightarrow {V_C} + 5(1) - 10 + 5(2) = {V_E}$
On rearranging, we get
$\Rightarrow {V_C} - {V_E} = - 5{\text{V}}$
Or ${V_{CE}} = - 5{\text{V}}$
For ${V_{AG}}$, we travel along the path ABHG to get
$\Rightarrow {V_A} - 6{I_1} - 10 - 7{I_2} = {V_G}$
$\Rightarrow {V_A} - 6(1) - 10 - 7(2) = {V_G}$
On rearranging, we get
$\Rightarrow {V_A} - {V_G} = 30{\text{V}}$
Or ${V_{AG}} = 30{\text{V}}$
Hence, we have ${V_{CE}} = - 5{\text{V}}$ and ${V_{AG}} = 30{\text{V}}$.
Note
Before using the KVL, fix a sign convention of your choice. Do not confuse between the two sign conventions possible. We can use any sign convention of our choice. The choice of the sign convention does not affect the final answer.
-But while finding the potential difference between two points, there is no sign convention. As all the values of the currents are already found before this method is applied, so there is no need to think about any sign convention.
-We can choose any path between the initial point and the final point to find the potential difference. The potential difference between any two points in a circuit is not path dependent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




