
How do you find the vertex and the intercepts for $y=3{{x}^{2}}+12x$?
Answer
552k+ views
Hint: The equation $y=3{{x}^{2}}+12x$ is linear in $y$ but quadratic in $x$. So this means that this is an equation of a parabola. For determining the x-intercept, we will put $y=0$ in the given equation. And for determining the y-intercept, we will put $x=0$. But for the determination of the vertex, we will differentiate the given equation and equate the derivative to zero. This is because at the vertex of a parabola, its slope is equal to zero.
Complete step by step solution:
The given equation is
$y=3{{x}^{2}}+12x........\left( i \right)$
We know that the x-intercepts are the points where the graph cuts the x-axis. Therefore, we put $y=0$ in (i) to get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 0=3{{x}^{2}}+12x \\
& \Rightarrow 3{{x}^{2}}+12x=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Taking $x$ common we have
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x\left( 3x+12 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=0,x=\dfrac{-12}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow x=0,x=-4 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the x-intercepts are $\left( 0,0 \right)$ and $\left( -4,0 \right)$.
Now, the y-intercepts are the points where the graph cuts the y-axis. Therefore, we put $x=0$ in (i) to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=3{{\left( 0 \right)}^{2}}+12\left( 0 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y=0 \\
\end{align}$
So the y-intercept is $\left( 0,0 \right)$.
Now, since the given equation is quadratic in $x$ and linear in $y$, this means that it is an equation of a parabola whose axis is vertical. We know that at the vertex of a parabola having a vertical axis, its slope is equal to zero. Therefore, we differentiate both sides of the given equation (i) to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=3\left( 2x \right)+12 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=6x+12 \\
\end{align}$
For vertex, we put $\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0$ to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 6x+12=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{12}{6} \\
& \Rightarrow x=-2 \\
\end{align}$
So the x-coordinate of the vertex is equal to $-2$. For the y-coordinate, we substitute $x=-2$ in (i) to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=3{{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}+12\left( -2 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y=3\left( 4 \right)-24 \\
& \Rightarrow y=12-24 \\
& \Rightarrow y=-12 \\
\end{align}$
So the y-coordinate of the vertex is equal to $-12$. Therefore, the vertex of the given equation is at $\left( -2,-12 \right)$.
We can observe the vertex and the intercepts in the below graph.
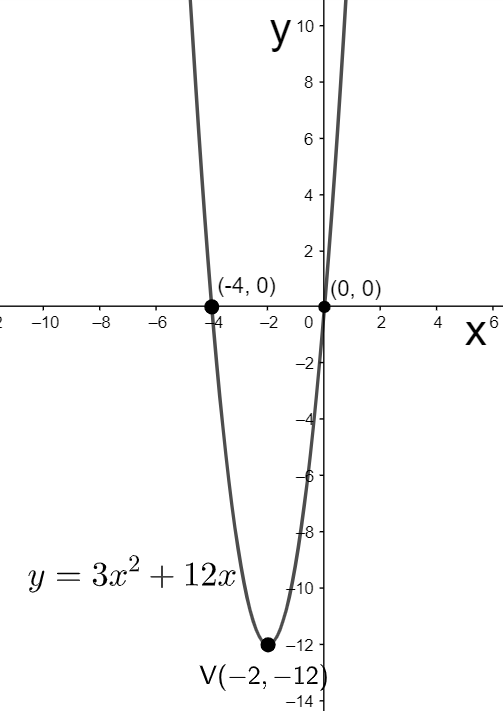
Note:
For determining the vertex, we can also use the completing the square method so that the given equation gets reduced to the standard equation of a parabola. The standard equation of a parabola is given as ${{X}^{2}}=4aY$, from which the vertex is at $X=0,Y=0$. By completing the square method, we will obtain the given equation as $\left( x+2 \right)=\dfrac{1}{3}\left( y+12 \right)$. Therefore, setting $x+2=0$ and $y+12=0$ we will get the vertex at $\left( -2,-12 \right)$.
Complete step by step solution:
The given equation is
$y=3{{x}^{2}}+12x........\left( i \right)$
We know that the x-intercepts are the points where the graph cuts the x-axis. Therefore, we put $y=0$ in (i) to get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 0=3{{x}^{2}}+12x \\
& \Rightarrow 3{{x}^{2}}+12x=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Taking $x$ common we have
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x\left( 3x+12 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=0,x=\dfrac{-12}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow x=0,x=-4 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the x-intercepts are $\left( 0,0 \right)$ and $\left( -4,0 \right)$.
Now, the y-intercepts are the points where the graph cuts the y-axis. Therefore, we put $x=0$ in (i) to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=3{{\left( 0 \right)}^{2}}+12\left( 0 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y=0 \\
\end{align}$
So the y-intercept is $\left( 0,0 \right)$.
Now, since the given equation is quadratic in $x$ and linear in $y$, this means that it is an equation of a parabola whose axis is vertical. We know that at the vertex of a parabola having a vertical axis, its slope is equal to zero. Therefore, we differentiate both sides of the given equation (i) to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=3\left( 2x \right)+12 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=6x+12 \\
\end{align}$
For vertex, we put $\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0$ to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 6x+12=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{12}{6} \\
& \Rightarrow x=-2 \\
\end{align}$
So the x-coordinate of the vertex is equal to $-2$. For the y-coordinate, we substitute $x=-2$ in (i) to get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=3{{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}+12\left( -2 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y=3\left( 4 \right)-24 \\
& \Rightarrow y=12-24 \\
& \Rightarrow y=-12 \\
\end{align}$
So the y-coordinate of the vertex is equal to $-12$. Therefore, the vertex of the given equation is at $\left( -2,-12 \right)$.
We can observe the vertex and the intercepts in the below graph.

Note:
For determining the vertex, we can also use the completing the square method so that the given equation gets reduced to the standard equation of a parabola. The standard equation of a parabola is given as ${{X}^{2}}=4aY$, from which the vertex is at $X=0,Y=0$. By completing the square method, we will obtain the given equation as $\left( x+2 \right)=\dfrac{1}{3}\left( y+12 \right)$. Therefore, setting $x+2=0$ and $y+12=0$ we will get the vertex at $\left( -2,-12 \right)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




