
Find the values of the other five trigonometric functions if \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}\], \[\theta \] in quadrant I.
Answer
610.2k+ views
Hint:First of all, try to recollect the signs of the various trigonometric ratios in the first quadrant. Now, find \[\operatorname{cosec}\theta \] by using \[\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }\], \[\cos \theta \] by \[\sqrt{1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta }\], \[\sec \theta \] by \[\dfrac{1}{\cos \theta }\], \[\tan \theta \] by \[\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }\] , and \[\cot \theta \] by \[\dfrac{1}{\tan \theta }\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we have to find the values of the other five trigonometric functions if \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}\], \[\theta \] in quadrant I. Before proceeding with this question, let us see the sign of different trigonometric ratios in different quadrants. We have 6 trigonometric ratios and that are \[\sin \theta ,\cos \theta ,\tan \theta ,\cot \theta ,\operatorname{cosec}\theta \] and \[\sec \theta \].
1. In the first quadrant, that is from 0 to \[{{90}^{o}}\] or 0 to \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\], all the trigonometric ratios are positive.
2. In the second quadrant, that is from \[{{90}^{o}}\] to \[{{180}^{o}}\] or \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\] to \[\pi \], only \[\sin \theta \] and \[\operatorname{cosec}\theta \] are positive.
3. In the third quadrant, that is from \[{{180}^{o}}\] to \[{{270}^{o}}\] or \[\pi \] to \[\dfrac{3\pi }{2}\], only \[\tan \theta \] and \[\cot \theta \] are positive.
4. In the fourth quadrant, that is from \[{{270}^{o}}\] to \[{{360}^{o}}\] or \[\dfrac{3\pi }{2}\] to \[2\pi \], only \[\cos \theta \] and \[\sec \theta \] are positive.
This cycle would repeat after \[{{360}^{o}}\].
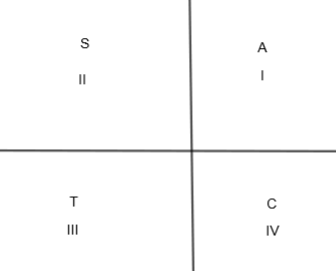
In this figure, A means all are positive, S means \[\sin \theta \] and \[\operatorname{cosec}\theta \] are positive, T means \[\tan \theta \] and \[\cot \theta \] are positive and C means \[\cos \theta \] and \[\sec \theta \] are positive.
Here, we are given that \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}\] and \[\theta \] is in the first quadrant. So, in this quadrant, all the trigonometric ratios would be positive.
We know that \[\operatorname{cosec}\theta =\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }\]
By substituting the value of \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}\], we get,
\[\operatorname{cosec}\theta =\dfrac{1}{\left( \dfrac{3}{5} \right)}\]
\[\operatorname{cosec}\theta =\dfrac{5}{3}\]
We know that \[{{\sin }^{2}}\theta +{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1\].
By substituting \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}\], we get,
\[{{\left( \dfrac{3}{5} \right)}^{2}}+{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1\]
\[{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1-{{\left( \dfrac{3}{5} \right)}^{2}}\]
\[{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1-\dfrac{9}{25}\]
\[{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =\dfrac{16}{25}\]
\[\cos \theta =\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{25}}\]
\[\cos \theta =\pm \dfrac{4}{5}\]
Here, we take \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{4}{5}\] because in the first quadrant all the trigonometric ratios are positive. We know that \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }\]. So, by substituting \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}\] and \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{4}{5}\], we get,
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{\dfrac{3}{5}}{\dfrac{4}{5}}\]
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}\]
We also know that \[\sec \theta =\dfrac{1}{\cos \theta }\]
By substituting \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{4}{5}\], we get,
\[\sec \theta =\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{4}{5}}=\dfrac{5}{4}\]
We know that \[\cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\tan \theta }\]. By substituting the value of \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}\], we get,
\[\cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{3}{4}}=\dfrac{4}{3}\]
So, if \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}\] and \[\theta \] is in the first quadrant, the other 5 values we get as,
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{4}{5}\]
\[\sec \theta =\dfrac{5}{4}\]
\[\operatorname{cosec}\theta =\dfrac{5}{3}\]
\[\cot \theta =\dfrac{4}{3}\]
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}\]
Note: In this question, we can also find the value of the magnitude of all the trigonometric ratios by constructing a triangle and using \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}\] in this way.
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{perpendicular}}{\text{hypotenuse}}=\dfrac{3}{5}=\dfrac{AB}{AC}\]
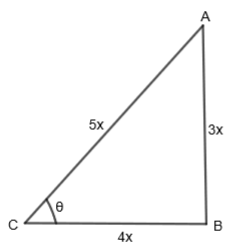
From Pythagoras theorem, we get, CB = 4x.
Now, \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{\text{Base}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}=\dfrac{4x}{5x}=\dfrac{4}{5}\]
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{AB}{BC}=\dfrac{3x}{4x}=\dfrac{3}{4}\]
Similarly, we can find all the other trigonometric ratios.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we have to find the values of the other five trigonometric functions if \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}\], \[\theta \] in quadrant I. Before proceeding with this question, let us see the sign of different trigonometric ratios in different quadrants. We have 6 trigonometric ratios and that are \[\sin \theta ,\cos \theta ,\tan \theta ,\cot \theta ,\operatorname{cosec}\theta \] and \[\sec \theta \].
1. In the first quadrant, that is from 0 to \[{{90}^{o}}\] or 0 to \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\], all the trigonometric ratios are positive.
2. In the second quadrant, that is from \[{{90}^{o}}\] to \[{{180}^{o}}\] or \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\] to \[\pi \], only \[\sin \theta \] and \[\operatorname{cosec}\theta \] are positive.
3. In the third quadrant, that is from \[{{180}^{o}}\] to \[{{270}^{o}}\] or \[\pi \] to \[\dfrac{3\pi }{2}\], only \[\tan \theta \] and \[\cot \theta \] are positive.
4. In the fourth quadrant, that is from \[{{270}^{o}}\] to \[{{360}^{o}}\] or \[\dfrac{3\pi }{2}\] to \[2\pi \], only \[\cos \theta \] and \[\sec \theta \] are positive.
This cycle would repeat after \[{{360}^{o}}\].

In this figure, A means all are positive, S means \[\sin \theta \] and \[\operatorname{cosec}\theta \] are positive, T means \[\tan \theta \] and \[\cot \theta \] are positive and C means \[\cos \theta \] and \[\sec \theta \] are positive.
Here, we are given that \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}\] and \[\theta \] is in the first quadrant. So, in this quadrant, all the trigonometric ratios would be positive.
We know that \[\operatorname{cosec}\theta =\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }\]
By substituting the value of \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}\], we get,
\[\operatorname{cosec}\theta =\dfrac{1}{\left( \dfrac{3}{5} \right)}\]
\[\operatorname{cosec}\theta =\dfrac{5}{3}\]
We know that \[{{\sin }^{2}}\theta +{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1\].
By substituting \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}\], we get,
\[{{\left( \dfrac{3}{5} \right)}^{2}}+{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1\]
\[{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1-{{\left( \dfrac{3}{5} \right)}^{2}}\]
\[{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1-\dfrac{9}{25}\]
\[{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =\dfrac{16}{25}\]
\[\cos \theta =\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{25}}\]
\[\cos \theta =\pm \dfrac{4}{5}\]
Here, we take \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{4}{5}\] because in the first quadrant all the trigonometric ratios are positive. We know that \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }\]. So, by substituting \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}\] and \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{4}{5}\], we get,
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{\dfrac{3}{5}}{\dfrac{4}{5}}\]
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}\]
We also know that \[\sec \theta =\dfrac{1}{\cos \theta }\]
By substituting \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{4}{5}\], we get,
\[\sec \theta =\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{4}{5}}=\dfrac{5}{4}\]
We know that \[\cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\tan \theta }\]. By substituting the value of \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}\], we get,
\[\cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{3}{4}}=\dfrac{4}{3}\]
So, if \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}\] and \[\theta \] is in the first quadrant, the other 5 values we get as,
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{4}{5}\]
\[\sec \theta =\dfrac{5}{4}\]
\[\operatorname{cosec}\theta =\dfrac{5}{3}\]
\[\cot \theta =\dfrac{4}{3}\]
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}\]
Note: In this question, we can also find the value of the magnitude of all the trigonometric ratios by constructing a triangle and using \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5}\] in this way.
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{perpendicular}}{\text{hypotenuse}}=\dfrac{3}{5}=\dfrac{AB}{AC}\]

From Pythagoras theorem, we get, CB = 4x.
Now, \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{\text{Base}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}=\dfrac{4x}{5x}=\dfrac{4}{5}\]
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{AB}{BC}=\dfrac{3x}{4x}=\dfrac{3}{4}\]
Similarly, we can find all the other trigonometric ratios.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




