
Find the values of $g(0), g(2), g(4), g(6)$ and $g(12)$, if $g(x) = \int\limits_0^x {f(t)dt} $, where f is the function and the graph of function f is given below.
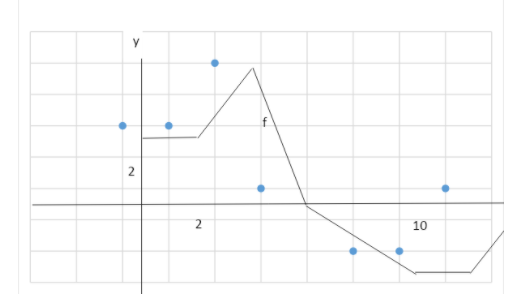
We found that $g(0) = 0$ and as the area is $4$ squares, we think that $g(2)$ should be $4$, but we have to find whether it is correct or not?

Answer
545.4k+ views
Hint:
In this problem we have given a composite function. Composite functions are those functions in which the one function is composed into another and these functions can solve any given value and the graph shown here shows the value of function f.
Formula Used:
Area of rectangle$ = $$l \times b$
Where, l is the length and b is the breadth.
Area of trapezium $ = \dfrac{1}{2}(a + b)x$
Where, a and b are the parallel sides and x is the distance between them.
Area of triangle$ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times h$
Where, b is the base and h is the height.
Complete step by step solution:
Since, we are to deal with composite functions. It is given that,
$g(x) = \int\limits_0^x {f(t)dt} $
Which means, it provides the area from the origin to x. Now, we will find the values,
Part 1-By definition
$
\Rightarrow g(0) = \int\limits_0^0 {f(t)dt} \\
\Rightarrow g(0) = 0 \\
$
Part 2- Area of rectangle $ = $ length $ \times $ breadth
$
\Rightarrow g(2) = \int\limits_0^2 {f(t)dt} \\
\Rightarrow g(2) = 4 \times 2 \\
\Rightarrow g(2) = 8 \\
$
Part 3- $g(4)$ covers the area of the rectangle and the area of trapezium.
Area of trapezium$ = $$\dfrac{1}{2} \times $ sum of parallel sides $ \times $ distance between the parallel sides
Then,
$
\Rightarrow g(4) = \int\limits_0^4 {f(t)dt} \\
\Rightarrow g(4) = g(2) + \dfrac{1}{2}(4 + 8)(2) \\
\Rightarrow g(4) = 8 + 12 \\
\Rightarrow g(4) = 20 \\
$
Part 4- $g(6)$ covers the area of $g(4)$ and the area of a triangle.
Area of a triangle$ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times $base$ \times $height
$
\Rightarrow g(6) = \int\limits_0^6 {f(t)dt} \\
\Rightarrow g(6) = g(4) + \dfrac{1}{2}(2)(8) \\
\Rightarrow g(6) = 20 + 8 \\
\Rightarrow g(6) = 28 \\
$
Part 5- The area of$g(12)$ is the area of $g(6)$ subtracting the area of the trapezium formed below.
$
\Rightarrow g(12) = \int\limits_0^{12} {f(t)dt} \\
\Rightarrow g(12) = g(6) - \dfrac{1}{2}(8 + 2)(4) \\
\Rightarrow g(12) = 28 - 20 \\
\Rightarrow g(12) = 8 \\
$
Note:
g is a composite function through which we can calculate the exact values by using the graph of f. We have easily found the values of $g(0), g(2), g(4), g(6)$ and $g(12)$ as the graph is formed by rectangle, triangle and trapezium.
In this problem we have given a composite function. Composite functions are those functions in which the one function is composed into another and these functions can solve any given value and the graph shown here shows the value of function f.
Formula Used:
Area of rectangle$ = $$l \times b$
Where, l is the length and b is the breadth.
Area of trapezium $ = \dfrac{1}{2}(a + b)x$
Where, a and b are the parallel sides and x is the distance between them.
Area of triangle$ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times h$
Where, b is the base and h is the height.
Complete step by step solution:
Since, we are to deal with composite functions. It is given that,
$g(x) = \int\limits_0^x {f(t)dt} $
Which means, it provides the area from the origin to x. Now, we will find the values,
Part 1-By definition
$
\Rightarrow g(0) = \int\limits_0^0 {f(t)dt} \\
\Rightarrow g(0) = 0 \\
$
Part 2- Area of rectangle $ = $ length $ \times $ breadth
$
\Rightarrow g(2) = \int\limits_0^2 {f(t)dt} \\
\Rightarrow g(2) = 4 \times 2 \\
\Rightarrow g(2) = 8 \\
$
Part 3- $g(4)$ covers the area of the rectangle and the area of trapezium.
Area of trapezium$ = $$\dfrac{1}{2} \times $ sum of parallel sides $ \times $ distance between the parallel sides
Then,
$
\Rightarrow g(4) = \int\limits_0^4 {f(t)dt} \\
\Rightarrow g(4) = g(2) + \dfrac{1}{2}(4 + 8)(2) \\
\Rightarrow g(4) = 8 + 12 \\
\Rightarrow g(4) = 20 \\
$
Part 4- $g(6)$ covers the area of $g(4)$ and the area of a triangle.
Area of a triangle$ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times $base$ \times $height
$
\Rightarrow g(6) = \int\limits_0^6 {f(t)dt} \\
\Rightarrow g(6) = g(4) + \dfrac{1}{2}(2)(8) \\
\Rightarrow g(6) = 20 + 8 \\
\Rightarrow g(6) = 28 \\
$
Part 5- The area of$g(12)$ is the area of $g(6)$ subtracting the area of the trapezium formed below.
$
\Rightarrow g(12) = \int\limits_0^{12} {f(t)dt} \\
\Rightarrow g(12) = g(6) - \dfrac{1}{2}(8 + 2)(4) \\
\Rightarrow g(12) = 28 - 20 \\
\Rightarrow g(12) = 8 \\
$
Note:
g is a composite function through which we can calculate the exact values by using the graph of f. We have easily found the values of $g(0), g(2), g(4), g(6)$ and $g(12)$ as the graph is formed by rectangle, triangle and trapezium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




