
Find the value of \[\cos \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\]
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Here we use the formula of \[2\sin x\cos x = \sin 2x\] repeatedly to lessen the values in the solution. We multiply and divide the given value with \[2\sin \dfrac {\pi }{{15}}\] and apply the trigonometric formula. We continue in this manner till we stop getting the corresponding cosine of the angle in the available terms. Then break the remaining angles in terms of subtraction or addition to \[\pi \] and use the quadrant diagram to solve for the value.
* In a quadrant diagram we have trigonometric functions specific to a quadrant where they are positive in nature. We always move in an anticlockwise direction when adding angles.
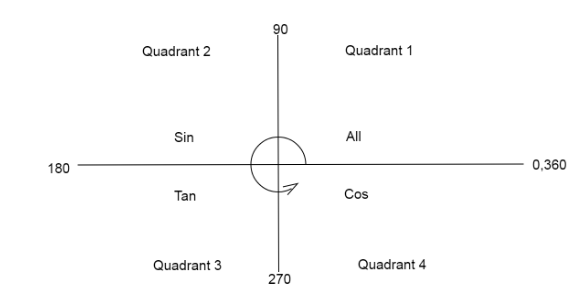
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given the equation \[\cos \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\]
First multiply and divide the equation by \[2\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\left\{ {2\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)} \right\}\cos \left( {\dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{2\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\]
Use the trigonometric formula \[2\sin x\cos x = \sin 2x\]. Substitute \[x = \dfrac {\pi }{{15}}\]
\[2\sin \dfrac {\pi }{{15}}\cos \dfrac {\pi }{{15}} = \sin 2\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}\]
Multiply the value in RHS
\[2\sin \dfrac {\pi }{{15}}\cos \dfrac {\pi }{{15}} = \sin \dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}\] … (2)
Substitute the value from equation (2) in equation (1)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\sin \left( {\dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{2\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\]
Multiply and divide the equation by 2
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\left\{ {2\sin \left( {\dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}} \right)} \right\}\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{2 \times 2\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\] … (3)
Use the trigonometric formula\[2\sin x\cos x = \sin 2x\]. Substitute \[x = \dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}\]
\[2\sin \dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}} = \sin 2\dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}\]
Multiply the value in RHS
\[2\sin \dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}} = \sin \dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}\] … (4)
Substitute the value from equation (4) in equation (3)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\sin \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{4\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\]
Multiply and divide the equation by 2
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\left\{ {2\sin \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)} \right\}\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{2 \times 4\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\] … (5)
Use the trigonometric formula\[2\sin x\cos x = \sin 2x\]. Substitute \[x = \dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}\]
\[2\sin \dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}} = \sin 2\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}\]
Multiply the value in RHS
\[2\sin \dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}} = \sin \dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}\] … (6)
Substitute the value from equation (6) in equation (5)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\sin \left( {\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{8\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\] … (7)
Now we know \[\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right) = \cos \left( {\pi - \dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\]
We find the value of \[\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\] from the quadrant diagram.
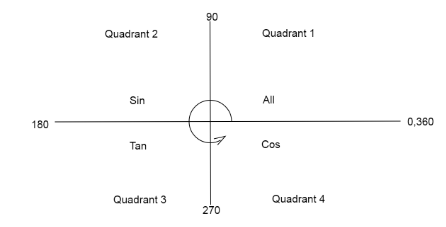
As we subtract an angle from \[\pi \], only the function sin remains positive.
Therefore, \[\cos \left( {\pi - \dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right) = - \cos \left( {\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\]
Substitute the value of \[\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right) = - \cos \left( {\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\] in equation (7)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{ - \sin \left( {\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{8\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\]
Multiply and divide the equation by 2
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{ - \left\{ {2\sin \left( {\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right)} \right\}\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{2 \times 8\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\] … (8)
Use the trigonometric formula\[2\sin x\cos x = \sin 2x\]. Substitute \[x = \dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}\]
\[2\sin \dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}} = \sin 2\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}\]
Multiply the value in RHS
\[2\sin \dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}} = \sin \dfrac {{16\pi }}{{15}}\] … (9)
Substitute the value from equation (9) in equation (8)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{ - \sin \left( {\dfrac {{16\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{16\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\] … (10)
Now we know \[\sin \left( {\dfrac {{16\pi }}{{15}}} \right) = \sin \left( {\pi + \dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)\]
We find the value of \[\sin \left( {\dfrac {{16\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\] from the quadrant diagram.
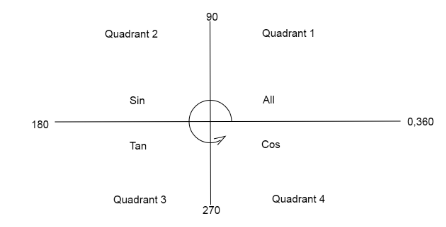
As we add an angle to \[\pi \], only the function tan remains positive.
Therefore, \[\sin \left( {\pi + \dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right) = - \sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)\]
Substitute the value of \[\sin \left( {\dfrac {{16\pi }}{{15}}} \right) = - \sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)\] in equation (10)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{ - ( - \sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right))\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{16\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\]
Cancel the same terms from numerator and denominator.
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{16}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{3}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{16}}\]
Substitute the value of \[\cos \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{3}} \right) = \dfrac {1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{16 \times 2}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{32}}\] … (11)
First multiply and divide the equation by \[2\sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\left\{ {2\sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)} \right\}\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{32 \times 2\sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}\] … (12)
Use the trigonometric formula \[2\sin x\cos x = \sin 2x\]. Substitute \[x = \dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}\]
\[2\sin \dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}} = \sin 2\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}\]
Multiply the value in RHS
\[2\sin \dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}} = \sin \dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}\] … (13)
Substitute the value from equation (13) in equation (12)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\sin \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{64\sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}\]
Multiply and divide the equation by 2
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\left\{ {2\sin \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)} \right\}}}{{2 \times 64\sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}\] … (14)
Use the trigonometric formula \[2\sin x\cos x = \sin 2x\]. Substitute \[x = \dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}\]
\[2\sin \dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}} = \sin 2\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}\]
Multiply the value in RHS
\[2\sin \dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}} = \sin \dfrac {{12\pi }}{{15}}\] … (15)
Substitute the value from equation (15) in equation (14)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\sin \left( {\dfrac {{12\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{128\sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}\] … (16)
Now we know \[\sin \left( {\dfrac {{12\pi }}{{15}}} \right) = \sin \left( {\pi - \dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\]
We find the value of \[\sin \left( {\dfrac {{12\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\]from the quadrant diagram.
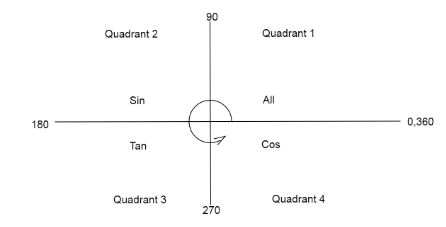
As we subtract an angle from\[\pi \], only the function sin remains positive.
Therefore, \[\sin \left( {\pi - \dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right) = \sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\]
Substitute the value of \[\sin \left( {\dfrac {{12\pi }}{{15}}} \right) = \sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\] in equation (16)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{128\sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}\]
Cancel the same terms from numerator and denominator.
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {1}{{128}}\]
Therefore, value of \[\cos \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\] is\[\dfrac {1}{{128}}\].
Note: Students are likely to get confused while pairing up the values for cos and sin after the value of angle as \[\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}\], keep in mind we break the angle with addition and subtraction to \[\pi \]. Always check the angle from the quadrant diagram as when we add an angle we move in anticlockwise direction and when we subtract an angle we move in clockwise direction.
* In a quadrant diagram we have trigonometric functions specific to a quadrant where they are positive in nature. We always move in an anticlockwise direction when adding angles.

Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given the equation \[\cos \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\]
First multiply and divide the equation by \[2\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\left\{ {2\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)} \right\}\cos \left( {\dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{2\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\]
Use the trigonometric formula \[2\sin x\cos x = \sin 2x\]. Substitute \[x = \dfrac {\pi }{{15}}\]
\[2\sin \dfrac {\pi }{{15}}\cos \dfrac {\pi }{{15}} = \sin 2\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}\]
Multiply the value in RHS
\[2\sin \dfrac {\pi }{{15}}\cos \dfrac {\pi }{{15}} = \sin \dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}\] … (2)
Substitute the value from equation (2) in equation (1)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\sin \left( {\dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{2\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\]
Multiply and divide the equation by 2
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\left\{ {2\sin \left( {\dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}} \right)} \right\}\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{2 \times 2\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\] … (3)
Use the trigonometric formula\[2\sin x\cos x = \sin 2x\]. Substitute \[x = \dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}\]
\[2\sin \dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}} = \sin 2\dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}\]
Multiply the value in RHS
\[2\sin \dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}} = \sin \dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}\] … (4)
Substitute the value from equation (4) in equation (3)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\sin \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{4\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\]
Multiply and divide the equation by 2
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\left\{ {2\sin \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)} \right\}\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{2 \times 4\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\] … (5)
Use the trigonometric formula\[2\sin x\cos x = \sin 2x\]. Substitute \[x = \dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}\]
\[2\sin \dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}} = \sin 2\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}\]
Multiply the value in RHS
\[2\sin \dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}} = \sin \dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}\] … (6)
Substitute the value from equation (6) in equation (5)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\sin \left( {\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{8\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\] … (7)
Now we know \[\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right) = \cos \left( {\pi - \dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\]
We find the value of \[\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\] from the quadrant diagram.

As we subtract an angle from \[\pi \], only the function sin remains positive.
Therefore, \[\cos \left( {\pi - \dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right) = - \cos \left( {\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\]
Substitute the value of \[\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right) = - \cos \left( {\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\] in equation (7)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{ - \sin \left( {\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{8\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\]
Multiply and divide the equation by 2
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{ - \left\{ {2\sin \left( {\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}} \right)} \right\}\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{2 \times 8\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\] … (8)
Use the trigonometric formula\[2\sin x\cos x = \sin 2x\]. Substitute \[x = \dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}\]
\[2\sin \dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}} = \sin 2\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}\]
Multiply the value in RHS
\[2\sin \dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}} = \sin \dfrac {{16\pi }}{{15}}\] … (9)
Substitute the value from equation (9) in equation (8)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{ - \sin \left( {\dfrac {{16\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{16\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\] … (10)
Now we know \[\sin \left( {\dfrac {{16\pi }}{{15}}} \right) = \sin \left( {\pi + \dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)\]
We find the value of \[\sin \left( {\dfrac {{16\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\] from the quadrant diagram.

As we add an angle to \[\pi \], only the function tan remains positive.
Therefore, \[\sin \left( {\pi + \dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right) = - \sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)\]
Substitute the value of \[\sin \left( {\dfrac {{16\pi }}{{15}}} \right) = - \sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)\] in equation (10)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{ - ( - \sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right))\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{16\sin \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)}}\]
Cancel the same terms from numerator and denominator.
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{16}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{3}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{16}}\]
Substitute the value of \[\cos \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{3}} \right) = \dfrac {1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{16 \times 2}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{32}}\] … (11)
First multiply and divide the equation by \[2\sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\left\{ {2\sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)} \right\}\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{32 \times 2\sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}\] … (12)
Use the trigonometric formula \[2\sin x\cos x = \sin 2x\]. Substitute \[x = \dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}\]
\[2\sin \dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}} = \sin 2\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}\]
Multiply the value in RHS
\[2\sin \dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}} = \sin \dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}\] … (13)
Substitute the value from equation (13) in equation (12)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\sin \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{64\sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}\]
Multiply and divide the equation by 2
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\left\{ {2\sin \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)} \right\}}}{{2 \times 64\sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}\] … (14)
Use the trigonometric formula \[2\sin x\cos x = \sin 2x\]. Substitute \[x = \dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}\]
\[2\sin \dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}} = \sin 2\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}\]
Multiply the value in RHS
\[2\sin \dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}\cos \dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}} = \sin \dfrac {{12\pi }}{{15}}\] … (15)
Substitute the value from equation (15) in equation (14)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\sin \left( {\dfrac {{12\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{128\sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}\] … (16)
Now we know \[\sin \left( {\dfrac {{12\pi }}{{15}}} \right) = \sin \left( {\pi - \dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\]
We find the value of \[\sin \left( {\dfrac {{12\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\]from the quadrant diagram.

As we subtract an angle from\[\pi \], only the function sin remains positive.
Therefore, \[\sin \left( {\pi - \dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right) = \sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\]
Substitute the value of \[\sin \left( {\dfrac {{12\pi }}{{15}}} \right) = \sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\] in equation (16)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {{\sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}{{128\sin \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)}}\]
Cancel the same terms from numerator and denominator.
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac {1}{{128}}\]
Therefore, value of \[\cos \left( {\dfrac {\pi }{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{2\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{3\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{4\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{5\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{6\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\cos \left( {\dfrac {{7\pi }}{{15}}} \right)\] is\[\dfrac {1}{{128}}\].
Note: Students are likely to get confused while pairing up the values for cos and sin after the value of angle as \[\dfrac {{8\pi }}{{15}}\], keep in mind we break the angle with addition and subtraction to \[\pi \]. Always check the angle from the quadrant diagram as when we add an angle we move in anticlockwise direction and when we subtract an angle we move in clockwise direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




