
Find the sum of oxidation state of s-atom in thio - sulfuric acid.
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint: As we know oxidation state shows us the degree of oxidation for an atom in a chemical compound; it is a hypothetical charge that an atom would possess if all bonds to atoms of different elements were completely ionic. Oxidation states are typically represented by integers, which can be positive, negative, or zero; it can even be a fraction also in some cases.
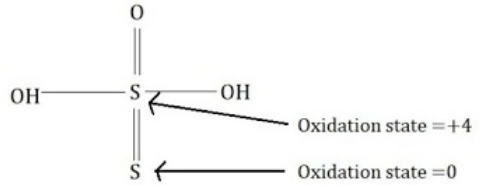
Complete step-by-step answer:Thio sulfuric acid is of the formula ${H_2}{S_2}{O_3}$ .
The oxidation states of the two sulfur atoms are $0$ and $ + 4$ . Hence their sum would be $0 + 4 = 4$
Additional information:
The underlying principle behind oxidation state is that the ionic charge is "the oxidation state of an atom, after ionic approximation of its bonds", where by ionic approximation we mean that all bonds are ionic. Certain criteria were considered for the ionic approximation:
a.Extrapolation of the bond’s polarity; from the electronegativity difference, from the dipole moment, and from quantum‐chemical calculations of charges.
b.Assignment of electrons according to the atom’s contribution to the bonding molecular orbital or the electron's allegiance in a linear combination of atomic orbitals model.
Note:Always note that the oxidation state of a pure element is zero and the oxidation state for a pure ion is equivalent to its ionic charge. The sum of the oxidation states of all atoms in a neutral molecule must be equal to zero. Remember that reduction is the gain of electrons, which causes a decrease in oxidation state while oxidation is the loss of electrons, which makes the oxidation state to increase.
Complete step-by-step answer:Thio sulfuric acid is of the formula ${H_2}{S_2}{O_3}$ .
The oxidation states of the two sulfur atoms are $0$ and $ + 4$ . Hence their sum would be $0 + 4 = 4$

Additional information:
The underlying principle behind oxidation state is that the ionic charge is "the oxidation state of an atom, after ionic approximation of its bonds", where by ionic approximation we mean that all bonds are ionic. Certain criteria were considered for the ionic approximation:
a.Extrapolation of the bond’s polarity; from the electronegativity difference, from the dipole moment, and from quantum‐chemical calculations of charges.
b.Assignment of electrons according to the atom’s contribution to the bonding molecular orbital or the electron's allegiance in a linear combination of atomic orbitals model.
Note:Always note that the oxidation state of a pure element is zero and the oxidation state for a pure ion is equivalent to its ionic charge. The sum of the oxidation states of all atoms in a neutral molecule must be equal to zero. Remember that reduction is the gain of electrons, which causes a decrease in oxidation state while oxidation is the loss of electrons, which makes the oxidation state to increase.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




