
Find the product ${\text{B}}$ in the following chemical reaction.
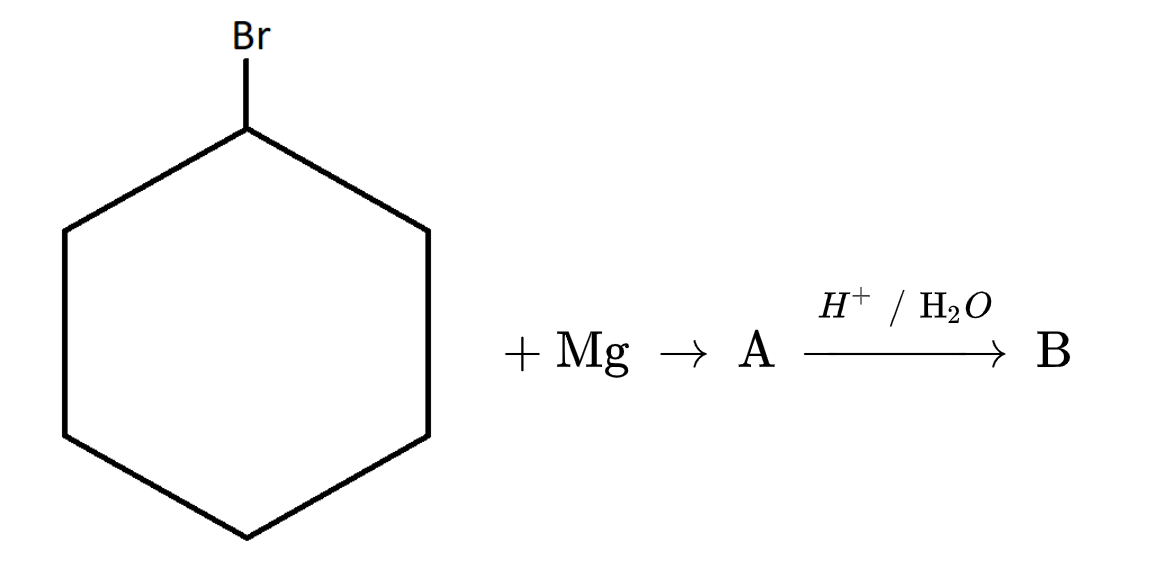
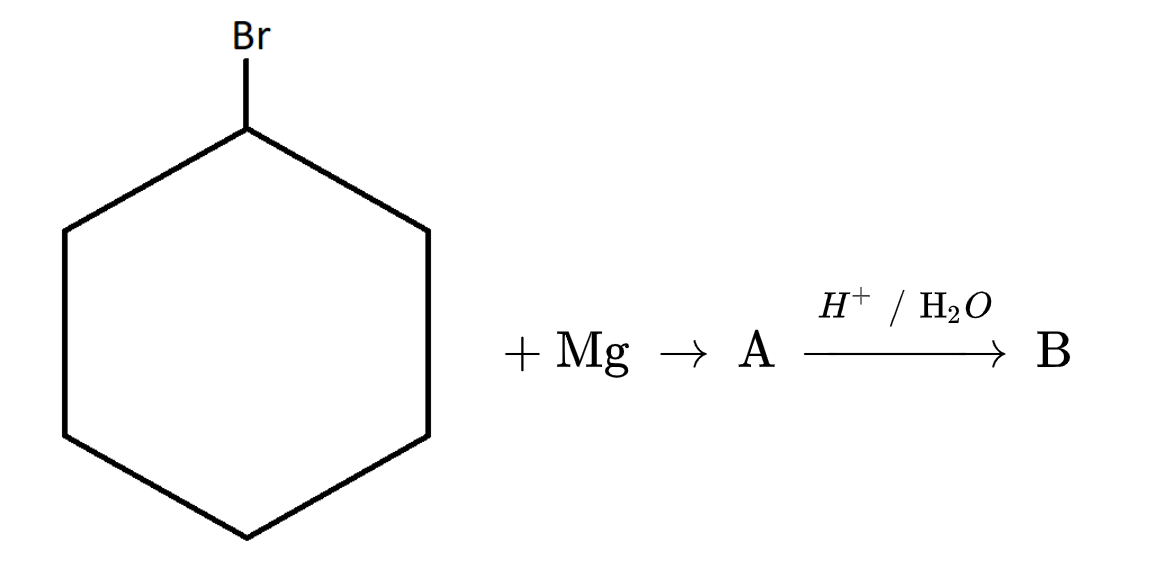
Answer
493.5k+ views
Hint: Magnesium has two valence electrons. Therefore it will combine with the bromine. Use the concept of Grignard reagent .We can use one of the properties of Grignard reagent . Recall the process of hydrolysis of Grignard reagent.
Complete answer:
The given compound is $ + {\text{ Mg - Br - OH}}$$1 - Bromo{\text{ cyclohexane}}$.
$1.$It will react with Magnesium. Since magnesium has two valence electrons. One electron it donate to bromine and second electron to cyclohexane in the following way:
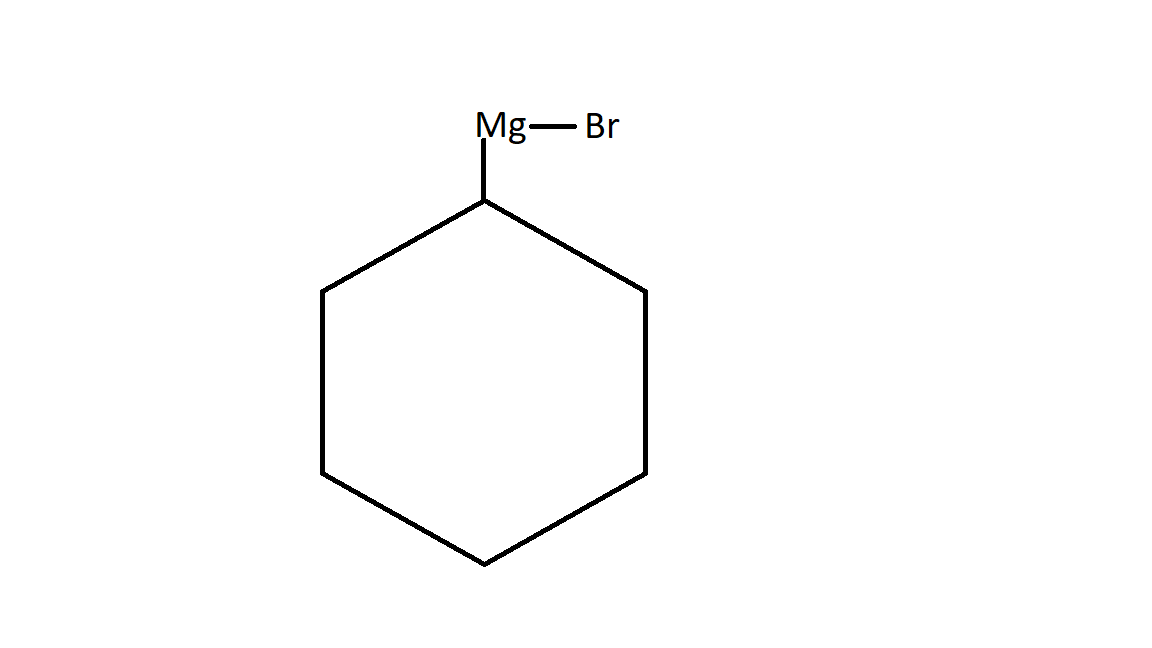
This is the product A of the given question. It is also called Grignard reagent which is represent as $R - Mg - X$.
Here R is any alkyl group. It may be cyclic or acyclic or aromatic .
Here X belongs to the halogen family. It may be chlorine , bromine or iodine. In most of the cases we will find bromine.
$2.$ Now the Grignard reagent thus formed will undergo hydrolysis with water.
${H_2}O{\text{ }}\xrightarrow{{}}{\text{ }}{{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{ + O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }$
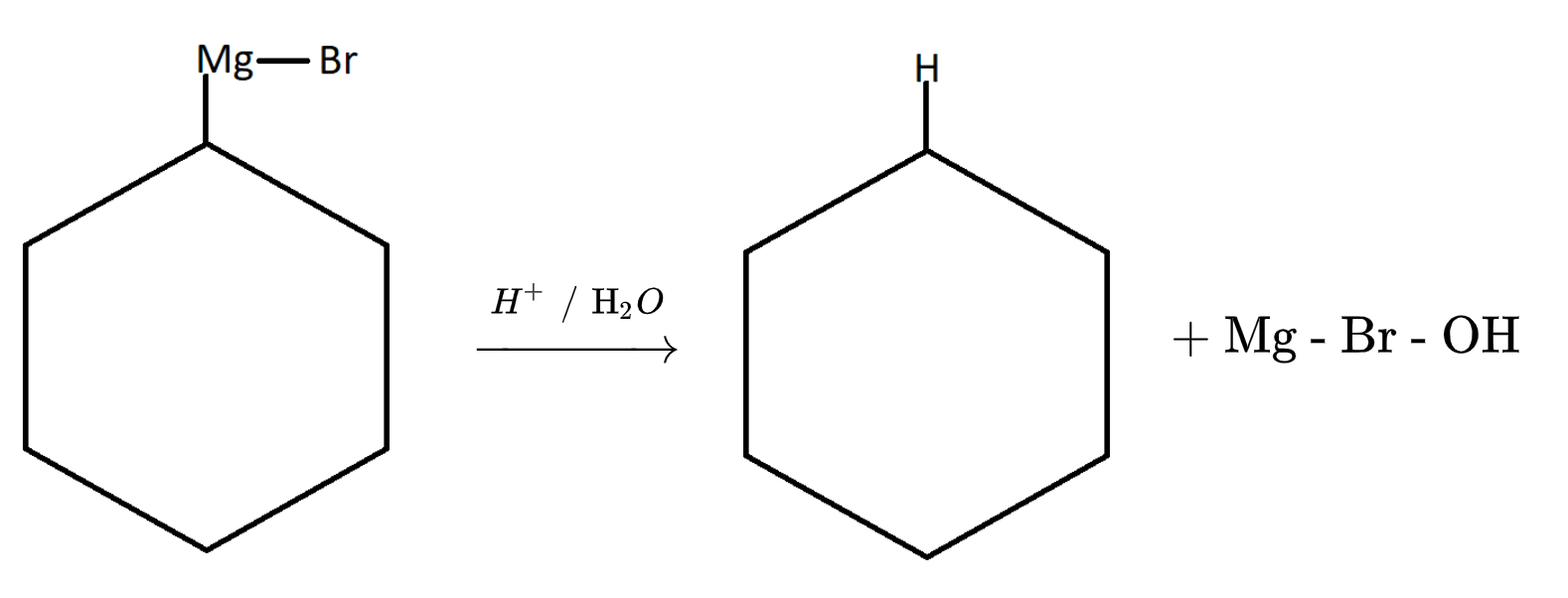
Therefore on hydrolysis of Grignard reagent we will get a pure form of alkyl group. Here it is cyclohexane.
It is also one of the properties of Grignard reagent which is shown above. Hence it is advised to use Grignard reagent in absence of water. The reason is explained in the above reactions.
Therefore the product B is:
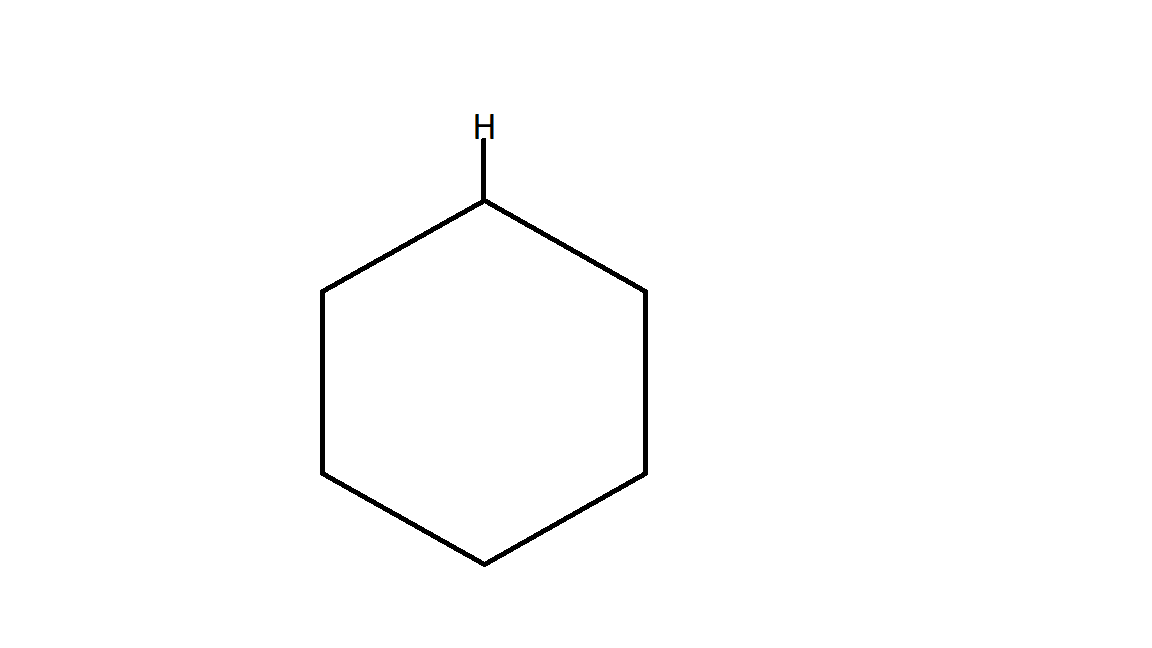 which is a cyclohexane.
which is a cyclohexane.
Additional Information:
Grignard reagent is an organometallic compound because it is made up of alkyl group and metal mainly magnesium. Reaction involving the Grignard reagent does not use water as a reagent.
Note:
Only magnesium reacts with the alkyl group to form Grignard reagent. If we use iodine or fluorine instead of chlorine or bromine the reaction can be different as abnormal behavior of fluorine. Pure forms of organic compound can be obtained using the above reactions.
Complete answer:
The given compound is $ + {\text{ Mg - Br - OH}}$$1 - Bromo{\text{ cyclohexane}}$.
$1.$It will react with Magnesium. Since magnesium has two valence electrons. One electron it donate to bromine and second electron to cyclohexane in the following way:

This is the product A of the given question. It is also called Grignard reagent which is represent as $R - Mg - X$.
Here R is any alkyl group. It may be cyclic or acyclic or aromatic .
Here X belongs to the halogen family. It may be chlorine , bromine or iodine. In most of the cases we will find bromine.
$2.$ Now the Grignard reagent thus formed will undergo hydrolysis with water.
${H_2}O{\text{ }}\xrightarrow{{}}{\text{ }}{{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{ + O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }$

Therefore on hydrolysis of Grignard reagent we will get a pure form of alkyl group. Here it is cyclohexane.
It is also one of the properties of Grignard reagent which is shown above. Hence it is advised to use Grignard reagent in absence of water. The reason is explained in the above reactions.
Therefore the product B is:

Additional Information:
Grignard reagent is an organometallic compound because it is made up of alkyl group and metal mainly magnesium. Reaction involving the Grignard reagent does not use water as a reagent.
Note:
Only magnesium reacts with the alkyl group to form Grignard reagent. If we use iodine or fluorine instead of chlorine or bromine the reaction can be different as abnormal behavior of fluorine. Pure forms of organic compound can be obtained using the above reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




