
Find the principal value of $\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( 2 \right)$.
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: We will be using the concept of inverse trigonometric functions to solve the problem. We will first write 2 as $\cos ec\theta $ then we will use the fact that $\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( \cos ecx \right)=x$ for $x\in \left[ -\dfrac{\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right]-\left\{ 0 \right\}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, we have to find the value of $\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( 2 \right)$.
Now, we will first represent 2 in terms of cosecant of an angle. So, we know that the value of $\cos ec\left(\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)$ is 2.
$2=\cos ec\left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right).........\left( 1 \right)$
We have taken $2=\cos ec\left(\dfrac{\pi }{6}\right)$ as in the view of the principal value convention x is confined to$x\in \left[ -\dfrac{\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right]-\left\{ 0 \right\}$.
Now, we know that the graph of $\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( \cos ecx \right)$ is,
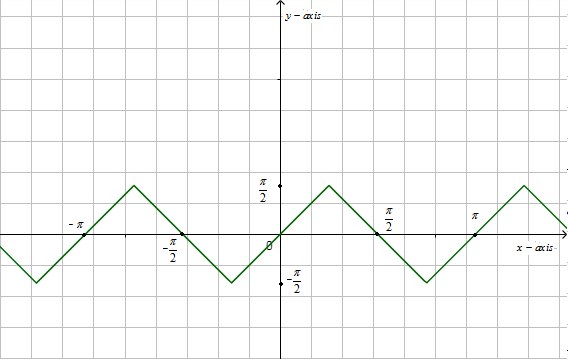
Now, we have to find the value of$\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( 2 \right)$.
We will use the equation (1) to substitute the value of 2. So, we have,
$\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( \cos ec\left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right) \right)$
Also, we know that $\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( \cos ecx \right)=x$. So, we have,
$\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( \cos ec\left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right) \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{6}$
So, the correct answer is “$\dfrac{\pi }{6}$”.
Note: To solve these type of question it is important to note that we have used a fact that $\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( \cos ecx \right)=x$ only for $x\in \left[ -\dfrac{\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right]-\left\{ 0 \right\}$. For another value of x the graph of $\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( \cos ecx \right)$ must be used to find the value.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, we have to find the value of $\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( 2 \right)$.
Now, we will first represent 2 in terms of cosecant of an angle. So, we know that the value of $\cos ec\left(\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)$ is 2.
$2=\cos ec\left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right).........\left( 1 \right)$
We have taken $2=\cos ec\left(\dfrac{\pi }{6}\right)$ as in the view of the principal value convention x is confined to$x\in \left[ -\dfrac{\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right]-\left\{ 0 \right\}$.
Now, we know that the graph of $\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( \cos ecx \right)$ is,

Now, we have to find the value of$\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( 2 \right)$.
We will use the equation (1) to substitute the value of 2. So, we have,
$\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( \cos ec\left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right) \right)$
Also, we know that $\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( \cos ecx \right)=x$. So, we have,
$\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( \cos ec\left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right) \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{6}$
So, the correct answer is “$\dfrac{\pi }{6}$”.
Note: To solve these type of question it is important to note that we have used a fact that $\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( \cos ecx \right)=x$ only for $x\in \left[ -\dfrac{\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right]-\left\{ 0 \right\}$. For another value of x the graph of $\cos e{{c}^{-1}}\left( \cos ecx \right)$ must be used to find the value.
Recently Updated Pages
Find out the centre of mass of an isosceles triangle class 12 physics CBSE

A beam of light converges at a point P Now a lens is class 12 physics CBSE

Attached ear lobe in humans is aRecessive trait bDominant class 12 biology CBSE

State four points of difference between a concave mirror class 12 physics CBSE

A monochromatic beam of light has a frequency v dfrac32pi class 12 physics CBSE

Chemical reaction of aldehydes and ketones class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




