
Find the power dissipation in resistance \[12\Omega \] in the circuit shown above figure.
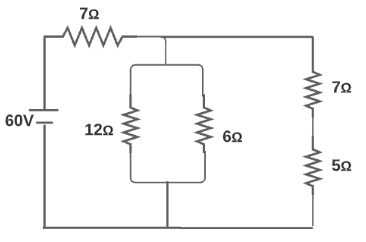
A. \[27W\]
B. \[20W\]
C. \[50W\]
D. \[100W\]

Answer
516.6k+ views
Hint: In this problem we have to find the power dissipated in resistance \[12\Omega \]. We will first find the equivalent resistance between \[CD\] as they are in series connection. We will then find the equivalent resistance between \[AB\]. We will then find the power supplied into \[12\Omega \] resistance. We will use the fact that voltage across resistance connected in parallel is the same. And voltage across resistance connected in series divides.
Complete step by step answer:
This problem is based on resistance and ohm's law. Resistance is the property of any material through which it opposes the flow of current. It is denoted by symbol $R$. Ohm's law states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across the conductor. Let as draw the given Circuit diagram with the resistance AB and CD is mentioned as follows
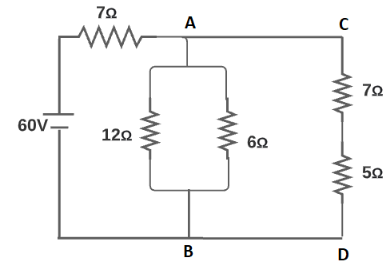
The resistance across \[CD\] are in series.
So the equivalent resistance across \[CD\] is given as \[{R_{CD}} = (7 + 5) = 35\Omega \].
Now the resistance across \[AB\] are in parallel.
Therefore equivalent resistance across \[AB\] is given by \[\dfrac{1}{{{R_{AB}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}}\]
\[\dfrac{1}{{{R_{AB}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{12}} + \dfrac{1}{6} + \dfrac{1}{{12}} = \dfrac{1}{3}\]
Hence, \[{R_{AB}} = 3\]
Given voltage in the circuit \[ = \]\[60V\]
Voltage between \[AB\] \[ = \]\[{V_{AB}} = \dfrac{3}{{3 + 7}} \times 60\] on solving we have
Hence \[{V_{AB}} = 18V\]
Hence the voltage across resistor \[12\Omega \] is \[{V_{AB}} = 18V\]
Power dissipated in \[12\Omega \] resistance is \[P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R}\]
Therefore, \[\ P = \dfrac{{{{18}^2}}}{{12}} = 27W\]
Hence, Power dissipated in \[12\Omega \] resistance is \[27W\].
Therefore, option \[A\] is correct.
Note: Resistance is the property of material, due to which it opposes the flow of current in the circuit. Equivalent resistance in series is given by \[{R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2}\]. Equivalent resistance in parallel is given by \[\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}}\]. Voltage across resistance in parallel is the same.Voltage across the resistor in series is different.
Complete step by step answer:
This problem is based on resistance and ohm's law. Resistance is the property of any material through which it opposes the flow of current. It is denoted by symbol $R$. Ohm's law states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across the conductor. Let as draw the given Circuit diagram with the resistance AB and CD is mentioned as follows

The resistance across \[CD\] are in series.
So the equivalent resistance across \[CD\] is given as \[{R_{CD}} = (7 + 5) = 35\Omega \].
Now the resistance across \[AB\] are in parallel.
Therefore equivalent resistance across \[AB\] is given by \[\dfrac{1}{{{R_{AB}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}}\]
\[\dfrac{1}{{{R_{AB}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{12}} + \dfrac{1}{6} + \dfrac{1}{{12}} = \dfrac{1}{3}\]
Hence, \[{R_{AB}} = 3\]
Given voltage in the circuit \[ = \]\[60V\]
Voltage between \[AB\] \[ = \]\[{V_{AB}} = \dfrac{3}{{3 + 7}} \times 60\] on solving we have
Hence \[{V_{AB}} = 18V\]
Hence the voltage across resistor \[12\Omega \] is \[{V_{AB}} = 18V\]
Power dissipated in \[12\Omega \] resistance is \[P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R}\]
Therefore, \[\ P = \dfrac{{{{18}^2}}}{{12}} = 27W\]
Hence, Power dissipated in \[12\Omega \] resistance is \[27W\].
Therefore, option \[A\] is correct.
Note: Resistance is the property of material, due to which it opposes the flow of current in the circuit. Equivalent resistance in series is given by \[{R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2}\]. Equivalent resistance in parallel is given by \[\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}}\]. Voltage across resistance in parallel is the same.Voltage across the resistor in series is different.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




