
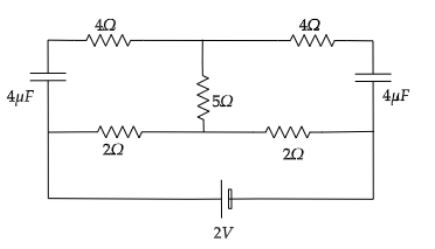
Find the power consumed in the circuit (in steady state).
A) $1.5W$
B) $2W$
C) $1W$
D) $3W$

Answer
489.6k+ views
Hint: When a capacitor connected in a circuit is in a steady state, the capacitor works as an open circuit. The power $\left( P \right)$ consumed by a load in a given circuit is equal to the ratio of square of voltage drop $\left( V \right)$ across the load and the resistance $\left( R \right)$ of the load i.e., $P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R}$.
Complete step by step answer:
There are two capacitors in the given circuit. Since the capacitors in steady state work as open circuit, no current flows through it. Let’s redraw the circuit in steady state by removing the capacitor.
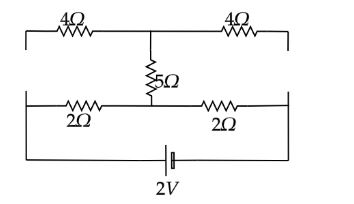
From the above figure, it is clear that there is no current flowing through the resistor of $5\Omega $. So, the final circuit consists of two $2\Omega $ resistors connected in series and the battery of $2V$.
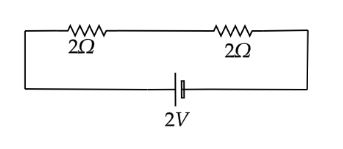
The effective resistance of the final circuit is,
$R = 2\Omega + 2\Omega $
$\Rightarrow R = 4\Omega $
The power consumed in the circuit is,
$P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R}$
Substitute the values of $V$ and $R$in the above power formula.
$P = \dfrac{{{2^2}}}{4}W$
$\therefore P = 1W$
Therefore, the power consumed in the circuit is $1W$. So, the correct option is (C).
Additional information: A capacitor is a device that is capable of storing electrical energy. It consists of two conducting surfaces separated by air or insulator. There are different forms of capacitor such as parallel plates, concentric cylinders or other forms.For any capacitor, the capacitance,
\[C = \dfrac{q}{V}\]
Where, $q$ is the amount of charge stored in the capacitor and $V$ is the voltage drop across the plates of the capacitor.
The capacitance of a spherical capacitor is,
$C = 4\pi K{\varepsilon _0}r$
Where, $K$ is the dielectric constant of a medium and for air $K = 1$. ${\varepsilon _0}$ is the permittivity of free space and $r$ is the radius of the spherical capacitor.
The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor is,
$C = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}KA}}{d}$
Where, $A$ is the surface area of each plate and $d$ is the distance between the plates.
Note: The circuit is at steady state when the voltage and the current reach their saturated values and stop changing. When a capacitor connected in a circuit is in a steady state, the capacitor has voltage across it but no current flows through it. Therefore, the capacitor behaves like an open circuit in steady state.
Complete step by step answer:
There are two capacitors in the given circuit. Since the capacitors in steady state work as open circuit, no current flows through it. Let’s redraw the circuit in steady state by removing the capacitor.

From the above figure, it is clear that there is no current flowing through the resistor of $5\Omega $. So, the final circuit consists of two $2\Omega $ resistors connected in series and the battery of $2V$.

The effective resistance of the final circuit is,
$R = 2\Omega + 2\Omega $
$\Rightarrow R = 4\Omega $
The power consumed in the circuit is,
$P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R}$
Substitute the values of $V$ and $R$in the above power formula.
$P = \dfrac{{{2^2}}}{4}W$
$\therefore P = 1W$
Therefore, the power consumed in the circuit is $1W$. So, the correct option is (C).
Additional information: A capacitor is a device that is capable of storing electrical energy. It consists of two conducting surfaces separated by air or insulator. There are different forms of capacitor such as parallel plates, concentric cylinders or other forms.For any capacitor, the capacitance,
\[C = \dfrac{q}{V}\]
Where, $q$ is the amount of charge stored in the capacitor and $V$ is the voltage drop across the plates of the capacitor.
The capacitance of a spherical capacitor is,
$C = 4\pi K{\varepsilon _0}r$
Where, $K$ is the dielectric constant of a medium and for air $K = 1$. ${\varepsilon _0}$ is the permittivity of free space and $r$ is the radius of the spherical capacitor.
The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor is,
$C = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}KA}}{d}$
Where, $A$ is the surface area of each plate and $d$ is the distance between the plates.
Note: The circuit is at steady state when the voltage and the current reach their saturated values and stop changing. When a capacitor connected in a circuit is in a steady state, the capacitor has voltage across it but no current flows through it. Therefore, the capacitor behaves like an open circuit in steady state.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




