
Find the perimeter of the square with diagonal $ 12\;cm $ ?
Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: To find the perimeter of a square, first we need the value of any one side of the square. As they have given another clue that they have given the value of the diagonal, by using this value we can find the value of the sides. And don’t forget that all sides of the square are equal.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First of all, the formula for the perimeter of the square is $ 4a $ , where $ a $ is the side of the square. To find the side of the square, let’s solve by using Pythagora's theorem. In that right angled triangle, let consider the diagonal value as the hypotenuse side and other two sides of the triangle are considered the same in case of the square. Applying Pythagoras theorem, we get,
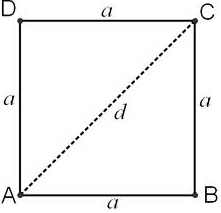
Diagonal $ {d^2} $ = $ {a^2} + {b^2} $
Here in the case of square $ a = b $ and substituting the value of $ d $ in the above equation we get,
$
12 = \sqrt {{a^2} + {a^2}} \\
\Rightarrow {12^2} = 2{a^2} \\
\Rightarrow 144 = 2{a^2} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{144}}{2} = {a^2} \\
\Rightarrow {a^2} = 72 \\
\Rightarrow a = 6\sqrt2 \;
$
The side of the square cannot be in negative value, so we take $ a = 8 $ , substituting the value of $ a $ in the perimeter of the square we get,
Perimeter of the square
$
= 4a \\
= 4\times 6\sqrt2 \\
= 24 \sqrt2\;
$
Perimeter of the square $ = 24 \sqrt2 $
This is our required solution.
So, the correct answer is “ $ 24 \sqrt2 $ cm”.
Note: Pythagoras theorem states that, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of the square of the other two sides and Pythagoras theorem only applicable to the right-angles triangle. It is one of the most important theorems, which is most frequently used in many mathematical problems.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First of all, the formula for the perimeter of the square is $ 4a $ , where $ a $ is the side of the square. To find the side of the square, let’s solve by using Pythagora's theorem. In that right angled triangle, let consider the diagonal value as the hypotenuse side and other two sides of the triangle are considered the same in case of the square. Applying Pythagoras theorem, we get,

Diagonal $ {d^2} $ = $ {a^2} + {b^2} $
Here in the case of square $ a = b $ and substituting the value of $ d $ in the above equation we get,
$
12 = \sqrt {{a^2} + {a^2}} \\
\Rightarrow {12^2} = 2{a^2} \\
\Rightarrow 144 = 2{a^2} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{144}}{2} = {a^2} \\
\Rightarrow {a^2} = 72 \\
\Rightarrow a = 6\sqrt2 \;
$
The side of the square cannot be in negative value, so we take $ a = 8 $ , substituting the value of $ a $ in the perimeter of the square we get,
Perimeter of the square
$
= 4a \\
= 4\times 6\sqrt2 \\
= 24 \sqrt2\;
$
Perimeter of the square $ = 24 \sqrt2 $
This is our required solution.
So, the correct answer is “ $ 24 \sqrt2 $ cm”.
Note: Pythagoras theorem states that, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of the square of the other two sides and Pythagoras theorem only applicable to the right-angles triangle. It is one of the most important theorems, which is most frequently used in many mathematical problems.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

The number of corners in a cube are A 4 B 6 C 8 D class 8 maths CBSE

The pH of the gastric juices released during digestion class 8 biology CBSE

What are the methods of reducing friction. Explain

Advantages and disadvantages of science





