
How would you find the perihelion distance of Mars?
Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint:The orbits of planets revolving around the sun are elliptical. When the planet is at its minimum distance from the Sun, that is called perihelion where Perry represents near in Latin and helion represents the Sun in Latin. When a planet is at its maximum distance from the Sun, that is called aphelion where apo means furthest in Latin and helion means Sun in Latin. Further, study the geometry of ellipse to find perihelion distance.
Complete step-by-step solution:
For a geometrical ellipse, Eccentricity, $e=\sqrt{\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}$
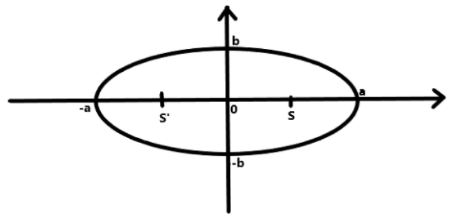
Where,
a= semi - major axis
b= semi - minor axis
For Mars, e = 0.0934
The astronomical formula for calculating Mars’ eccentricity is given as:
$e=\dfrac{\left( {{D}_{a}}-{{D}_{p}} \right)}{\left( {{D}_{a}}+{{D}_{p}} \right)}$
Where,
${{D}_{a}}=$aphelion distance between Mars and the Sun
${{D}_{p}}=$perihelion distance between Mars and the Sun
Therefore, Mars perihelion distance = 206,700,000 Km and Mars aphelion distance = 249,200,000 Km.
The greater aphelion and perihelion distances of Mars cause extreme climates on the planet.
When Mars is closest to the Sun (aphelion), it just so happens to be a southern summer which means the Southern hemisphere gets a lot warmer and vice-versa. When Mars is furthest from the Sun (perihelion), it just so happens to be a southern winter therefore it gets a lot colder.
Note:
Since Earth’s orbit is elliptical but really close to circular, the Aphelion is just 1% further than its average distance from the Sun and the perihelion is just 1% closer to its average distance from the Sun. However, mars aphelion is about 10% further than its average distance from the Sun and the perihelion is approximately 10% closer to its average distance from the Sun.
Complete step-by-step solution:
For a geometrical ellipse, Eccentricity, $e=\sqrt{\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}$

Where,
a= semi - major axis
b= semi - minor axis
For Mars, e = 0.0934
The astronomical formula for calculating Mars’ eccentricity is given as:
$e=\dfrac{\left( {{D}_{a}}-{{D}_{p}} \right)}{\left( {{D}_{a}}+{{D}_{p}} \right)}$
Where,
${{D}_{a}}=$aphelion distance between Mars and the Sun
${{D}_{p}}=$perihelion distance between Mars and the Sun
Therefore, Mars perihelion distance = 206,700,000 Km and Mars aphelion distance = 249,200,000 Km.
The greater aphelion and perihelion distances of Mars cause extreme climates on the planet.
When Mars is closest to the Sun (aphelion), it just so happens to be a southern summer which means the Southern hemisphere gets a lot warmer and vice-versa. When Mars is furthest from the Sun (perihelion), it just so happens to be a southern winter therefore it gets a lot colder.
Note:
Since Earth’s orbit is elliptical but really close to circular, the Aphelion is just 1% further than its average distance from the Sun and the perihelion is just 1% closer to its average distance from the Sun. However, mars aphelion is about 10% further than its average distance from the Sun and the perihelion is approximately 10% closer to its average distance from the Sun.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




