
Find the length of the diagonal of a square of side $12cm.$

Answer
507.9k+ views
Hint: The most important hint of this question is that the given figure is a square. If someone knows the property of a square, he can easily answer this question. Also, an important theorem called the Pythagoras theorem is used here. Try to apply it wherever it is necessary.
Formula used: $A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
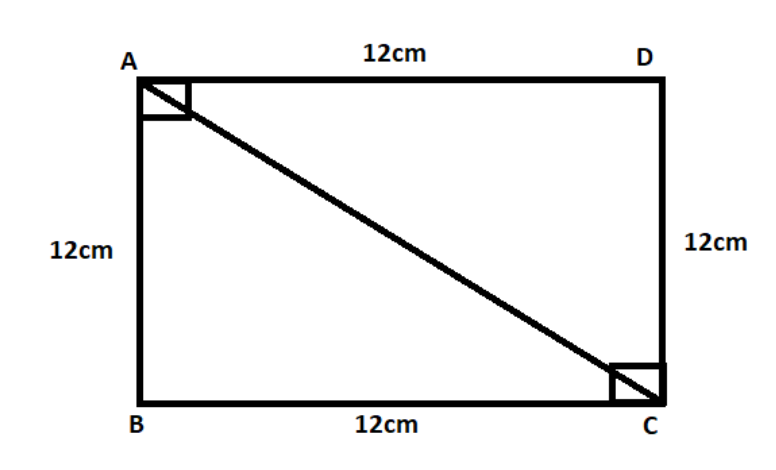
In given figure,
Let ABCD be the square and AC be the diagonal as shown.
We know that in a square all the sides are equal and the angle between adjacent sides is ${90^ \circ }$
Therefore,
$AB = BC = CD = DA = 12cm$
Also,
$\angle A = \angle B = \angle C = \angle D = {90^ \circ }$
Now,
In $\vartriangle ABC$
$AB = 12cm\,,\,BC = 12cm\,,\,\angle B = {90^ \circ }$
We know that, according to the Pythagoras theorem
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
Now,
Putting the values of AB and BC.
$A{C^2} = {\left( {12} \right)^2} + {\left( {12} \right)^2}$
We know that, ${\left( {12} \right)^2} = 144$
$A{C^2} = 144 + 144$
On adding, we get
$A{C^2} = 288$
Taking the square root both sides
$\sqrt {{{\left( {AC} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {288} $
$AC = \sqrt {144 \times 2} $
We know that, ${\left( {12} \right)^2} = 144$
$AC = \sqrt {{{\left( {12} \right)}^2} \times 2} $
We can also write,
$AC = 12\sqrt 2 cm$
Hence, the length of the diagonal is $12\sqrt 2 cm$.
Note: It is given that the figure is square. We know that all the sides of a square are equal and the angle between two adjacent sides is ${90^ \circ }$. Also, the length of both the diagonals is equal and both the diagonals intersect each other at ${90^ \circ }$ and bisect each other at the point of intersection. Pythagoras theorem is a very important theorem when we deal with right-angled triangles.
Formula used: $A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
In given figure,
Let ABCD be the square and AC be the diagonal as shown.
We know that in a square all the sides are equal and the angle between adjacent sides is ${90^ \circ }$
Therefore,
$AB = BC = CD = DA = 12cm$
Also,
$\angle A = \angle B = \angle C = \angle D = {90^ \circ }$
Now,
In $\vartriangle ABC$
$AB = 12cm\,,\,BC = 12cm\,,\,\angle B = {90^ \circ }$
We know that, according to the Pythagoras theorem
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
Now,
Putting the values of AB and BC.
$A{C^2} = {\left( {12} \right)^2} + {\left( {12} \right)^2}$
We know that, ${\left( {12} \right)^2} = 144$
$A{C^2} = 144 + 144$
On adding, we get
$A{C^2} = 288$
Taking the square root both sides
$\sqrt {{{\left( {AC} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {288} $
$AC = \sqrt {144 \times 2} $
We know that, ${\left( {12} \right)^2} = 144$
$AC = \sqrt {{{\left( {12} \right)}^2} \times 2} $
We can also write,
$AC = 12\sqrt 2 cm$
Hence, the length of the diagonal is $12\sqrt 2 cm$.
Note: It is given that the figure is square. We know that all the sides of a square are equal and the angle between two adjacent sides is ${90^ \circ }$. Also, the length of both the diagonals is equal and both the diagonals intersect each other at ${90^ \circ }$ and bisect each other at the point of intersection. Pythagoras theorem is a very important theorem when we deal with right-angled triangles.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

The number of corners in a cube are A 4 B 6 C 8 D class 8 maths CBSE

Advantages and disadvantages of science

The pH of the gastric juices released during digestion class 8 biology CBSE

What are the methods of reducing friction. Explain





