
Find the interval in which the smallest positive of the equation $\tan x-x=0$ lies
(a) $\left( 0,\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$
(b) $\left( \dfrac{\pi }{2},\pi \right)$
(c) $\left( \pi ,\dfrac{3\pi }{2} \right)$
(d) $\left( \dfrac{3\pi }{2},2\pi \right)$
Answer
610.8k+ views
Hint: Roots of any equation $f\left( x \right)=g\left( x \right)$ or $f\left( x \right)-g\left( x \right)=0$ can be calculated by drawing the curves of both $f\left( x \right)$ and $g\left( x \right)$ and get the intersection points which will be the roots of equations. Verify that $y=x$ will touch $\tan x$ or not. Tangent equation for any curve $f\left( x \right)$ at $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is given as
$y-{{y}_{1}}={{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)}}\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$
Complete step-by-step solution -
As, we know the solution or roots of any equation $f\left( x \right)=g\left( x \right)$ or $f\left( x \right)-g\left( x \right)=0$will be given by drawing the graphs of $f\left( x \right)$ and $g\left( x \right)$ and the value of $x$ at which $f\left( x \right)$ will be equal to $g\left( x \right)$ will be a solution of the given equation i.e. the intersection points of $f\left( x \right)$ and $g\left( x \right)$ will give the roots of the equation $f\left( x \right)=g\left( x \right)$
Now, coming to the question as we need to determine the smallest positive root of the equation $\tan x - x=0$ or . So, let us draw the graph of $y=\tan x$ and $y=x$ and get the intersection points, which will determine the roots of the equation $\tan x=x$ and hence, we can get the least positive value of $x,$ which satisfy the equation $\tan x=x$
As we know curve $y=x$ can be given as
And curve $y=\tan x$ can be given as
As we know, we have to calculate the range of the first positive root of the equation $\tan x=x$ .So, Let us draw curves of $y=\tan x$ and $y=x$ in the same coordinate plane. So, we get
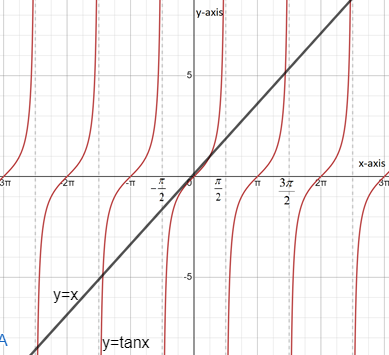
Now, let us calculate the equation of tangent for curve $y=\tan x$ at (0,0)
As we know equation of a tangent for any curve $f\left( x \right)$ at $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is given as
$y-{{y}_{1}}={{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)}}\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)..........\left( i \right)$
So $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is given as (0,0). Let us calculate value of $\dfrac{dy}{dx}$ by following way:
We have
$y=\tan x$
Differentiating the equation w.r.t. $x$ we get
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \tan x \right)$
We know $\dfrac{d}{d\theta }={{\sec }^{2}}\theta $
Hence, we get $\dfrac{dy}{dx}={{\sec }^{2}}x$
So, we get
${{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{\left( 0,0 \right)}}={{\sec }^{2}}0={{1}^{2}}=1$
Hence, slope of the tangent i.e. ${{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{\left( 0,0 \right)}}=1$ . Hence equation of tangent to the curve $y=\tan x$ at (0,0) is given as
$\begin{align}
& y-0=1\left( x-0 \right) \\
& y=x.......\left( ii \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we get that $y=x$ is acting as a tangent to the curve $y=\tan x$ at (0,0). It means curve $y=\tan x$ will not meet the curve \[y=\tan x\] between $-\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ at anywhere else other (0, 0).
So, we can easily observe that $y=x$ will intersect $y=\tan x$ between $x=\pi $ to $x=\dfrac{3\pi }{2}$ , as value of $y=\tan x$ will be negative from $x=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ to $x=\pi $ .So, the exact interval for the first positive root of the equation $\tan x=x$ will be given as $\left( \pi ,\dfrac{3\pi }{2} \right)$
So, option(c) is the correct answer.
Note: $x=0$ is not a positive root of the equation $\tan x=x$ as 0 is not considered as a positive number, it comes under non-negative integers. So, don’t confuse with this point in the solution. One may go wrong if/she does not check for the tangent equation of $y=\tan x$ at (0,0), one may answer the questions as $\left( 0,\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$ if he/she intersect the equation $y=x$ and $y=\tan x$ in between 0 to $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ , which is wrong as $y=x$ is acting as a tangent for $y=\tan x$ at (0,0). So, be careful with this part of the solution.
$y-{{y}_{1}}={{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)}}\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$
Complete step-by-step solution -
As, we know the solution or roots of any equation $f\left( x \right)=g\left( x \right)$ or $f\left( x \right)-g\left( x \right)=0$will be given by drawing the graphs of $f\left( x \right)$ and $g\left( x \right)$ and the value of $x$ at which $f\left( x \right)$ will be equal to $g\left( x \right)$ will be a solution of the given equation i.e. the intersection points of $f\left( x \right)$ and $g\left( x \right)$ will give the roots of the equation $f\left( x \right)=g\left( x \right)$
Now, coming to the question as we need to determine the smallest positive root of the equation $\tan x - x=0$ or . So, let us draw the graph of $y=\tan x$ and $y=x$ and get the intersection points, which will determine the roots of the equation $\tan x=x$ and hence, we can get the least positive value of $x,$ which satisfy the equation $\tan x=x$
As we know curve $y=x$ can be given as

And curve $y=\tan x$ can be given as

As we know, we have to calculate the range of the first positive root of the equation $\tan x=x$ .So, Let us draw curves of $y=\tan x$ and $y=x$ in the same coordinate plane. So, we get

Now, let us calculate the equation of tangent for curve $y=\tan x$ at (0,0)
As we know equation of a tangent for any curve $f\left( x \right)$ at $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is given as
$y-{{y}_{1}}={{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)}}\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)..........\left( i \right)$
So $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is given as (0,0). Let us calculate value of $\dfrac{dy}{dx}$ by following way:
We have
$y=\tan x$
Differentiating the equation w.r.t. $x$ we get
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \tan x \right)$
We know $\dfrac{d}{d\theta }={{\sec }^{2}}\theta $
Hence, we get $\dfrac{dy}{dx}={{\sec }^{2}}x$
So, we get
${{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{\left( 0,0 \right)}}={{\sec }^{2}}0={{1}^{2}}=1$
Hence, slope of the tangent i.e. ${{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{\left( 0,0 \right)}}=1$ . Hence equation of tangent to the curve $y=\tan x$ at (0,0) is given as
$\begin{align}
& y-0=1\left( x-0 \right) \\
& y=x.......\left( ii \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we get that $y=x$ is acting as a tangent to the curve $y=\tan x$ at (0,0). It means curve $y=\tan x$ will not meet the curve \[y=\tan x\] between $-\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ at anywhere else other (0, 0).
So, we can easily observe that $y=x$ will intersect $y=\tan x$ between $x=\pi $ to $x=\dfrac{3\pi }{2}$ , as value of $y=\tan x$ will be negative from $x=\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ to $x=\pi $ .So, the exact interval for the first positive root of the equation $\tan x=x$ will be given as $\left( \pi ,\dfrac{3\pi }{2} \right)$
So, option(c) is the correct answer.
Note: $x=0$ is not a positive root of the equation $\tan x=x$ as 0 is not considered as a positive number, it comes under non-negative integers. So, don’t confuse with this point in the solution. One may go wrong if/she does not check for the tangent equation of $y=\tan x$ at (0,0), one may answer the questions as $\left( 0,\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$ if he/she intersect the equation $y=x$ and $y=\tan x$ in between 0 to $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ , which is wrong as $y=x$ is acting as a tangent for $y=\tan x$ at (0,0). So, be careful with this part of the solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




