
Find the hydrolysis product when a phosphodiester bond of nucleotide breaks.
(A) $3 - {\text{OH}} - {\text{deoxyribose}} - 5 - {\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$
(B) $5 - {\text{OH}} - {\text{deoxyribose}} - 3 - {\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$
(C) $2 - {\text{OH}} - {\text{deoxyribose}} - 2 - {\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$
(D) $4 - {\text{OH}} - {\text{deoxyribose}} - 2 - {\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: In nucleotides, the nitrogenous base and the five carbon sugars are linked through a glycosidic bond and are collectively known as a nucleoside. The phosphate group is linked to the nucleoside through a phosphodiester bond. The hydrolysis of phosphodiester bond means adding water molecules through the phosphodiester bond.
Complete Step by step answer: We know that a nucleotide is made of three subunits: a five-carbon sugar, a nitrogenous base and one phosphate group.
The nitrogenous base is linked to the five-carbon sugar through glycosidic bond. The nitrogenous base and the five carbon sugar is collectively known as a nucleoside. The phosphate group is linked to the nucleoside through a phosphodiester bond. The phosphate group is linked to the nucleoside at $5' - {\text{OH}}$ end. Thus, the phosphodiester bond is a strong covalent bond between a phosphate group and two other molecules.
In nucleotides, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the third $\left( {\text{3}} \right)$ carbon atom of one sugar molecule and the fifth $\left( {\text{5}} \right)$ carbon atom of another sugar molecule.
The hydrolysis of phosphodiester bond is as follows:
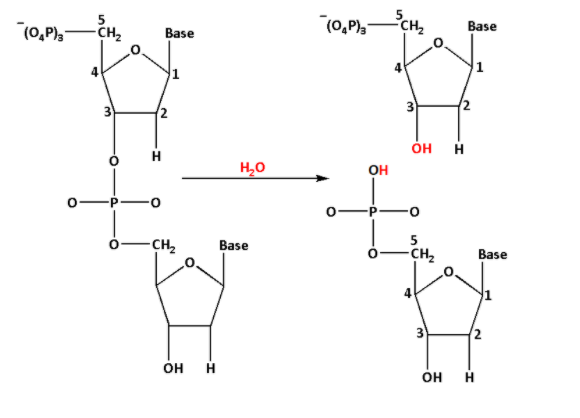
From the reaction, we can see that the hydroxyl $\left( { - {\text{OH}}} \right)$ group is at the third carbon $\left( {\text{3}} \right)$ and the phosphate group is at the fifth carbon of the deoxyribose sugar.
Thus, when the phosphodiester bond is hydrolysed, the phosphodiester bond breaks and forms $3 - {\text{OH}} - {\text{deoxyribose}} - 5 - {\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$.
Thus, the correct option is (A) $3 - {\text{OH}} - {\text{deoxyribose}} - 5 - {\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$.
Note: The basic building blocks of nucleic acids are known as nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of nucleosides and phosphate. Nucleotides play an important role in the metabolism. The hydrolysis of phosphodiester bonds is catalysed by the enzyme phosphodiesterases.
Complete Step by step answer: We know that a nucleotide is made of three subunits: a five-carbon sugar, a nitrogenous base and one phosphate group.
The nitrogenous base is linked to the five-carbon sugar through glycosidic bond. The nitrogenous base and the five carbon sugar is collectively known as a nucleoside. The phosphate group is linked to the nucleoside through a phosphodiester bond. The phosphate group is linked to the nucleoside at $5' - {\text{OH}}$ end. Thus, the phosphodiester bond is a strong covalent bond between a phosphate group and two other molecules.
In nucleotides, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the third $\left( {\text{3}} \right)$ carbon atom of one sugar molecule and the fifth $\left( {\text{5}} \right)$ carbon atom of another sugar molecule.
The hydrolysis of phosphodiester bond is as follows:

From the reaction, we can see that the hydroxyl $\left( { - {\text{OH}}} \right)$ group is at the third carbon $\left( {\text{3}} \right)$ and the phosphate group is at the fifth carbon of the deoxyribose sugar.
Thus, when the phosphodiester bond is hydrolysed, the phosphodiester bond breaks and forms $3 - {\text{OH}} - {\text{deoxyribose}} - 5 - {\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$.
Thus, the correct option is (A) $3 - {\text{OH}} - {\text{deoxyribose}} - 5 - {\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$.
Note: The basic building blocks of nucleic acids are known as nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of nucleosides and phosphate. Nucleotides play an important role in the metabolism. The hydrolysis of phosphodiester bonds is catalysed by the enzyme phosphodiesterases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




