
Find the equivalent capacitance between A and B.
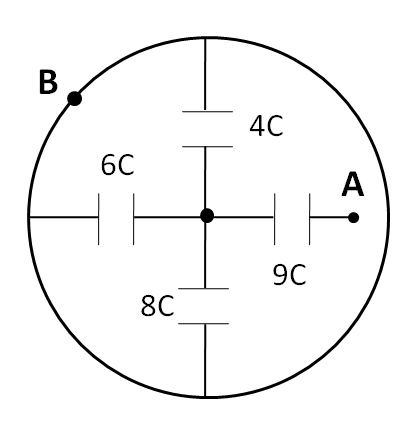
(A) $ 6C $
(B) $ 7C $
(C) $ C $
(D) $ 5C $

Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint
To solve this question, we have to classify each capacitor according to its potential difference. Then, we need to redesign the given circuit using this classification.
Complete step by step answer
Let us label the centre point as O.
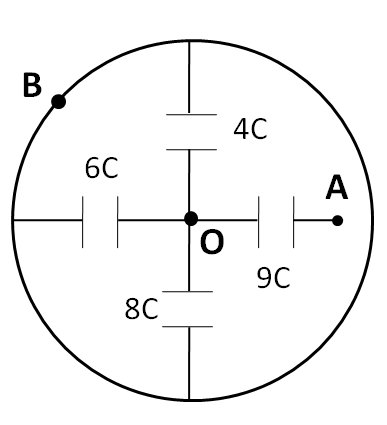
We know that a conducting wire has no drop. So, we label the potentials across the capacitors as
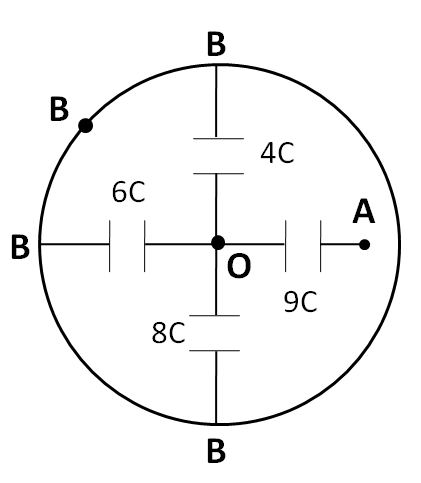
Now, we classify each capacitor according to the potential difference across it. The classification is shown in the table below.
As can be seen from the above table, potential differences across the capacitances $ 4C $ , $ 6C $ , and $ 8C $ are the same, that is, VOB. So, these three capacitances are in parallel combination with each other. Hence, we redraw the given circuit as
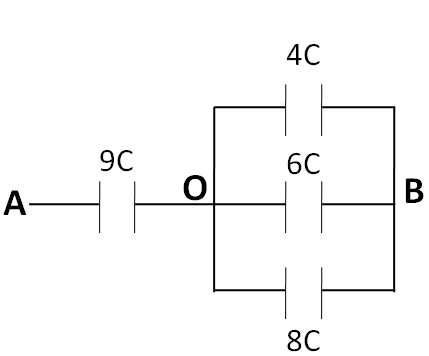
As the capacitances $ 4C $ , $ 6C $ , and $ 8C $ are in parallel combination, so the equivalent capacitance of these can be written as
$ \Rightarrow {C_p} = 4C + 6C + 9C $
$ \Rightarrow {C_p} = 18C $
So, the above circuit reduces to
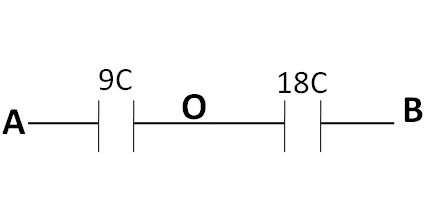
Since the capacitances $ 4C $ and $ 4C $ are in series, so finally, the equivalent capacitance between the points A and B is given by
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{C_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{9C}} + \dfrac{1}{{18C}} $
Taking the LCM
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{C_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{{2 + 1}}{{18C}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{C_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{6C}} $
Finally, taking the reciprocal, we get
$ \Rightarrow {C_{eq}} = 6C $
So the equivalent capacitance between A and B is $ 6C $
Hence, the correct answer is option A, $ 6C $ .
Note
While redesigning the original circuit using the voltage division method, do not make mistakes. Always set the capacitors having the end points connected to the same points parallel to each other first. Then, set other combinations in series keeping a check that the other combination should have a potential point common with the given combination.
To solve this question, we have to classify each capacitor according to its potential difference. Then, we need to redesign the given circuit using this classification.
Complete step by step answer
Let us label the centre point as O.

We know that a conducting wire has no drop. So, we label the potentials across the capacitors as

Now, we classify each capacitor according to the potential difference across it. The classification is shown in the table below.
| Capacitance | Potential Difference |
| $ 4C $ | VOB |
| $ 6C $ | VOB |
| $ 8C $ | VOB |
| $ 9C $ | VOB |
As can be seen from the above table, potential differences across the capacitances $ 4C $ , $ 6C $ , and $ 8C $ are the same, that is, VOB. So, these three capacitances are in parallel combination with each other. Hence, we redraw the given circuit as

As the capacitances $ 4C $ , $ 6C $ , and $ 8C $ are in parallel combination, so the equivalent capacitance of these can be written as
$ \Rightarrow {C_p} = 4C + 6C + 9C $
$ \Rightarrow {C_p} = 18C $
So, the above circuit reduces to

Since the capacitances $ 4C $ and $ 4C $ are in series, so finally, the equivalent capacitance between the points A and B is given by
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{C_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{9C}} + \dfrac{1}{{18C}} $
Taking the LCM
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{C_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{{2 + 1}}{{18C}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{C_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{6C}} $
Finally, taking the reciprocal, we get
$ \Rightarrow {C_{eq}} = 6C $
So the equivalent capacitance between A and B is $ 6C $
Hence, the correct answer is option A, $ 6C $ .
Note
While redesigning the original circuit using the voltage division method, do not make mistakes. Always set the capacitors having the end points connected to the same points parallel to each other first. Then, set other combinations in series keeping a check that the other combination should have a potential point common with the given combination.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




