
Find the effective resistance of the circuit given:
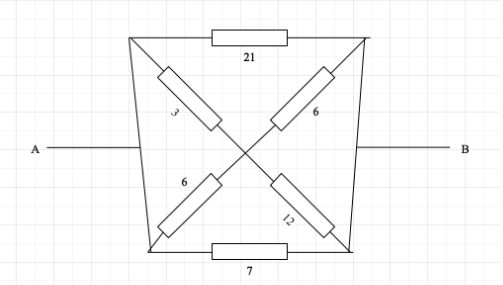

Answer
596.4k+ views
Hint: Find the points which are at equal potentials. Simply the circuit by drawing another circuit having the same resistances. Find the parallel and series connections, and calculate the equivalent resistance step by step.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The original circuit diagram is:
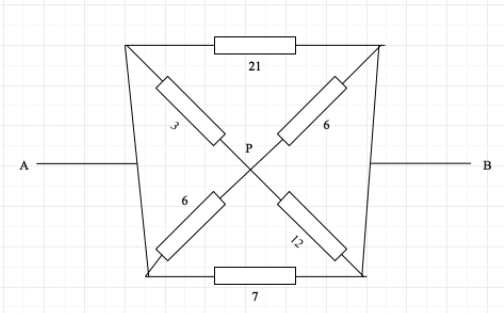
We can consider 3Ω and 6Ω resistances in parallel and connected between A and P.
We can consider 6Ω and 12Ω resistances in parallel and connected between P and B.
Hence, we can modify the circuit diagram in this way,
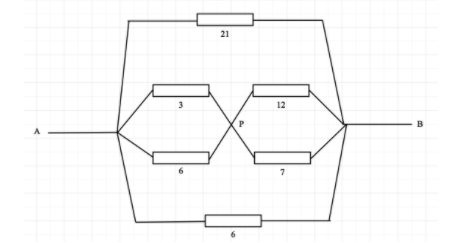
So, the equivalent resistance of 3Ω and 6Ω is given by,
$\dfrac{3\times 6}{3+6}=\dfrac{18}{9}=2$
The equivalent resistance of 6Ω and 12Ω is given by,
$\dfrac{6\times 12}{6+12}=\dfrac{72}{18}=4$
These two resistances are connected in series.
The new circuit diagram is as follows:
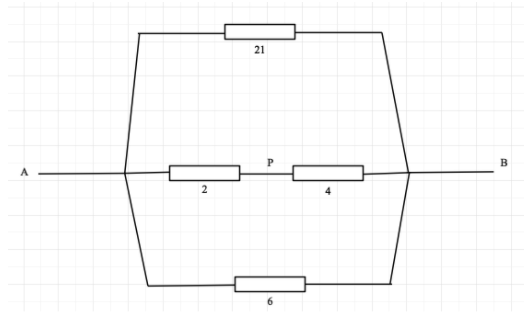
Now the 2Ω and 4Ω resistances are in series.
Hence, the equivalent resistance of the middle branch is 6Ω
Now, 6Ω, 6Ω, and 21Ω resistances are in parallel connection.
Hence, the equivalent resistance can be given by,
$\dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{3}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{1}{6}+\dfrac{1}{6}+\dfrac{1}{21}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{21}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{7+1}{21}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{8}{21}$
$\Rightarrow R=\dfrac{21}{8}$
We are using the parallel connection formula in this case.
So, the equivalent resistance between points A and B are,
$\dfrac{21}{8}$
Note:The trick to solving this kind of question is to find the points with equal potential. For example, in this question, the point P will have the same potential. Redrawing the circuit into a conventional format is crucial as well. When two or more resistances are connected to the same two potentials, the resistances will be in parallel.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The original circuit diagram is:

We can consider 3Ω and 6Ω resistances in parallel and connected between A and P.
We can consider 6Ω and 12Ω resistances in parallel and connected between P and B.
Hence, we can modify the circuit diagram in this way,

So, the equivalent resistance of 3Ω and 6Ω is given by,
$\dfrac{3\times 6}{3+6}=\dfrac{18}{9}=2$
The equivalent resistance of 6Ω and 12Ω is given by,
$\dfrac{6\times 12}{6+12}=\dfrac{72}{18}=4$
These two resistances are connected in series.
The new circuit diagram is as follows:

Now the 2Ω and 4Ω resistances are in series.
Hence, the equivalent resistance of the middle branch is 6Ω
Now, 6Ω, 6Ω, and 21Ω resistances are in parallel connection.
Hence, the equivalent resistance can be given by,
$\dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{3}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{1}{6}+\dfrac{1}{6}+\dfrac{1}{21}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{21}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{7+1}{21}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{8}{21}$
$\Rightarrow R=\dfrac{21}{8}$
We are using the parallel connection formula in this case.
So, the equivalent resistance between points A and B are,
$\dfrac{21}{8}$
Note:The trick to solving this kind of question is to find the points with equal potential. For example, in this question, the point P will have the same potential. Redrawing the circuit into a conventional format is crucial as well. When two or more resistances are connected to the same two potentials, the resistances will be in parallel.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




