
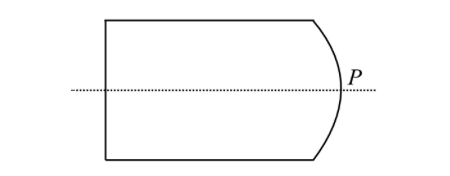
Find the distance of the object placed in the slab of refractive index $\mu $ from point $P$ of the curved surface with radius $R$ so that the image is formed at infinity.
A) $\dfrac{{(\mu - 1)R}}{\mu }$
B) $\dfrac{{\mu R}}{{(\mu - 1)}}$
C) $\dfrac{R}{{\mu - 1}}$
D) $\dfrac{{(\mu - 1)R}}{{2\mu }}$

Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint:In this question, use the concept of the refraction of the light due to the special surface of the object which depends on the refractive index of the material of the object and the medium. In this question, first discuss how the refraction phenomenon is happening in the medium. Then write down the formula of refraction in spherical surfaces and discuss various terms of the formula. Finally solve this by applying this formula.
Complete step by step solution:
As we know that when the light changes its direction while travelling from a medium to another medium this is called refraction. The main cause of refraction of light is the change in refractive index of medium.
As we know the formula of the refraction in spherical surfaces is,
$\dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2} - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Where, $v$ is the distance of the image from the spherical surface and it is negative by sign convention, $u$ is the distance of the object from the spherical surface ${\mu _1}$ is the refractive index of a medium from which rays are incident, and ${\mu _2}$ is the refractive index of another medium.
Here it is said that the image formation will be at infinity so $v = \infty $, also ${\mu _1} = 1$ and ${\mu _1} = \mu $
Now we substitute the values in the above equation as,
$\dfrac{1}{\infty } - \dfrac{\mu }{u} = \dfrac{{\mu - 1}}{R}$
$ \Rightarrow 0 - \dfrac{\mu }{u} = \dfrac{{\mu - 1}}{R}$
On simplification we get,
$\Rightarrow u = - \dfrac{{\mu R}}{{\mu - 1}}$
Here the negative sign has come out due to sign convention.
So, the distance of the object placed in the slab will be $\dfrac{{\mu R}}{{\mu - 1}}$.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: While solving this problem we have to be very much aware about the sign convention of the terms in the formula. The refractive index of a medium is understood by the speed of the light in the first medium through which the light is travelling to the speed of the light in the second medium where the light gets refracted. The refractive index of the air is $1$.
Complete step by step solution:
As we know that when the light changes its direction while travelling from a medium to another medium this is called refraction. The main cause of refraction of light is the change in refractive index of medium.
As we know the formula of the refraction in spherical surfaces is,
$\dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{v} - \dfrac{{{\mu _1}}}{u} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2} - {\mu _1}}}{R}$
Where, $v$ is the distance of the image from the spherical surface and it is negative by sign convention, $u$ is the distance of the object from the spherical surface ${\mu _1}$ is the refractive index of a medium from which rays are incident, and ${\mu _2}$ is the refractive index of another medium.
Here it is said that the image formation will be at infinity so $v = \infty $, also ${\mu _1} = 1$ and ${\mu _1} = \mu $
Now we substitute the values in the above equation as,
$\dfrac{1}{\infty } - \dfrac{\mu }{u} = \dfrac{{\mu - 1}}{R}$
$ \Rightarrow 0 - \dfrac{\mu }{u} = \dfrac{{\mu - 1}}{R}$
On simplification we get,
$\Rightarrow u = - \dfrac{{\mu R}}{{\mu - 1}}$
Here the negative sign has come out due to sign convention.
So, the distance of the object placed in the slab will be $\dfrac{{\mu R}}{{\mu - 1}}$.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: While solving this problem we have to be very much aware about the sign convention of the terms in the formula. The refractive index of a medium is understood by the speed of the light in the first medium through which the light is travelling to the speed of the light in the second medium where the light gets refracted. The refractive index of the air is $1$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




