
Find the distance and first, second, third, fourth nearest neighbour in B.C.C lattice.
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: For solving this question first we need to understand the basics of BCC lattice. A unit cell is the smallest array of atoms present in a crystal. The third most common arrangement of metals is known as the body-centered cubic or BCC unit cell. In a BCC unit cell, there are atoms present at every eight corners of a cube plus and one more atom present at the center of the cube.
Complete step by step answer:
In the body-centered cubic arrangement model, we have an atom at the center, and there are eight more atoms situated at the cube's eight corners. These are the most proximal neighbors for the particle at the center. So, there are in total eight atoms. The distance between the atoms is equal to the
2 (diagonal of a cube) = \[2\sqrt {3a} \]
Where 'a' is the size of a cube in the lattice
In case if we revolve the cubes around, then we can see six cubes, one at each face of the cube. At the center of the cube, we can see an adjacent cube to our cube, nearest to the next level. Here, the distance 'a' = size of the cube in the lattice.
Now, let's consider that we are sitting in the center of a cell. So, our first, second, third and fourth neighbors will be the following:
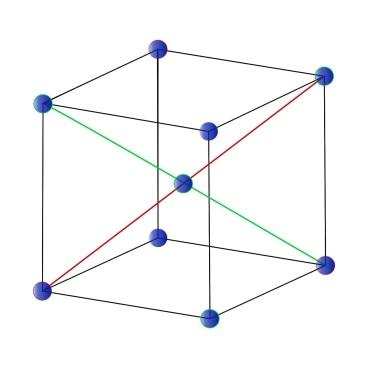
Your first neighbors are present at the corners of the same section.
Second, neighbors are at the centers of the most proximate adjacent cells.
Third, the neighbor is the center of the next adjoining cell shared by two corners of your section.
Fourth, neighbors are the far corners of the most approaching adjacent cells.
Note:
We must know that in BCC lattice, the packing efficiency is 68%. The packing efficiency of ccp and hcp is the highest i.e., equal to 74%.and also the face-centered cubic (fcc) has 12 coordinates and is composed of 4 atoms per unit cell. The body-centered cubic (bcc) has an 8-coordinate number and contains two atoms per cell unit. The simple cubic has a 6-coordinate number and contains 1 atom per cell unit.
Complete step by step answer:
In the body-centered cubic arrangement model, we have an atom at the center, and there are eight more atoms situated at the cube's eight corners. These are the most proximal neighbors for the particle at the center. So, there are in total eight atoms. The distance between the atoms is equal to the
2 (diagonal of a cube) = \[2\sqrt {3a} \]
Where 'a' is the size of a cube in the lattice
In case if we revolve the cubes around, then we can see six cubes, one at each face of the cube. At the center of the cube, we can see an adjacent cube to our cube, nearest to the next level. Here, the distance 'a' = size of the cube in the lattice.
Now, let's consider that we are sitting in the center of a cell. So, our first, second, third and fourth neighbors will be the following:

Your first neighbors are present at the corners of the same section.
Second, neighbors are at the centers of the most proximate adjacent cells.
Third, the neighbor is the center of the next adjoining cell shared by two corners of your section.
Fourth, neighbors are the far corners of the most approaching adjacent cells.
Note:
We must know that in BCC lattice, the packing efficiency is 68%. The packing efficiency of ccp and hcp is the highest i.e., equal to 74%.and also the face-centered cubic (fcc) has 12 coordinates and is composed of 4 atoms per unit cell. The body-centered cubic (bcc) has an 8-coordinate number and contains two atoms per cell unit. The simple cubic has a 6-coordinate number and contains 1 atom per cell unit.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




