
Find the current through the $ 6\Omega $ and $ 4\Omega $ resistances.
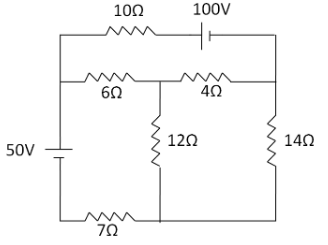

Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, consider the three meshes given in the circuit and find the currents in each mesh. Then, using the values of mesh currents, find the values of current through the resistances.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us consider the current in the three meshes as $ {I_1} $ , $ {I_2} $ and $ {I_3} $ respectively, as in the given diagram.
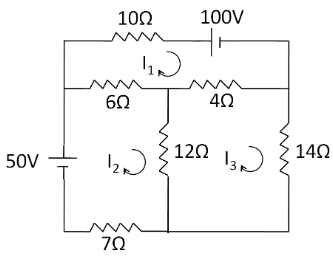
Applying KVL in the mesh containing $ {I_1} $ current, we have
$ 10{I_1} + 100 + 4({I_1} - {I_3}) + 6({I_1} - {I_2}) = 0 $
$ 20{I_1} + 100 - 4{I_3} - 6{I_2} = 0 $
On rearranging, we get
$ - 20{I_1} + 6{I_2} + 4{I_3} = 100 $
Dividing both sides by $ 2 $
$ - 10{I_1} + 3{I_2} + 2{I_3} = 50 $ …………….(1)
Now, applying KVL in the mesh containing $ {I_2} $
$ 6({I_2} - {I_1}) + 12({I_2} - {I_3}) + 7{I_2} - 50 = 0 $
$ - 6{I_1} + 25{I_2} - 12{I_3} = 50 $…………….(2)
Finally, applying KVL in the mesh containing $ {I_3} $
$ 4({I_3} - {I_1}) + 14{I_3} + 12({I_3} - {I_2}) = 0 $
$ - 4{I_1} - 12{I_2} + 30{I_3} = 0 $
Dividing both sides by $ - 2 $
$ 2{I_1} + 6{I_2} - 15{I_3} = 0 $ …………….(3)
Subtracting (1) from (2), we have
$ - 6{I_1} + 25{I_2} - 12{I_3} - ( - 10{I_1} + 3{I_2} + 2{I_3}) = 50 - 50 $
$ 4{I_1} + 22{I_2} - 14{I_3} = 0 $
Dividing both sides by $ 2 $
$ 2{I_1} + 11{I_2} - 7{I_3} = 0 $ …………….(4)
Applying cross-multiplication method in (3) and (4), we have
$ \dfrac{{{I_1}}}{{123}} = \dfrac{{{I_2}}}{{ - 16}} = \dfrac{{{I_3}}}{{10}} = \lambda $ , where $ \lambda $ is some real number
$ \therefore {I_1} = 123\lambda ,{\text{ }}{I_2} = - 16\lambda ,{\text{ }}{I_3} = 10\lambda $...............(5)
Substituting these in (1), we get
$ - 10(123\lambda ) + 3( - 16\lambda ) + 2(10\lambda ) = 50 $
$ - 1258\lambda = 50 $
So, we get
$ \lambda = - \dfrac{{50}}{{1258}} $
Putting this in (5)
$ {I_1} = - \dfrac{{6150}}{{1258}} = - 4.89A $ , $ {I_2} = \dfrac{{800}}{{1258}} = 0.64A $ , and $ {I_3} = - \dfrac{{500}}{{1258}} = - 0.39A $
Now, current through the $ 6\,\Omega $ resistance
$ {I_{6\Omega }} = {I_2} - {I_1} $
Putting the values, we get
$ {I_{6\Omega }} = 0.64 - ( - 4.89) $
$ {I_{6\Omega }} = 5.53A $
Also, the current through the $ 4\Omega $ resistance
$ {I_{4\Omega }} = {I_3} - {I_1} $
Putting the values
$ {I_{4\Omega }} = - 0.39 - ( - 4.89) $
$ {I_{4\Omega }} = 4.5A $
Hence $ {I_{6\Omega }} = 5.53A $ and $ {I_{4\Omega }} = 4.5A $ .
Note:
While using KVL, first select a sign convention and then proceed. Do not get confused due to the sign convention. The choice of sign convention doesn’t change the final answer. We can use any one of the two sign conventions for the resistances and the batteries.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us consider the current in the three meshes as $ {I_1} $ , $ {I_2} $ and $ {I_3} $ respectively, as in the given diagram.

Applying KVL in the mesh containing $ {I_1} $ current, we have
$ 10{I_1} + 100 + 4({I_1} - {I_3}) + 6({I_1} - {I_2}) = 0 $
$ 20{I_1} + 100 - 4{I_3} - 6{I_2} = 0 $
On rearranging, we get
$ - 20{I_1} + 6{I_2} + 4{I_3} = 100 $
Dividing both sides by $ 2 $
$ - 10{I_1} + 3{I_2} + 2{I_3} = 50 $ …………….(1)
Now, applying KVL in the mesh containing $ {I_2} $
$ 6({I_2} - {I_1}) + 12({I_2} - {I_3}) + 7{I_2} - 50 = 0 $
$ - 6{I_1} + 25{I_2} - 12{I_3} = 50 $…………….(2)
Finally, applying KVL in the mesh containing $ {I_3} $
$ 4({I_3} - {I_1}) + 14{I_3} + 12({I_3} - {I_2}) = 0 $
$ - 4{I_1} - 12{I_2} + 30{I_3} = 0 $
Dividing both sides by $ - 2 $
$ 2{I_1} + 6{I_2} - 15{I_3} = 0 $ …………….(3)
Subtracting (1) from (2), we have
$ - 6{I_1} + 25{I_2} - 12{I_3} - ( - 10{I_1} + 3{I_2} + 2{I_3}) = 50 - 50 $
$ 4{I_1} + 22{I_2} - 14{I_3} = 0 $
Dividing both sides by $ 2 $
$ 2{I_1} + 11{I_2} - 7{I_3} = 0 $ …………….(4)
Applying cross-multiplication method in (3) and (4), we have
$ \dfrac{{{I_1}}}{{123}} = \dfrac{{{I_2}}}{{ - 16}} = \dfrac{{{I_3}}}{{10}} = \lambda $ , where $ \lambda $ is some real number
$ \therefore {I_1} = 123\lambda ,{\text{ }}{I_2} = - 16\lambda ,{\text{ }}{I_3} = 10\lambda $...............(5)
Substituting these in (1), we get
$ - 10(123\lambda ) + 3( - 16\lambda ) + 2(10\lambda ) = 50 $
$ - 1258\lambda = 50 $
So, we get
$ \lambda = - \dfrac{{50}}{{1258}} $
Putting this in (5)
$ {I_1} = - \dfrac{{6150}}{{1258}} = - 4.89A $ , $ {I_2} = \dfrac{{800}}{{1258}} = 0.64A $ , and $ {I_3} = - \dfrac{{500}}{{1258}} = - 0.39A $
Now, current through the $ 6\,\Omega $ resistance
$ {I_{6\Omega }} = {I_2} - {I_1} $
Putting the values, we get
$ {I_{6\Omega }} = 0.64 - ( - 4.89) $
$ {I_{6\Omega }} = 5.53A $
Also, the current through the $ 4\Omega $ resistance
$ {I_{4\Omega }} = {I_3} - {I_1} $
Putting the values
$ {I_{4\Omega }} = - 0.39 - ( - 4.89) $
$ {I_{4\Omega }} = 4.5A $
Hence $ {I_{6\Omega }} = 5.53A $ and $ {I_{4\Omega }} = 4.5A $ .
Note:
While using KVL, first select a sign convention and then proceed. Do not get confused due to the sign convention. The choice of sign convention doesn’t change the final answer. We can use any one of the two sign conventions for the resistances and the batteries.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




