
Find the current “I” by using the superposition theorem.
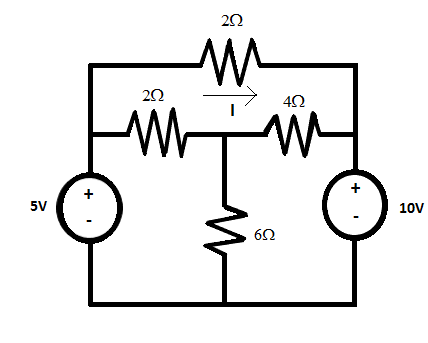

Answer
543.6k+ views
Hint : In this question, we need to determine the value of ‘I’ by following the superposition theorem only. For this, we will take one source at a time and evaluate the value of the current passing through the resistance of 2 ohms.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
According to the Superposition theorem, in a circuit containing more than one independent source, the current through or voltage across an element is the sum of the effect caused due to sources acting one at a time.
Let us take the effect of 5 volts first so the 10 volts side will be short-circuited.
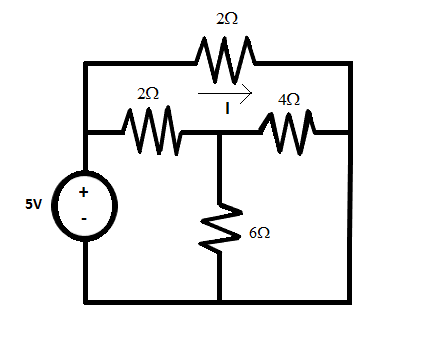
Here, 4 ohms and 6 ohms are connected in parallel. And upper 2 ohms resistance is connected in parallel with the series combination of lower 2 ohms and (4 ll 6).
The circuit diagram will be reduced to
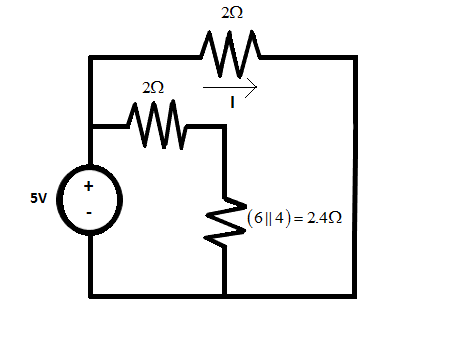
A voltage of 5 volts is applied to the upper 2 ohms resistance. So, following ohms’ law, we get
$
{I_2} = \dfrac{5}{2} \\
= 2.5A(clock - wise) - - - - (i) \\
$
Now, considering 10 ohms resistance to be acting alone.
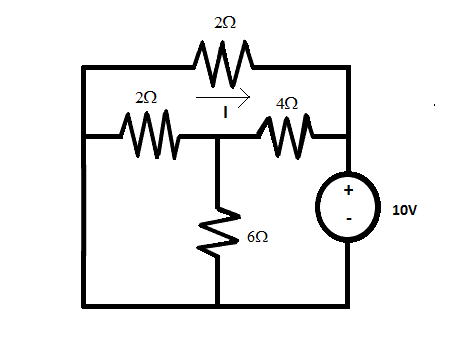
Here, lower 2 ohms and 6 ohms are connected in parallel. And upper 2 ohms resistance is connected in parallel with the series combination of lower 4 ohms and (2 ll 6).
The circuit diagram will be reduced to
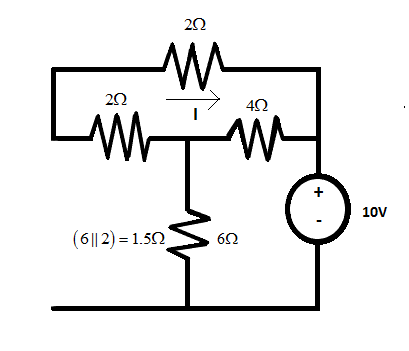
A voltage of 10 volts is applied to the upper 2 ohms resistance. So, following ohms’ law, we get
$
{I_2} = \dfrac{{10}}{2} \\
= 5A(anticlock - wise) - - - - (ii) \\
$
By equation (i) and (ii), we can say that the equivalent current flowing through the resistance of 2 ohms is
$
I = 2.5 - 5 \\
= - 2.5(clockwise) \\
$
Or,
$
I = 5 - 2.5 \\
= 2.5(anticlockwise) \\
$
Hence, the value of “I” is 2.5 Amperes in an anti-clockwise direction.
Note :
When a voltage source is zero then, the circuit is short-circuited, and when the current source is made zero then, the circuit is open-circuited. It should be noted here that the direction of the current plays a vital role in determining the net current through the resistance.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
According to the Superposition theorem, in a circuit containing more than one independent source, the current through or voltage across an element is the sum of the effect caused due to sources acting one at a time.
Let us take the effect of 5 volts first so the 10 volts side will be short-circuited.

Here, 4 ohms and 6 ohms are connected in parallel. And upper 2 ohms resistance is connected in parallel with the series combination of lower 2 ohms and (4 ll 6).
The circuit diagram will be reduced to

A voltage of 5 volts is applied to the upper 2 ohms resistance. So, following ohms’ law, we get
$
{I_2} = \dfrac{5}{2} \\
= 2.5A(clock - wise) - - - - (i) \\
$
Now, considering 10 ohms resistance to be acting alone.

Here, lower 2 ohms and 6 ohms are connected in parallel. And upper 2 ohms resistance is connected in parallel with the series combination of lower 4 ohms and (2 ll 6).
The circuit diagram will be reduced to

A voltage of 10 volts is applied to the upper 2 ohms resistance. So, following ohms’ law, we get
$
{I_2} = \dfrac{{10}}{2} \\
= 5A(anticlock - wise) - - - - (ii) \\
$
By equation (i) and (ii), we can say that the equivalent current flowing through the resistance of 2 ohms is
$
I = 2.5 - 5 \\
= - 2.5(clockwise) \\
$
Or,
$
I = 5 - 2.5 \\
= 2.5(anticlockwise) \\
$
Hence, the value of “I” is 2.5 Amperes in an anti-clockwise direction.
Note :
When a voltage source is zero then, the circuit is short-circuited, and when the current source is made zero then, the circuit is open-circuited. It should be noted here that the direction of the current plays a vital role in determining the net current through the resistance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




