
Find the common tangents of ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=2{{a}^{2}},{{y}^{2}}=8ax.$
Answer
604.5k+ views
Hint: Equation of tangent in slope form for a parabola of type ${{y}^{2}}=4ax\to y=mx+\dfrac{a}{m}$.
The perpendicular length of a tangent from the center of a circle is equal to the radius of the circle, use this property to solve the problem.
Perpendicular length of a line $Ax+By+C=0$ from a point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$is given as
$\left| \dfrac{A{{x}_{1}}+B{{y}_{1}}+C}{\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}}} \right|$
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we need to determine the equation of common tangent to the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=2{{a}^{2}}$and parabola ${{y}^{2}}=8ax$.
As we can get centre of circle is $\left( {{0}_{1}}0 \right),\text{radius = }\sqrt{\text{2a}}$, by comparing the given equation of circle with the standard form of circle i.e. ${{\left( {{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)={{r}^{2}}$ , where, $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is center and r is the radius.
As, we know the tangent in slope form of parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax\to y=mx+\dfrac{a}{m}$ ,
Where m is the slope of the tangent and we can compare the relation ${{y}^{2}}=8ax$ with the standard form of parabola i.e. ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$(with symmetric to x axis).
Hence, we know the tangent through parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$is given as
$y=mx+\dfrac{a}{m}$ …………………. (i)
So, similarly, tangent through ${{y}^{2}}=8ax$ can be given as
$y=mx+\dfrac{2a}{m}$ ………….. (ii)
So, we can get diagram with the help of above information as
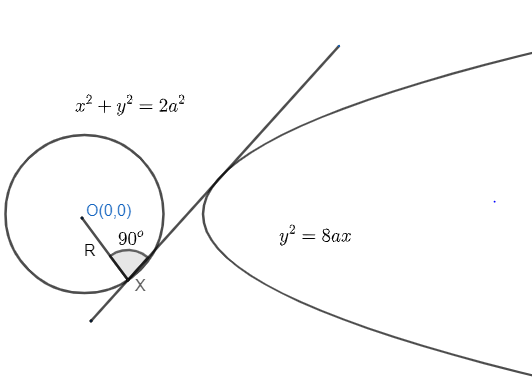
Common tangent $=y=mx+\dfrac{2a}{m}$
As, we know tangent through a point on a circle is perpendicular to the radius to that point.
Hence, in other words, we can say that the perpendicular length from the centre of any circle to the tangent on a point is equal to radius to that point.
As we know perpendicular length of any line $A{{x}_{1}}+B{{y}_{1}}+C=0$ from a point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$can be given as
Perpendicular length = $\left| \dfrac{A{{x}_{1}}+B{{y}_{1}}+C}{\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}}} \right|$ ………………. (iii)
Hence, tangent $y=mx+\dfrac{2a}{m}$ will have perpendicular length from centre $\left( {{0}_{1}}0 \right)\to \sqrt{2}$units (radius). So, we can write the equation with the help of equation (iii) as:
As, tangent can be written as
$mx-y+\dfrac{2a}{m}$
So, we get
$\begin{align}
& \left| \dfrac{m\left( 0 \right)-0+\dfrac{2a}{m}}{\sqrt{{{m}^{2}}+1}} \right|=\sqrt{2a,} \\
& \dfrac{\dfrac{2a}{m}}{\sqrt{{{m}^{2}}+1}}=\sqrt{2a,}\dfrac{2}{m\sqrt{{{m}^{2}}+1}}=\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
On squaring both sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{4}{{{m}^{2}}\sqrt{{{m}^{2}}+1}}=2 \\
& {{m}^{2}}\left( {{m}^{2}}+1 \right)=2,{{m}^{4}}+{{m}^{2}}-2=0 \\
& {{m}^{2}}+2{{m}^{2}}-{{m}^{2}}-2=0 \\
& {{m}^{2}}\left( {{m}^{2}}+2 \right)-1\left( {{m}^{2}}+2 \right)=0 \\
& \left( {{m}^{2}}-1 \right)\left( {{m}^{2}}+2 \right)=0 \\
& {{m}^{2}}=1,{{m}^{2}}+2=0 \\
\end{align}$
As, ${{m}^{2}}+2\ne 0$, because ${{m}^{2}}$ cannot be negative.
So, we have
$\begin{align}
& {{m}^{2}}=1 \\
& m=\pm 1 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, equation of common tangents can be given as
y = x + 2a, y = - x – 2a
x – y + 2a = 0, x + y + 2a = 0.
Note: Another approach for this problem would be that we can suppose the tangent for the given circle and hence, find slope of tangent by using this tangent as tangent of the given parabola. As, we know tangent through ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}$ can be given as:
$y=mx\pm a\sqrt{{{m}^{2}}+1}$ . Now, put the value of ‘y’ or ‘x’ in the equation of the parabola and put the discriminant of the quadratic formed in ‘x’ or ‘y’ to 0. Because tangent will touch to the parabola at only one point, so quadratic forms should have equal roots or one root.
One may prove the direct used tangent equation $y=mx+\dfrac{a}{m}\to {{y}^{2}}=4ax$ by supposing the line $y=mx+c$ as a tangent for ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$. And solve them to get the value of c.
The perpendicular length of a tangent from the center of a circle is equal to the radius of the circle, use this property to solve the problem.
Perpendicular length of a line $Ax+By+C=0$ from a point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$is given as
$\left| \dfrac{A{{x}_{1}}+B{{y}_{1}}+C}{\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}}} \right|$
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we need to determine the equation of common tangent to the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=2{{a}^{2}}$and parabola ${{y}^{2}}=8ax$.
As we can get centre of circle is $\left( {{0}_{1}}0 \right),\text{radius = }\sqrt{\text{2a}}$, by comparing the given equation of circle with the standard form of circle i.e. ${{\left( {{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)={{r}^{2}}$ , where, $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ is center and r is the radius.
As, we know the tangent in slope form of parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax\to y=mx+\dfrac{a}{m}$ ,
Where m is the slope of the tangent and we can compare the relation ${{y}^{2}}=8ax$ with the standard form of parabola i.e. ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$(with symmetric to x axis).
Hence, we know the tangent through parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$is given as
$y=mx+\dfrac{a}{m}$ …………………. (i)
So, similarly, tangent through ${{y}^{2}}=8ax$ can be given as
$y=mx+\dfrac{2a}{m}$ ………….. (ii)
So, we can get diagram with the help of above information as

Common tangent $=y=mx+\dfrac{2a}{m}$
As, we know tangent through a point on a circle is perpendicular to the radius to that point.
Hence, in other words, we can say that the perpendicular length from the centre of any circle to the tangent on a point is equal to radius to that point.
As we know perpendicular length of any line $A{{x}_{1}}+B{{y}_{1}}+C=0$ from a point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$can be given as
Perpendicular length = $\left| \dfrac{A{{x}_{1}}+B{{y}_{1}}+C}{\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}}} \right|$ ………………. (iii)
Hence, tangent $y=mx+\dfrac{2a}{m}$ will have perpendicular length from centre $\left( {{0}_{1}}0 \right)\to \sqrt{2}$units (radius). So, we can write the equation with the help of equation (iii) as:
As, tangent can be written as
$mx-y+\dfrac{2a}{m}$
So, we get
$\begin{align}
& \left| \dfrac{m\left( 0 \right)-0+\dfrac{2a}{m}}{\sqrt{{{m}^{2}}+1}} \right|=\sqrt{2a,} \\
& \dfrac{\dfrac{2a}{m}}{\sqrt{{{m}^{2}}+1}}=\sqrt{2a,}\dfrac{2}{m\sqrt{{{m}^{2}}+1}}=\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
On squaring both sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{4}{{{m}^{2}}\sqrt{{{m}^{2}}+1}}=2 \\
& {{m}^{2}}\left( {{m}^{2}}+1 \right)=2,{{m}^{4}}+{{m}^{2}}-2=0 \\
& {{m}^{2}}+2{{m}^{2}}-{{m}^{2}}-2=0 \\
& {{m}^{2}}\left( {{m}^{2}}+2 \right)-1\left( {{m}^{2}}+2 \right)=0 \\
& \left( {{m}^{2}}-1 \right)\left( {{m}^{2}}+2 \right)=0 \\
& {{m}^{2}}=1,{{m}^{2}}+2=0 \\
\end{align}$
As, ${{m}^{2}}+2\ne 0$, because ${{m}^{2}}$ cannot be negative.
So, we have
$\begin{align}
& {{m}^{2}}=1 \\
& m=\pm 1 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, equation of common tangents can be given as
y = x + 2a, y = - x – 2a
x – y + 2a = 0, x + y + 2a = 0.
Note: Another approach for this problem would be that we can suppose the tangent for the given circle and hence, find slope of tangent by using this tangent as tangent of the given parabola. As, we know tangent through ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}$ can be given as:
$y=mx\pm a\sqrt{{{m}^{2}}+1}$ . Now, put the value of ‘y’ or ‘x’ in the equation of the parabola and put the discriminant of the quadratic formed in ‘x’ or ‘y’ to 0. Because tangent will touch to the parabola at only one point, so quadratic forms should have equal roots or one root.
One may prove the direct used tangent equation $y=mx+\dfrac{a}{m}\to {{y}^{2}}=4ax$ by supposing the line $y=mx+c$ as a tangent for ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$. And solve them to get the value of c.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




