
How can we find the charge of a particular compound like ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$…. as I want to take out the oxidation state of ${\left( {{\text{Ni}}{{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right)^{{\text{ + 2}}}}$?
Answer
572.4k+ views
Hint For finding the particular charge of ammonia (${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$), first we have to calculate the formal charge of whole molecule by adding the formal charge of each atom present in the ammonia.
Complete step by step solution:
As we know that structure of ammonia is shown as-
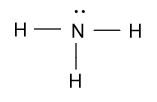
And formal charge of any compound will be calculated as follow:
Formal Charge (F.C. ) = No. of valence electrons – No. of non - bonded electrons – No. of bonds
First we calculate formal charge of each atom present in the ammonia molecule.
-F.C. on Nitrogen (${\text{N}}$) = $5 - 2 - 3 = 0$
-F.C. on each hydrogen atom (${\text{H}}$) = $1 - 0 - 1 = 0$
-From above two data it is clear that formal charge on ammonia molecules is zero and it is a neutral molecule.
Now we are known about the charge of particular compound like ammonia by which we calculate the oxidation state of given compound i.e. ${\left( {{\text{Ni}}{{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right)^{{\text{ + 2}}}}$. And oxidation state of metal Nickel $\left( {{\text{Ni}}} \right)$ is calculated as follow:
-Let us take the oxidation state of nickel is $x$, and charge of ammonia is zero, then we get
$x - 0 = + 2$
Or $x = + 2$
Hence oxidation state of metal Nickel in the compound ${\left( {{\text{Ni}}{{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right)^{{\text{ + 2}}}}$ is $ + 2$.
Note: In this question some of you may do wrong calculation if you are not familiar with the atomic number as well as with the electronic configuration of the atoms present in the ammonia molecule.
Complete step by step solution:
As we know that structure of ammonia is shown as-

And formal charge of any compound will be calculated as follow:
Formal Charge (F.C. ) = No. of valence electrons – No. of non - bonded electrons – No. of bonds
First we calculate formal charge of each atom present in the ammonia molecule.
-F.C. on Nitrogen (${\text{N}}$) = $5 - 2 - 3 = 0$
-F.C. on each hydrogen atom (${\text{H}}$) = $1 - 0 - 1 = 0$
-From above two data it is clear that formal charge on ammonia molecules is zero and it is a neutral molecule.
Now we are known about the charge of particular compound like ammonia by which we calculate the oxidation state of given compound i.e. ${\left( {{\text{Ni}}{{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right)^{{\text{ + 2}}}}$. And oxidation state of metal Nickel $\left( {{\text{Ni}}} \right)$ is calculated as follow:
-Let us take the oxidation state of nickel is $x$, and charge of ammonia is zero, then we get
$x - 0 = + 2$
Or $x = + 2$
Hence oxidation state of metal Nickel in the compound ${\left( {{\text{Ni}}{{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right)^{{\text{ + 2}}}}$ is $ + 2$.
Note: In this question some of you may do wrong calculation if you are not familiar with the atomic number as well as with the electronic configuration of the atoms present in the ammonia molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




