
Find the area of the region bounded by the curve ${{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=4\left( x+1 \right)$ and the line $y=x-1$
Answer
597.6k+ views
Hint: For solving this question, first we will plot the given curves on the same $x-y$ plane. Then, we will find the desired region whose area is asked in the question. After that, we will solve the given equations and find the coordinates of the intersection points. Then, we will take an elementary horizontal strip of width $dy$ and try to write its length in terms of the variable $y$ . Then, we will write the area of the elementary in terms of $y$ and $dy$ by multiplying its length and width. And finally, we will integrate the area of the elementary strip with suitable limits to get the total area of the given region.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:
We have to find the area of the region bounded by the parabola ${{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=4\left( x+1 \right)$ and the line $y=x-1$ .
Now, before we proceed we should plot the curve ${{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=4\left( x+1 \right)$ and the line $y=x-1$ on the same $x-y$ plane. For more clarity, look at the figure given below:
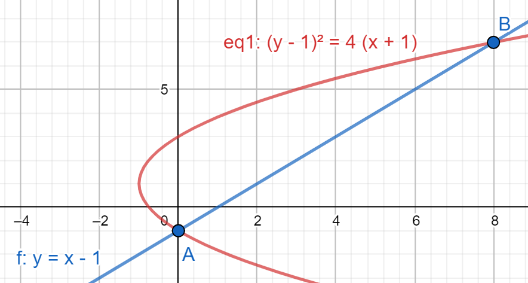
In the above figure, we have to find the area of the region bounded by the curve ${{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=4\left( x+1 \right)$ and the line $y=x-1$ .
Now, from the above figure, we can say that for the coordinates of points A and B we should equate the equations ${{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=4\left( x+1 \right)$ and $y=x-1$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& y=x-1 \\
& \Rightarrow x=y+1 \\
\end{align}$
Now, we put $x=y+1$ in the equation ${{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=4\left( x+1 \right)$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=4\left( x+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}+1-2y=4\left( y+1+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}-2y+1=4y+8 \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}-6y-7=0 \\
\end{align}$
We have got the quadratic equation in y so solving the quadratic equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}-7y+y-7=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y\left( y-7 \right)+\left( y-7 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( y-7 \right)\left( y+1 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}$
Equating $y-7$ to 0 we get,
$\begin{align}
& y-7=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=7 \\
\end{align}$
Equating $y+1$ to 0 we get,
$\begin{align}
& y+1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=-1 \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above result and the figure, we can say that to get the coordinates of point A we should put $y=-1$ and to get the coordinates of point B we should put $y=7$ in the equation $y=x-1$ . Then,
${{y}_{A}}={{x}_{A}}-1$
Substituting the value of ${{y}_{A}}=-1$ in the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{A}}={{y}_{A}}+1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{A}}=-1+1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{A}}=0 \\
& {{y}_{B}}={{x}_{B}}-1 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the value of ${{y}_{B}}=7$ in the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{B}}={{y}_{B}}+1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{B}}=7+1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{B}}=8 \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above result, we conclude that coordinates of points $A\equiv (0,-1)$ and $B\equiv (8,7)$ .
Now, we take an elementary horizontal strip at $y$ of width $dy$ . For more clarity, look at the figure given below:
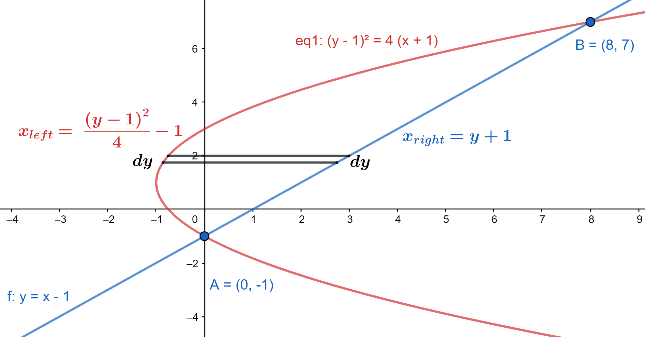
Now, to find the length of the elementary strip, we should subtract the ${{x}_{right}}=y+1$ and ${{x}_{left}}=\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}{4}-1$ . Then,
length of the elementary strip $={{x}_{right}}-{{x}_{left}}=y+1-\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}{4}+1=y+2-\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}{4}$ .
Now, as we know, the width of the elementary strip is $dy$ . So, the area of the elementary strip will be length multiplied by width. Then,
Area of the elementary strip $=dA=\left( y+2-\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}{4} \right)dy$ .
Now, to get the total area of the region ABC, we should add the area of such elementary strips from $y=-1$ to $y=7$ so, to get the desired area we should integrate the expression $\left( y+2-\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}{4} \right)dy$ from $y=-1$ to $y=7$ . Then,
Area of the desired region $=\int\limits_{-1}^{7}{\left( y+2-\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}{4} \right)dy}$ .
Now, we will use the formula $\int{{{y}^{n}}dy=\dfrac{{{y}^{n+1}}}{n+1}+c}$ to integrate the above integral. Then,
\[\begin{align}
& \int\limits_{-1}^{7}{\left( y+2-\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}{4} \right)dy} \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{2}+2y-\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{3}}}{12} \right]_{-1}^{7} \\
\end{align}\]
Applying the upper and the lower limit in the result of the integral we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left[ \left( \dfrac{{{7}^{2}}}{2}+2\times 7-\dfrac{{{\left( 7-1 \right)}^{3}}}{12} \right)-\left( \dfrac{{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}}{2}+2\times \left( -1 \right)-\dfrac{{{\left( -1-1 \right)}^{3}}}{12} \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \left( \dfrac{49}{2}+14-\dfrac{{{6}^{3}}}{12} \right)-\left( \dfrac{1}{2}-2-\dfrac{{{\left( -2 \right)}^{3}}}{12} \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \left( \dfrac{77}{2}-18 \right)-\left( -\dfrac{3}{2}+\dfrac{8}{12} \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \left( \dfrac{41}{2} \right)-\left( -\dfrac{5}{6} \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \dfrac{41}{2}+\dfrac{5}{6} \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{64}{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, from the above result, we conclude that the desired area will be $\dfrac{64}{3}\text{ sq}\text{.units}$ .
Thus, the area of the region bounded by the parabola ${{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=4\left( x+1 \right)$ and the line $y=x-1$ will be equal to $\dfrac{64}{3}\text{ sq}\text{.units}\approx 21.333\text{ sq}\text{.units}$ .
Note: Here, the student should first plot the given curves carefully and then find the desired region whose area is asked in the question and proceed in a stepwise manner. Then, we should be careful while writing the dimensions of the elementary strip and for that, we should take help from the plot of the given curves. Moreover, for easy calculation, we should take horizontal elementary strips, and we should take upper and lower limits correctly, to get the correct answer and whenever we get stuck at some point we should see the plot of the given curves and use the basic concepts of integral calculus.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:
We have to find the area of the region bounded by the parabola ${{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=4\left( x+1 \right)$ and the line $y=x-1$ .
Now, before we proceed we should plot the curve ${{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=4\left( x+1 \right)$ and the line $y=x-1$ on the same $x-y$ plane. For more clarity, look at the figure given below:

In the above figure, we have to find the area of the region bounded by the curve ${{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=4\left( x+1 \right)$ and the line $y=x-1$ .
Now, from the above figure, we can say that for the coordinates of points A and B we should equate the equations ${{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=4\left( x+1 \right)$ and $y=x-1$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& y=x-1 \\
& \Rightarrow x=y+1 \\
\end{align}$
Now, we put $x=y+1$ in the equation ${{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=4\left( x+1 \right)$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=4\left( x+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}+1-2y=4\left( y+1+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}-2y+1=4y+8 \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}-6y-7=0 \\
\end{align}$
We have got the quadratic equation in y so solving the quadratic equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}-7y+y-7=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y\left( y-7 \right)+\left( y-7 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( y-7 \right)\left( y+1 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}$
Equating $y-7$ to 0 we get,
$\begin{align}
& y-7=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=7 \\
\end{align}$
Equating $y+1$ to 0 we get,
$\begin{align}
& y+1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=-1 \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above result and the figure, we can say that to get the coordinates of point A we should put $y=-1$ and to get the coordinates of point B we should put $y=7$ in the equation $y=x-1$ . Then,
${{y}_{A}}={{x}_{A}}-1$
Substituting the value of ${{y}_{A}}=-1$ in the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{A}}={{y}_{A}}+1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{A}}=-1+1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{A}}=0 \\
& {{y}_{B}}={{x}_{B}}-1 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the value of ${{y}_{B}}=7$ in the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{B}}={{y}_{B}}+1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{B}}=7+1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{B}}=8 \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above result, we conclude that coordinates of points $A\equiv (0,-1)$ and $B\equiv (8,7)$ .
Now, we take an elementary horizontal strip at $y$ of width $dy$ . For more clarity, look at the figure given below:

Now, to find the length of the elementary strip, we should subtract the ${{x}_{right}}=y+1$ and ${{x}_{left}}=\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}{4}-1$ . Then,
length of the elementary strip $={{x}_{right}}-{{x}_{left}}=y+1-\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}{4}+1=y+2-\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}{4}$ .
Now, as we know, the width of the elementary strip is $dy$ . So, the area of the elementary strip will be length multiplied by width. Then,
Area of the elementary strip $=dA=\left( y+2-\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}{4} \right)dy$ .
Now, to get the total area of the region ABC, we should add the area of such elementary strips from $y=-1$ to $y=7$ so, to get the desired area we should integrate the expression $\left( y+2-\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}{4} \right)dy$ from $y=-1$ to $y=7$ . Then,
Area of the desired region $=\int\limits_{-1}^{7}{\left( y+2-\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}{4} \right)dy}$ .
Now, we will use the formula $\int{{{y}^{n}}dy=\dfrac{{{y}^{n+1}}}{n+1}+c}$ to integrate the above integral. Then,
\[\begin{align}
& \int\limits_{-1}^{7}{\left( y+2-\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}{4} \right)dy} \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{2}+2y-\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{3}}}{12} \right]_{-1}^{7} \\
\end{align}\]
Applying the upper and the lower limit in the result of the integral we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left[ \left( \dfrac{{{7}^{2}}}{2}+2\times 7-\dfrac{{{\left( 7-1 \right)}^{3}}}{12} \right)-\left( \dfrac{{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}}{2}+2\times \left( -1 \right)-\dfrac{{{\left( -1-1 \right)}^{3}}}{12} \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \left( \dfrac{49}{2}+14-\dfrac{{{6}^{3}}}{12} \right)-\left( \dfrac{1}{2}-2-\dfrac{{{\left( -2 \right)}^{3}}}{12} \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \left( \dfrac{77}{2}-18 \right)-\left( -\dfrac{3}{2}+\dfrac{8}{12} \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \left( \dfrac{41}{2} \right)-\left( -\dfrac{5}{6} \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \dfrac{41}{2}+\dfrac{5}{6} \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{64}{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, from the above result, we conclude that the desired area will be $\dfrac{64}{3}\text{ sq}\text{.units}$ .
Thus, the area of the region bounded by the parabola ${{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=4\left( x+1 \right)$ and the line $y=x-1$ will be equal to $\dfrac{64}{3}\text{ sq}\text{.units}\approx 21.333\text{ sq}\text{.units}$ .
Note: Here, the student should first plot the given curves carefully and then find the desired region whose area is asked in the question and proceed in a stepwise manner. Then, we should be careful while writing the dimensions of the elementary strip and for that, we should take help from the plot of the given curves. Moreover, for easy calculation, we should take horizontal elementary strips, and we should take upper and lower limits correctly, to get the correct answer and whenever we get stuck at some point we should see the plot of the given curves and use the basic concepts of integral calculus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




