
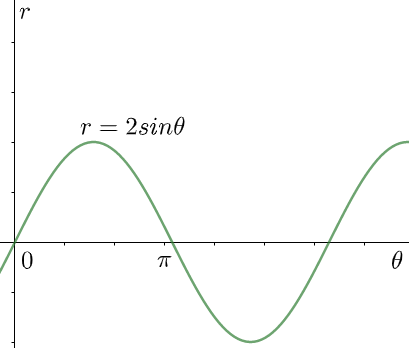
Find the area of the polar curve, $r=2\sin \theta $ from $0\le \theta \le \pi $ .
Answer
545.7k+ views
Hint: To find the area of the given curve, we need to integrate it with $\theta $ as variable from $\theta =0$ to $\theta =\pi $ .
Complete step by step solution:
There are various coordinate systems. There are cartesian coordinate systems, polar coordinate systems and spherical coordinate systems. The cartesian coordinate system incorporates the x, y, and z coordinates. The polar coordinate incorporates the r, $\theta $ , z coordinates and the spherical coordinate incorporates the r, $\theta $ , $\phi $ . In a two-dimensional system, r- $\theta $ denotes the spherical coordinate system.
Finding the area under the curve, however, remains the same in any coordinate system, which is by integration within limits. In the cartesian coordinate system, we find the area under the curve $y=f\left( x \right)$ by the help of the integration $I=\int{f\left( x \right)dx}$ . Similarly, we find the area under the curve $r=f\left( \theta \right)$ by the help of the integration $I=\int{f\left( \theta \right)d\theta }$ .
In this problem, the given curve that we have is $r=2\sin \theta $ . To find the area under this curve, we need to integrate it within the limits $\theta =0$ and $\theta =\pi $ . The integration thus is,
$\begin{align}
& I=\int\limits_{0}^{\pi }{2\sin \theta d\theta } \\
& \Rightarrow I=2\left[ -\cos \theta \right]_{0}^{\pi } \\
& \Rightarrow I=2\left[ -\cos \pi -\left( -\cos 0 \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow I=2\left[ 1+1 \right] \\
& \Rightarrow I=4 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we can conclude that the area of the given curve within $\theta =0$ and $\theta =\pi $ is $4$ .
Note: Finding area under a curve always means integrating it and nothing else. We should keep this in mind and should not get confused when we see any coordinate system other than the cartesian. We should also remember to apply the limits correctly.
Complete step by step solution:
There are various coordinate systems. There are cartesian coordinate systems, polar coordinate systems and spherical coordinate systems. The cartesian coordinate system incorporates the x, y, and z coordinates. The polar coordinate incorporates the r, $\theta $ , z coordinates and the spherical coordinate incorporates the r, $\theta $ , $\phi $ . In a two-dimensional system, r- $\theta $ denotes the spherical coordinate system.
Finding the area under the curve, however, remains the same in any coordinate system, which is by integration within limits. In the cartesian coordinate system, we find the area under the curve $y=f\left( x \right)$ by the help of the integration $I=\int{f\left( x \right)dx}$ . Similarly, we find the area under the curve $r=f\left( \theta \right)$ by the help of the integration $I=\int{f\left( \theta \right)d\theta }$ .
In this problem, the given curve that we have is $r=2\sin \theta $ . To find the area under this curve, we need to integrate it within the limits $\theta =0$ and $\theta =\pi $ . The integration thus is,
$\begin{align}
& I=\int\limits_{0}^{\pi }{2\sin \theta d\theta } \\
& \Rightarrow I=2\left[ -\cos \theta \right]_{0}^{\pi } \\
& \Rightarrow I=2\left[ -\cos \pi -\left( -\cos 0 \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow I=2\left[ 1+1 \right] \\
& \Rightarrow I=4 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we can conclude that the area of the given curve within $\theta =0$ and $\theta =\pi $ is $4$ .

Note: Finding area under a curve always means integrating it and nothing else. We should keep this in mind and should not get confused when we see any coordinate system other than the cartesian. We should also remember to apply the limits correctly.
Recently Updated Pages
Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

The coating formed on the metals such as iron silver class 12 chemistry CBSE

Metals are refined by using different methods Which class 12 chemistry CBSE

What do you understand by denaturation of proteins class 12 chemistry CBSE

Assertion Nitrobenzene is used as a solvent in FriedelCrafts class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




