
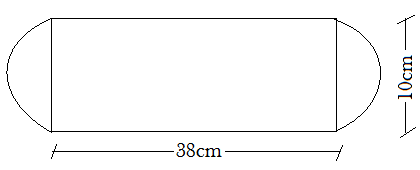
Find the area of the flower bed (with semi-circular ends) shown in the figure.
A) \[\left( {380{\text{ }} + {\text{ 12}}{\text{.5}}\pi } \right){\text{ }}c{m^2}\]
B) \[\left( {380{\text{ }} + {\text{ 10}}0\pi } \right){\text{ }}c{m^2}\]
C) \[\left( {380{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}50\pi } \right){\text{ }}c{m^2}\]
D) \[\left( {380{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}25\pi } \right){\text{ }}c{m^2}\]

Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint: The flower bed is in the shape of a rectangle with two semi-circles stuck to each of its ends. We know that the area of a rectangle with dimensions a and b is given by \[a \times b\], and area of a semicircle with radius r is given by $\dfrac{1}{2}\pi {r^2}$. The length of the rectangular part of the flower bed and the diameter of the semi-circles are given. Find the individual areas of the rectangle and the semi-circles.
Now note that the total area of the flower bed is the sum of the areas of the rectangle and the semi-circles.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given that, the flower bed has semi-circular ends.
Note that it contains one rectangle of dimensions \[38\;cm\; \times 10\;cm\] and two semi-circles of diameters 10 cm.
Let the length of rectangle be \[a = 38cm\] and breadth of it be \[b = 10cm\],
Also, the diameter of the semicircle is 10cm, so its radius will be \[\dfrac{{diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{{10cm}}{2} = 5cm\]
Therefore, total area of the flower bed \[ = \;area{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}rectangle\; + {\text{ }}(2 \times area{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}semicircle)\]
Now, we know that the area of a rectangle with dimensions a and b is given by \[a \times b\]
∴ the area of rectangle is $ = 38 \times 10{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}380\;c{m^2}$
Again, area of a semicircle with radius r is given by $\dfrac{1}{2}\pi {r^2}$
Therefore, area of each semicircle is $ = \dfrac{1}{2}\pi \times {5^2} = \dfrac{{25}}{2}\pi {\text{ }}c{m^2}$
∴ Area of the given figure = area of rectangle + (2×area of semi-circle)
\[ = 380 + \left( {2 \times \dfrac{{25}}{2}\pi } \right)\]
On simplification we get,
\[ = \left( {380 + 25\pi } \right)\;c{m^2}\]
Hence, the total area of the flower bed is \[\left( {380 + 25\pi } \right)\;c{m^2}\]
Hence, option D is the correct answer.
Note: Here, you should not substitute the value of \[\pi \] as in the options we can see that the area is in terms of \[\pi \], so if we substitute the value of \[\pi \] we complicate the question and get confused as then you can think that no option matches and the question is wrong.
Note that some formulae of finding the area of the following figures.
Now note that the total area of the flower bed is the sum of the areas of the rectangle and the semi-circles.
Complete step-by-step answer:

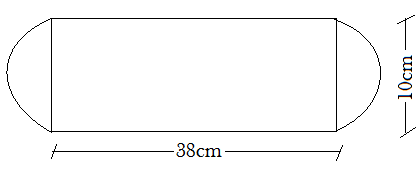
Given that, the flower bed has semi-circular ends.
Note that it contains one rectangle of dimensions \[38\;cm\; \times 10\;cm\] and two semi-circles of diameters 10 cm.
Let the length of rectangle be \[a = 38cm\] and breadth of it be \[b = 10cm\],
Also, the diameter of the semicircle is 10cm, so its radius will be \[\dfrac{{diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{{10cm}}{2} = 5cm\]
Therefore, total area of the flower bed \[ = \;area{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}rectangle\; + {\text{ }}(2 \times area{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}semicircle)\]
Now, we know that the area of a rectangle with dimensions a and b is given by \[a \times b\]
∴ the area of rectangle is $ = 38 \times 10{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}380\;c{m^2}$
Again, area of a semicircle with radius r is given by $\dfrac{1}{2}\pi {r^2}$
Therefore, area of each semicircle is $ = \dfrac{1}{2}\pi \times {5^2} = \dfrac{{25}}{2}\pi {\text{ }}c{m^2}$
∴ Area of the given figure = area of rectangle + (2×area of semi-circle)
\[ = 380 + \left( {2 \times \dfrac{{25}}{2}\pi } \right)\]
On simplification we get,
\[ = \left( {380 + 25\pi } \right)\;c{m^2}\]
Hence, the total area of the flower bed is \[\left( {380 + 25\pi } \right)\;c{m^2}\]
Hence, option D is the correct answer.
Note: Here, you should not substitute the value of \[\pi \] as in the options we can see that the area is in terms of \[\pi \], so if we substitute the value of \[\pi \] we complicate the question and get confused as then you can think that no option matches and the question is wrong.
Note that some formulae of finding the area of the following figures.
| Figure | Area |
| Square | \[{a^2}\] |
| Rectangle | \[a \times b\] |
| Triangle | $\dfrac{{{1}}}{{\text{2}}}{{ \times base \times height}}$ |
| Circle | $\pi {r^2}$ , r=radius |
| semi-circle | $\dfrac{1}{2}\pi {r^2}$ |
| Parallelogram | \[a \times h\;\] ; a =any side, h= height w.r.t that side |
| Rhombus | $\dfrac{1}{2}{d_1}{d_2}$ ; d1 and d2 are the diagonals |
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of a newspaper explaining class 10 english CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?




