
Find the angle between the circles
$S:{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x+6y+11=0$ and $S':{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2x+8y+13=0$
Answer
611.1k+ views
Hint:First compare the given equations of circle with the general equation of the circle, that is, ${{(x-{{x}_{0}})}^{2}}+{{(y-{{y}_{0}})}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$, to find out the centre and radius of both the circle. Then apply the formula $\cos \theta =|\dfrac{{{d}^{2}}-{{r}_{1}}^{2}-{{r}_{2}}^{2}}{2{{r}_{1}}{{r}_{2}}}|$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given equations of circle are:
$S:{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x+6y+11=0..................(i)$
$S':{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2x+8y+13=0...............................(ii)$
From equation (i) & (ii), we will find their centres ${{C}_{1}}$ and ${{C}_{2}}$ first, respectively for circles S and S’.
Adding $4+9$ to both sides of the equation, we get :
Equation (i): ${{x}^{2}}-4x+4+{{y}^{2}}+6y+9+11=4+9$
\[\begin{align}
& {{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+3 \right)}^{2}}=-11+4+9 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+3 \right)}^{2}}=2 \\
\end{align}\]
By comparing this equation to the form ${{(x-{{x}_{0}})}^{2}}+{{(y-{{y}_{0}})}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$, where the centre of the circle is $({{x}_{0}},{{y}_{0}})$, and its radius is $r$, we get ${{C}_{1}}\left( 2,-3 \right)$.
Now, for equation (ii): ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2x+8y+13=0$
Let’s add $1+16$ to both sides. Doing so, we get :
$\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x+1 \right)+{{y}^{2}}+8y+16+13=16+1$
\[\begin{align}
& {{\left( x-\underline{1} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+\underline{4} \right)}^{2}}=-13+16+1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-\underline{1} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+\underline{4} \right)}^{2}}=4 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence we get ${{C}_{2}}(1,-4)$
Now, we will find the radius; we get
\[{{r}_{1}}=\sqrt{g_{1}^{2}+f_{1}^{2}-C}\] and ${{r}_{2}}=\sqrt{{{g}_{2}}^{2}+{{f}_{2}}^{2}-C}$
As given with centre ${{C}_{1}}\left( 2,-3 \right)$ and ${{C}_{2}}\left( 1,-4 \right)$
Of the two circle equation in standard form, the standard equation is actually given by \[\]
So, we know that the Standard equation of a circle is
Now, for radius of ‘S’ for which the centre ${{C}_{1}}(2,-3)$ is given by,
\[\begin{align}
& {{r}_{1}}=\sqrt{{{g}_{1}}^{2}+{{f}_{1}}^{2}-C} \\
& =\sqrt{{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}-11} \\
\end{align}\]
$=\sqrt{2}$ units
Now, for radius of S’ for ${{C}_{2}}(1,-4)$ is given by;
\[\begin{align}
& {{r}_{2}}=\sqrt{{{g}_{2}}^{2}+{{f}_{2}}^{2}-C} \\
& =\sqrt{{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -4 \right)}^{2}}-13} \\
\end{align}\]
$\sqrt{4}=2$ units
Now, we find the distance between the centres using distance formula, that says that the distance between two points $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ and $({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})$ is given by :
$d=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}}$
Applying this formula for ${{C}_{1}}$ and ${{C}_{2}}$, we’ll see that :
$d=\sqrt{{{\left( 2-1 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -3+4 \right)}^{2}}}$
$\begin{align}
& =\sqrt{1+1} \\
& =\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
Now, for finding the angle, we will use the formula $\to \cos \theta =\left| \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}-{{r}_{1}}^{2}-{{r}_{2}}^{2}}{2{{r}_{1}}{{r}_{2}}} \right|$, where $\theta $ is the angle between the circles. So, applying that formula here, we get:
\[\begin{align}
& \cos \theta =\left| \dfrac{{{\left( \sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( \sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}}{2\times \sqrt{2}\times 2} \right| \\
& =\left| \dfrac{2-2-4}{4\sqrt{2}} \right| \\
& =\left| \dfrac{-{4}}{{4}\sqrt{2}} \right| \\
& \cos \theta =\pm \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \\
& \theta ={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \pm \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
\[=45{}^\circ ,135{}^\circ \]
We won’t consider the angles that are greater than $180{}^\circ $ over here, since the angle between two circles can at max be $180{}^\circ $ only.
$\therefore $ Therefore, the angle between two circle is $45{}^\circ or135{}^\circ $
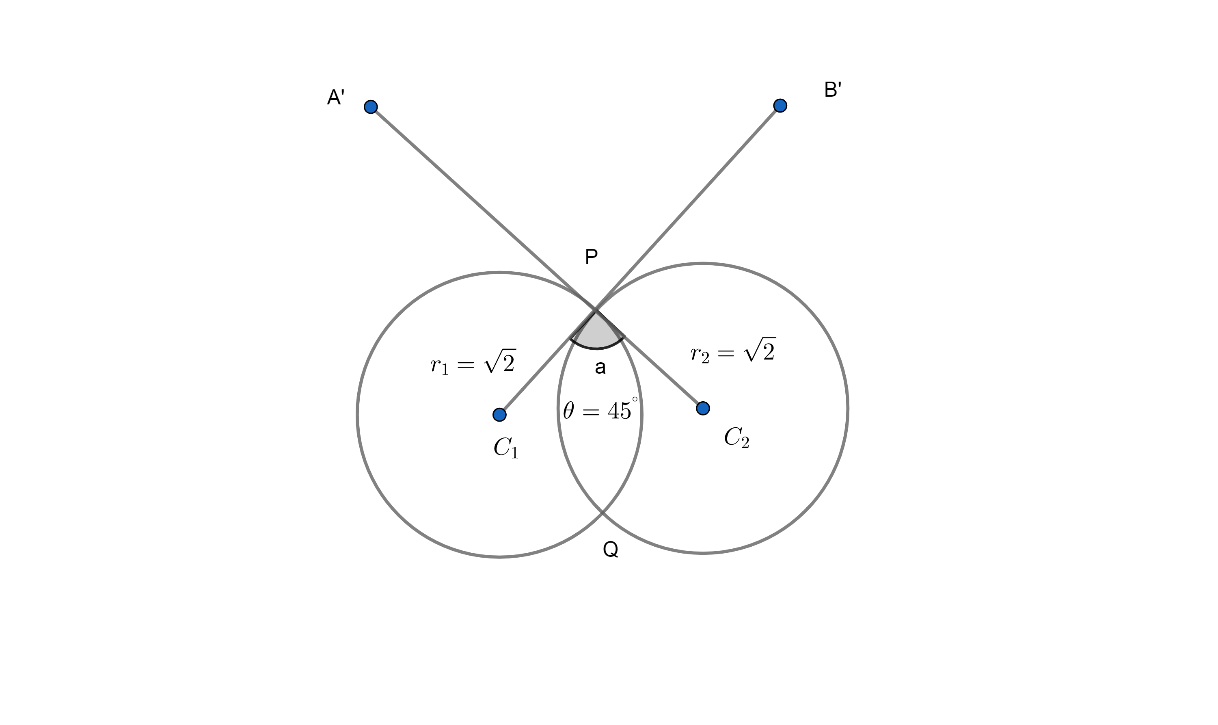
Note: Students should remember the formula i.e $\cos \theta =\left| \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}-{{r}_{1}}^{2}-{{r}_{2}}^{2}}{2.{{r}_{1}}.{{r}_{2}}} \right|$ to solve these types of questions.The general form of the equation of circle is given as ${x^2+y^2+2gx+2fy+c}$.The centre of circle is $(-g,-f)$ and radius of circle is ${\sqrt{g^2+f^2-c}}$.We can directly calculate centre from the equation $S:{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x+6y+11=0$ equating $-4=2g$ and $6=2f$ we get $g=-2$ and $f=3$ so centre of circle is $(-g,-f)$ i.e $(2,-3)$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given equations of circle are:
$S:{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x+6y+11=0..................(i)$
$S':{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2x+8y+13=0...............................(ii)$
From equation (i) & (ii), we will find their centres ${{C}_{1}}$ and ${{C}_{2}}$ first, respectively for circles S and S’.
Adding $4+9$ to both sides of the equation, we get :
Equation (i): ${{x}^{2}}-4x+4+{{y}^{2}}+6y+9+11=4+9$
\[\begin{align}
& {{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+3 \right)}^{2}}=-11+4+9 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+3 \right)}^{2}}=2 \\
\end{align}\]
By comparing this equation to the form ${{(x-{{x}_{0}})}^{2}}+{{(y-{{y}_{0}})}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$, where the centre of the circle is $({{x}_{0}},{{y}_{0}})$, and its radius is $r$, we get ${{C}_{1}}\left( 2,-3 \right)$.
Now, for equation (ii): ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2x+8y+13=0$
Let’s add $1+16$ to both sides. Doing so, we get :
$\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x+1 \right)+{{y}^{2}}+8y+16+13=16+1$
\[\begin{align}
& {{\left( x-\underline{1} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+\underline{4} \right)}^{2}}=-13+16+1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-\underline{1} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+\underline{4} \right)}^{2}}=4 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence we get ${{C}_{2}}(1,-4)$
Now, we will find the radius; we get
\[{{r}_{1}}=\sqrt{g_{1}^{2}+f_{1}^{2}-C}\] and ${{r}_{2}}=\sqrt{{{g}_{2}}^{2}+{{f}_{2}}^{2}-C}$
As given with centre ${{C}_{1}}\left( 2,-3 \right)$ and ${{C}_{2}}\left( 1,-4 \right)$
Of the two circle equation in standard form, the standard equation is actually given by \[\]
So, we know that the Standard equation of a circle is
Now, for radius of ‘S’ for which the centre ${{C}_{1}}(2,-3)$ is given by,
\[\begin{align}
& {{r}_{1}}=\sqrt{{{g}_{1}}^{2}+{{f}_{1}}^{2}-C} \\
& =\sqrt{{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}-11} \\
\end{align}\]
$=\sqrt{2}$ units
Now, for radius of S’ for ${{C}_{2}}(1,-4)$ is given by;
\[\begin{align}
& {{r}_{2}}=\sqrt{{{g}_{2}}^{2}+{{f}_{2}}^{2}-C} \\
& =\sqrt{{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -4 \right)}^{2}}-13} \\
\end{align}\]
$\sqrt{4}=2$ units
Now, we find the distance between the centres using distance formula, that says that the distance between two points $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ and $({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})$ is given by :
$d=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}}$
Applying this formula for ${{C}_{1}}$ and ${{C}_{2}}$, we’ll see that :
$d=\sqrt{{{\left( 2-1 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -3+4 \right)}^{2}}}$
$\begin{align}
& =\sqrt{1+1} \\
& =\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
Now, for finding the angle, we will use the formula $\to \cos \theta =\left| \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}-{{r}_{1}}^{2}-{{r}_{2}}^{2}}{2{{r}_{1}}{{r}_{2}}} \right|$, where $\theta $ is the angle between the circles. So, applying that formula here, we get:
\[\begin{align}
& \cos \theta =\left| \dfrac{{{\left( \sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( \sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}}{2\times \sqrt{2}\times 2} \right| \\
& =\left| \dfrac{2-2-4}{4\sqrt{2}} \right| \\
& =\left| \dfrac{-{4}}{{4}\sqrt{2}} \right| \\
& \cos \theta =\pm \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \\
& \theta ={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \pm \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
\[=45{}^\circ ,135{}^\circ \]
We won’t consider the angles that are greater than $180{}^\circ $ over here, since the angle between two circles can at max be $180{}^\circ $ only.
$\therefore $ Therefore, the angle between two circle is $45{}^\circ or135{}^\circ $

Note: Students should remember the formula i.e $\cos \theta =\left| \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}-{{r}_{1}}^{2}-{{r}_{2}}^{2}}{2.{{r}_{1}}.{{r}_{2}}} \right|$ to solve these types of questions.The general form of the equation of circle is given as ${x^2+y^2+2gx+2fy+c}$.The centre of circle is $(-g,-f)$ and radius of circle is ${\sqrt{g^2+f^2-c}}$.We can directly calculate centre from the equation $S:{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-4x+6y+11=0$ equating $-4=2g$ and $6=2f$ we get $g=-2$ and $f=3$ so centre of circle is $(-g,-f)$ i.e $(2,-3)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




