
How do you find the amplitude, period and graph $y = \sec \left( {3\theta } \right)$?
Answer
547.8k+ views
Hint: First find amplitude, period, phase shift, and vertical shift for given periodic function. Select a few points to graph. Find the points at $\theta = 0$, $\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{{18}}$, $\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{9}$, $\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{3}$, $\theta = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$. List the points in a table. Then graph the trigonometric function using the amplitude, period, phase shift, vertical shift and the points.
Formula used:
For the graph of $y = a\sec \left( {bx - c} \right) + d$
Amplitude: None
Period$ = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| b \right|}}$
Phase Shift $ = \dfrac{c}{b}$
Vertical Shift $ = d$
Complete step by step answer:
We will use the form $y = a\sec \left( {bx - c} \right) + d$ to find the amplitude, period, phase shift, and vertical shift.
Compare the given equation $y = \sec \left( {3\theta } \right)$ with $y = a\sec \left( {bx - c} \right) + d$ and find variables $a,b,c$ and $d$.
$a = 1$, $b = 3$, $c = 0$ and $d = 0$.
Since the graph of the function $\sec $ does not have a maximum or minimum value, there can be no value for the amplitude.
Amplitude: None
Now, find the period using the formula $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| b \right|}}$.
So, we will calculate the period of the function using $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| b \right|}}$.
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| b \right|}}$
Replace $b$ with $3$ in the formula for period.
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| 3 \right|}}$
Solve the equation.
Here, we can observe that the absolute value is the distance between a number and zero.
The distance between $0$ and $3$ is $3$.
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
Divide $2\pi $ by $3$.
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
Now, we will find the phase shift using the formula $\dfrac{c}{b}$.
So, we will calculate the phase shift of the function from $\dfrac{c}{b}$.
Phase Shift: $\dfrac{c}{b}$
Here, replace the values of $c$ and $b$ in the equation for phase shift.
Phase Shift: $\dfrac{0}{3}$
Divide $0$ by $3$.
Phase Shift: $0$
Find the vertical shift $d$.
Vertical Shift: $0$
List the properties of the trigonometric function.
Amplitude: None
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
Phase Shift: $0$($0$ to the right)
Vertical Shift: $0$
Select a few points to graph.
Find the point at $\theta = 0$.
Replace the variable $\theta $ with $0$ in the expression.
$f\left( 0 \right) = \sec \left( {3 \times 0} \right)$
Simplify the result.
The exact value of $\sec \left( 0 \right)$ is $1$.
$f\left( 0 \right) = 1$
The final answer is $1$.
Find the point at $\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{{18}}$.
Replace the variable $\theta $ with $\dfrac{\pi }{{18}}$ in the expression.
$f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{{18}}} \right) = \sec \left( {3 \times \dfrac{\pi }{{18}}} \right)$
Simplify the result.
The exact value of $\sec \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right)$ is $\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }}$.
$f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{{18}}} \right) = \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
The final answer is $\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }}$.
Find the point at $\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{9}$.
Replace the variable $\theta $ with $\dfrac{\pi }{9}$ in the expression.
$f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{9}} \right) = \sec \left( {3 \times \dfrac{\pi }{9}} \right)$
Simplify the result.
The exact value of $\sec \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)$ is $2$.
$f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{9}} \right) = 2$
The final answer is $2$.
Find the point at $\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{3}$.
Replace the variable $\theta $ with $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$ in the expression.
$f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right) = \sec \left( {3 \times \dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)$
Simplify the result.
The exact value of $\sec \left( \pi \right)$ is $ - 1$.
$f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right) = - 1$
The final answer is $ - 1$.
Find the point at $\theta = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$.
Replace the variable $\theta $ with $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$ in the expression.
$f\left( {\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}} \right) = \sec \left( {3 \times \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}} \right)$
Simplify the result.
The exact value of $\sec \left( {2\pi } \right)$ is $1$.
$f\left( {\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}} \right) = 1$
The final answer is $1$.
List the points in a table.
The trigonometric function can be graphed using the amplitude, period, phase shift, vertical shift and the points.
Amplitude: None
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
Phase Shift: $0$($0$ to the right)
Vertical Shift: $0$
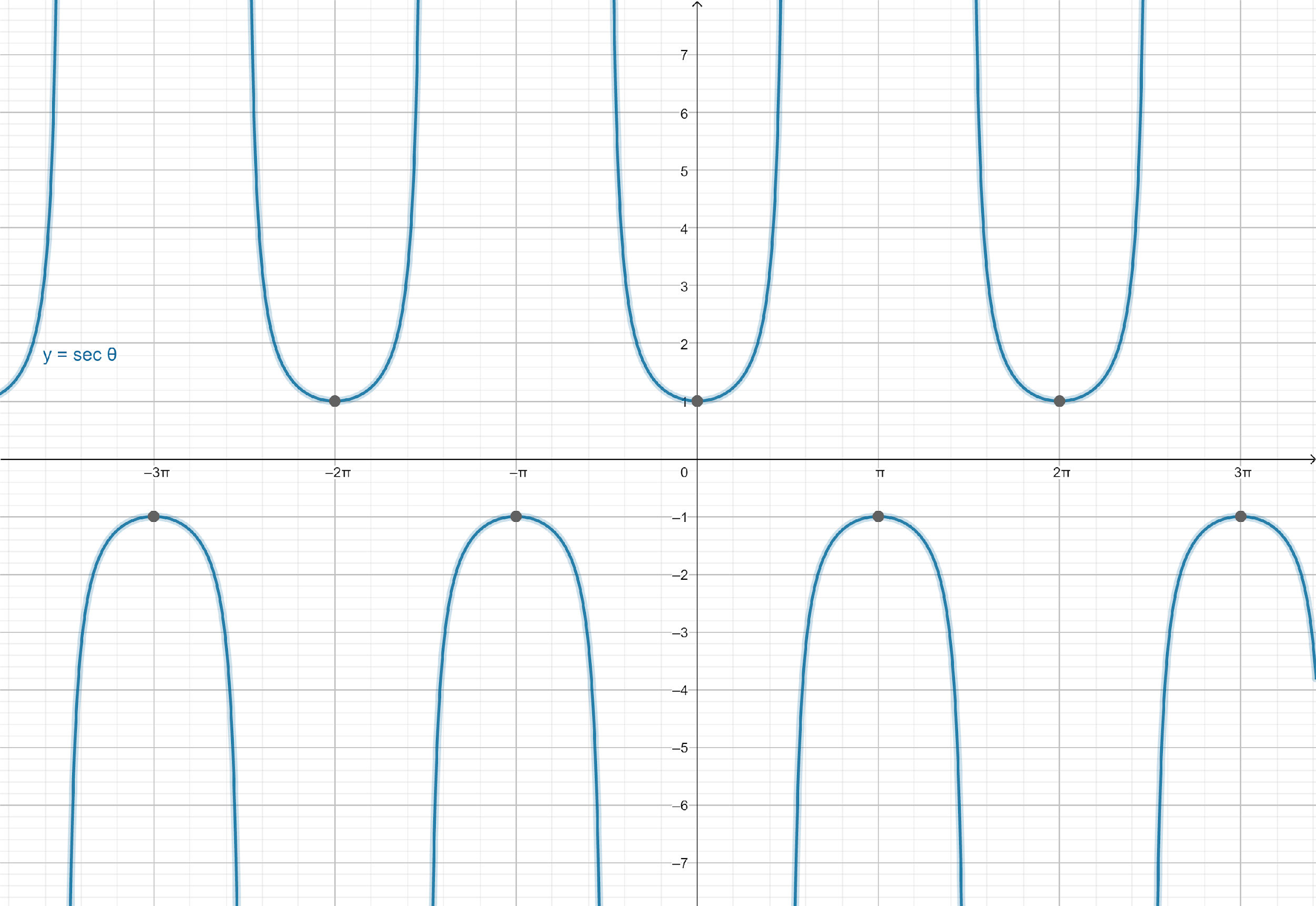
Note: $\sec 3\theta $ and $3\sec \theta $ are entirely different terms.
$3\sec \theta $ is thrice the secant of angle $\theta $. It lies between $ - 2$ and $2$.
$\sec 3\theta $ is the cosine of angle $3\theta $. It is three times the angle $\theta $. The value of $\sec 3\theta $ is between $ - 1$ and $1$.
Formula used:
For the graph of $y = a\sec \left( {bx - c} \right) + d$
Amplitude: None
Period$ = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| b \right|}}$
Phase Shift $ = \dfrac{c}{b}$
Vertical Shift $ = d$
Complete step by step answer:
We will use the form $y = a\sec \left( {bx - c} \right) + d$ to find the amplitude, period, phase shift, and vertical shift.
Compare the given equation $y = \sec \left( {3\theta } \right)$ with $y = a\sec \left( {bx - c} \right) + d$ and find variables $a,b,c$ and $d$.
$a = 1$, $b = 3$, $c = 0$ and $d = 0$.
Since the graph of the function $\sec $ does not have a maximum or minimum value, there can be no value for the amplitude.
Amplitude: None
Now, find the period using the formula $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| b \right|}}$.
So, we will calculate the period of the function using $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| b \right|}}$.
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| b \right|}}$
Replace $b$ with $3$ in the formula for period.
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| 3 \right|}}$
Solve the equation.
Here, we can observe that the absolute value is the distance between a number and zero.
The distance between $0$ and $3$ is $3$.
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
Divide $2\pi $ by $3$.
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
Now, we will find the phase shift using the formula $\dfrac{c}{b}$.
So, we will calculate the phase shift of the function from $\dfrac{c}{b}$.
Phase Shift: $\dfrac{c}{b}$
Here, replace the values of $c$ and $b$ in the equation for phase shift.
Phase Shift: $\dfrac{0}{3}$
Divide $0$ by $3$.
Phase Shift: $0$
Find the vertical shift $d$.
Vertical Shift: $0$
List the properties of the trigonometric function.
Amplitude: None
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
Phase Shift: $0$($0$ to the right)
Vertical Shift: $0$
Select a few points to graph.
Find the point at $\theta = 0$.
Replace the variable $\theta $ with $0$ in the expression.
$f\left( 0 \right) = \sec \left( {3 \times 0} \right)$
Simplify the result.
The exact value of $\sec \left( 0 \right)$ is $1$.
$f\left( 0 \right) = 1$
The final answer is $1$.
Find the point at $\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{{18}}$.
Replace the variable $\theta $ with $\dfrac{\pi }{{18}}$ in the expression.
$f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{{18}}} \right) = \sec \left( {3 \times \dfrac{\pi }{{18}}} \right)$
Simplify the result.
The exact value of $\sec \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right)$ is $\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }}$.
$f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{{18}}} \right) = \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
The final answer is $\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }}$.
Find the point at $\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{9}$.
Replace the variable $\theta $ with $\dfrac{\pi }{9}$ in the expression.
$f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{9}} \right) = \sec \left( {3 \times \dfrac{\pi }{9}} \right)$
Simplify the result.
The exact value of $\sec \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)$ is $2$.
$f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{9}} \right) = 2$
The final answer is $2$.
Find the point at $\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{3}$.
Replace the variable $\theta $ with $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$ in the expression.
$f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right) = \sec \left( {3 \times \dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)$
Simplify the result.
The exact value of $\sec \left( \pi \right)$ is $ - 1$.
$f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right) = - 1$
The final answer is $ - 1$.
Find the point at $\theta = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$.
Replace the variable $\theta $ with $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$ in the expression.
$f\left( {\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}} \right) = \sec \left( {3 \times \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}} \right)$
Simplify the result.
The exact value of $\sec \left( {2\pi } \right)$ is $1$.
$f\left( {\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}} \right) = 1$
The final answer is $1$.
List the points in a table.
| $x$ | $f\left( x \right)$ |
| $0$ | $1$ |
| $\dfrac{\pi }{{18}}$ | $\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ |
| $\dfrac{\pi }{9}$ | $ - 1$ |
| $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$ | $ - \dfrac{1}{2}$ |
| $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$ | $1$ |
The trigonometric function can be graphed using the amplitude, period, phase shift, vertical shift and the points.
Amplitude: None
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
Phase Shift: $0$($0$ to the right)
Vertical Shift: $0$
| $x$ | $f\left( x \right)$ |
| $0$ | $1$ |
| $\dfrac{\pi }{{18}}$ | $\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ |
| $\dfrac{\pi }{9}$ | $ - 1$ |
| $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$ | $ - \dfrac{1}{2}$ |
| $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$ | $1$ |

Note: $\sec 3\theta $ and $3\sec \theta $ are entirely different terms.
$3\sec \theta $ is thrice the secant of angle $\theta $. It lies between $ - 2$ and $2$.
$\sec 3\theta $ is the cosine of angle $3\theta $. It is three times the angle $\theta $. The value of $\sec 3\theta $ is between $ - 1$ and $1$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




