
How do you find the amplitude and period of f (x) = \[3\cos \left( \dfrac{2}{3} \right)x\]?
Answer
563.7k+ views
Hint: First understand the meaning of the terms ‘amplitude’ and ‘period’ of a function. Now, draw the graph of the function \[\cos x\] and observe the minimum and maximum value it approaches to find the amplitude of the given function f (x). Now, to find the period of f (x) apply the formula: - \[T'=\dfrac{T}{\left| a \right|}\], where T’ is the period of f (x), T is the period of \[\cos x\] and ‘a’ is coefficient of ‘x’ in the function f (x).
Complete step by step answer:
Here, we have been provided with the function, \[f\left( x \right)=3\cos \left( \dfrac{2}{3} \right)x\] and we are asked to find its amplitude and period. But first we need to understand the meaning of these two terms. So, let us check them one – by – one.
(i) Amplitude of a function is defined as the minimum and maximum value that a function can approach. Here, we have a cosine function. Let us draw its graph to check the minima and maximum of the function \[\cos x\].
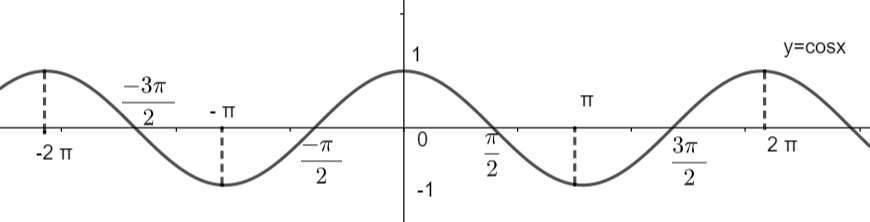
Clearly, we can see that the cosine function lies in the interval [-1, 1]. So, we can say that the range of \[\cos \left( \dfrac{2}{3} \right)x\] will be [-1, 1].
\[\Rightarrow -1\le \cos \left( \dfrac{2}{3} \right)x\le 1\]
Multiplying all the terms with 3, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow -3\le 3\cos \left( \dfrac{2}{3} \right)x\le 3 \\
& \Rightarrow -3\le f\left( x \right)\le 3 \\
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)\in \left[ -3,3 \right] \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the above relation represents the amplitude of f (x).
(ii) Now, the time period of a function is defined as the value of x after which the value of the function starts repeating itself. It is also simply called a period and the function is known as periodic function.
From the above graph, it can be clearly seen that the value of the function \[\cos x\] starts repeating itself after \[2\pi \], so it can be concluded that the period of \[\cos x\] is \[2\pi \]. Now, we have the function \[3\cos \left( \dfrac{2}{3} \right)x\]. Here, we have a linear term \[\left( \dfrac{2}{3} \right)x\] in place of x. We already know that, if T is the period of the function g (x) then the period of the function \[g\left( ax+b \right)\] is given as: - \[\dfrac{T}{\left| a \right|}\], where \[\left( ax+b \right)\] is linear in x. So, for the given function f (x), we have,
\[\because T=2\pi ,a=\dfrac{2}{3}\]
\[\Rightarrow T'=\] Time period of f (x)
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow T'=\dfrac{T}{\left| a \right|} \\
& \Rightarrow T'=\dfrac{2\pi }{\dfrac{2}{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow T'=\dfrac{3\times 2\pi }{2} \\
& \Rightarrow T'=3\pi \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the period of f (x) is \[3\pi \].
Note: One may note that the constant 3 that is multiplied to the cosine function in f (x) does not alter the value of T’. This is because it is a constant and has nothing to do with the domain of the function. However, it does alter the amplitude, i.e., range of the function. You must draw the graph before solving the question as it will help us to understand the situation in a better way. Remember the formula: - \[T'=\dfrac{T}{\left| a \right|}\] as it will be used in chapters like integration.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, we have been provided with the function, \[f\left( x \right)=3\cos \left( \dfrac{2}{3} \right)x\] and we are asked to find its amplitude and period. But first we need to understand the meaning of these two terms. So, let us check them one – by – one.
(i) Amplitude of a function is defined as the minimum and maximum value that a function can approach. Here, we have a cosine function. Let us draw its graph to check the minima and maximum of the function \[\cos x\].

Clearly, we can see that the cosine function lies in the interval [-1, 1]. So, we can say that the range of \[\cos \left( \dfrac{2}{3} \right)x\] will be [-1, 1].
\[\Rightarrow -1\le \cos \left( \dfrac{2}{3} \right)x\le 1\]
Multiplying all the terms with 3, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow -3\le 3\cos \left( \dfrac{2}{3} \right)x\le 3 \\
& \Rightarrow -3\le f\left( x \right)\le 3 \\
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)\in \left[ -3,3 \right] \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the above relation represents the amplitude of f (x).
(ii) Now, the time period of a function is defined as the value of x after which the value of the function starts repeating itself. It is also simply called a period and the function is known as periodic function.
From the above graph, it can be clearly seen that the value of the function \[\cos x\] starts repeating itself after \[2\pi \], so it can be concluded that the period of \[\cos x\] is \[2\pi \]. Now, we have the function \[3\cos \left( \dfrac{2}{3} \right)x\]. Here, we have a linear term \[\left( \dfrac{2}{3} \right)x\] in place of x. We already know that, if T is the period of the function g (x) then the period of the function \[g\left( ax+b \right)\] is given as: - \[\dfrac{T}{\left| a \right|}\], where \[\left( ax+b \right)\] is linear in x. So, for the given function f (x), we have,
\[\because T=2\pi ,a=\dfrac{2}{3}\]
\[\Rightarrow T'=\] Time period of f (x)
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow T'=\dfrac{T}{\left| a \right|} \\
& \Rightarrow T'=\dfrac{2\pi }{\dfrac{2}{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow T'=\dfrac{3\times 2\pi }{2} \\
& \Rightarrow T'=3\pi \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the period of f (x) is \[3\pi \].
Note: One may note that the constant 3 that is multiplied to the cosine function in f (x) does not alter the value of T’. This is because it is a constant and has nothing to do with the domain of the function. However, it does alter the amplitude, i.e., range of the function. You must draw the graph before solving the question as it will help us to understand the situation in a better way. Remember the formula: - \[T'=\dfrac{T}{\left| a \right|}\] as it will be used in chapters like integration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




