
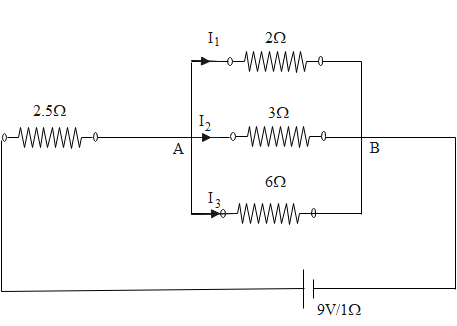
Find ${I_1}$ and ${I_2}$ in the given figure.
$
{\text{A}}{\text{. 2}}{\text{.0}}A{\text{, }}\dfrac{4}{3}A \\
{\text{B}}{\text{. 1}}A{\text{, }}\dfrac{2}{3}A \\
{\text{C}}{\text{. 2}}A{\text{, }}\dfrac{2}{3}A \\
{\text{D}}{\text{. 1}}A{\text{, }}\dfrac{1}{3}A \\
$

Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: We can calculate the total current in the circuit by using the Ohm’s law as values of voltage and resistance for battery are given. Then by using the facts that current remains same in series combination of resistance while the voltage remains same in the parallel combination of resistances, we can obtain the required answer.
Formula used:
The Ohm’s law for electrical circuits is given as
$V = IR$
Here V is the potential difference or voltage, I represents the current while R represents the resistance of the circuit.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given circuit, the battery has voltage 9V and the internal resistance of the battery is equal to 1 ohm.
The resultant of three resistances connected in parallel is calculated in the following way.
$
\dfrac{1}{{{R_P}}} = \dfrac{1}{2} + \dfrac{1}{3} + \dfrac{1}{6} = \dfrac{{3 + 2 + 1}}{6} = 1 \\
\Rightarrow {R_P} = 1V \\
$
Therefore, by using Ohm's law, we get the total current through the circuit to be equal to $\dfrac{{9V}}{{1\Omega + 1\Omega + 2.5\Omega }} = 2A$.
Since the current remains the same in the series combination of resistances, the total current through the three branches is 9A. Therefore, we can write that
${I_1} + {I_2} + {I_3} = 2A$
Now in parallel combinations, the voltage remains the same while it gets distributed between the resistances in series combination. Now the voltage through parallel branches is $2 \times {R_P} = 2V$
Since this voltage is the same for all three branches, we can now easily calculate the values of various currents from the resistances in the respective branches by using Ohm's law.
$
{I_1} = \dfrac{{{V_P}}}{{2\Omega }} = \dfrac{2}{2} = 1A \\
{I_2} = \dfrac{{{V_P}}}{{3\Omega }} = \dfrac{2}{3}A \\
$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: It should be noted that we can also verify if our answer is correct by calculating the current ${I_3}$ in the same way as the other two values have been found. If the sum of the three obtained values of current is equal to 2A then our answer is correct.
Formula used:
The Ohm’s law for electrical circuits is given as
$V = IR$
Here V is the potential difference or voltage, I represents the current while R represents the resistance of the circuit.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given circuit, the battery has voltage 9V and the internal resistance of the battery is equal to 1 ohm.
The resultant of three resistances connected in parallel is calculated in the following way.
$
\dfrac{1}{{{R_P}}} = \dfrac{1}{2} + \dfrac{1}{3} + \dfrac{1}{6} = \dfrac{{3 + 2 + 1}}{6} = 1 \\
\Rightarrow {R_P} = 1V \\
$
Therefore, by using Ohm's law, we get the total current through the circuit to be equal to $\dfrac{{9V}}{{1\Omega + 1\Omega + 2.5\Omega }} = 2A$.
Since the current remains the same in the series combination of resistances, the total current through the three branches is 9A. Therefore, we can write that
${I_1} + {I_2} + {I_3} = 2A$
Now in parallel combinations, the voltage remains the same while it gets distributed between the resistances in series combination. Now the voltage through parallel branches is $2 \times {R_P} = 2V$
Since this voltage is the same for all three branches, we can now easily calculate the values of various currents from the resistances in the respective branches by using Ohm's law.
$
{I_1} = \dfrac{{{V_P}}}{{2\Omega }} = \dfrac{2}{2} = 1A \\
{I_2} = \dfrac{{{V_P}}}{{3\Omega }} = \dfrac{2}{3}A \\
$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: It should be noted that we can also verify if our answer is correct by calculating the current ${I_3}$ in the same way as the other two values have been found. If the sum of the three obtained values of current is equal to 2A then our answer is correct.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




