
Find $i$ from the figure below.
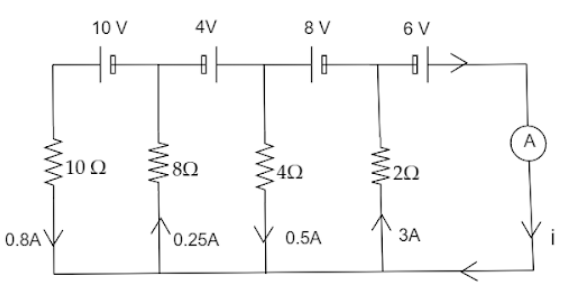

Answer
509.1k+ views
Hint: We will use Kirchhoff’s Current Law to find the value of $i$. At every node where current either concentrates or divert, the summation of current flowing inward or outward is equal to $0$. By substituting values and using the nodes from the diagram we will find $i$ in three steps.
Complete step by step answer:
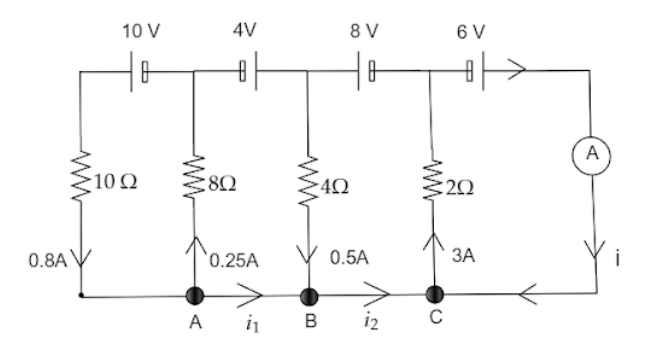
From the given diagram we can find out $i$, firstly, at node $A$ from the above figure using Kirchhoff’s Current Law we get that, $0.8{\text{ }}A$ current flows inward into the node $A$ while $0.25{\text{ }}A$ and ${i_1}$ current flows outward.So, the summation of current flowing inward is equal to outward flowing current.
$0.8 = 0.25 + {i_1} \\
\Rightarrow {i_1} = 0.55{\text{ }}A - - - - - \left( 1 \right) \\ $
Now, from node $B$ using the same Kirchhoff’s Law of current we get, $0.5{\text{ }}A$ current and ${i_1}$ current flows inward while ${i_2}$ flows outward from the circuit.Substituting the value of ${i_1}$ from equation $\left( 1 \right)$ we get,
$0.5 + 0.55 = {i_2} \\
\Rightarrow {i_2} = 1.05{\text{ }}A - - - - \left( 2 \right) \\ $
Similarly, at node $C$ we get to know that ${i_2}$ and $i$ flows inward into the node while $3{\text{ }}A$ flows outward the circuit,
${i_2} + i = 3$
Substituting the value of ${i_2}$ from equation $\left( 2 \right)$ we get,
$1.05 + i = 3 \\
\Rightarrow i = 1.95{\text{ }}A \\ $
Thus, we had found out that $i$ is equal to $1.95{\text{ }}A$.
Note: Kirchhoff’s Law (KCL) states that the total amount of current flowing into the circuit is equal to the total amount of current flowing outward from the circuit. For such type of problems we can use the Loop Method also. Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) states that the algebraic sum of all the voltages around a closed path is equal to $0$. Mesh Method can also be implied here but it is not very effective here and will become clumsy.
Complete step by step answer:

From the given diagram we can find out $i$, firstly, at node $A$ from the above figure using Kirchhoff’s Current Law we get that, $0.8{\text{ }}A$ current flows inward into the node $A$ while $0.25{\text{ }}A$ and ${i_1}$ current flows outward.So, the summation of current flowing inward is equal to outward flowing current.
$0.8 = 0.25 + {i_1} \\
\Rightarrow {i_1} = 0.55{\text{ }}A - - - - - \left( 1 \right) \\ $
Now, from node $B$ using the same Kirchhoff’s Law of current we get, $0.5{\text{ }}A$ current and ${i_1}$ current flows inward while ${i_2}$ flows outward from the circuit.Substituting the value of ${i_1}$ from equation $\left( 1 \right)$ we get,
$0.5 + 0.55 = {i_2} \\
\Rightarrow {i_2} = 1.05{\text{ }}A - - - - \left( 2 \right) \\ $
Similarly, at node $C$ we get to know that ${i_2}$ and $i$ flows inward into the node while $3{\text{ }}A$ flows outward the circuit,
${i_2} + i = 3$
Substituting the value of ${i_2}$ from equation $\left( 2 \right)$ we get,
$1.05 + i = 3 \\
\Rightarrow i = 1.95{\text{ }}A \\ $
Thus, we had found out that $i$ is equal to $1.95{\text{ }}A$.
Note: Kirchhoff’s Law (KCL) states that the total amount of current flowing into the circuit is equal to the total amount of current flowing outward from the circuit. For such type of problems we can use the Loop Method also. Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) states that the algebraic sum of all the voltages around a closed path is equal to $0$. Mesh Method can also be implied here but it is not very effective here and will become clumsy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




