
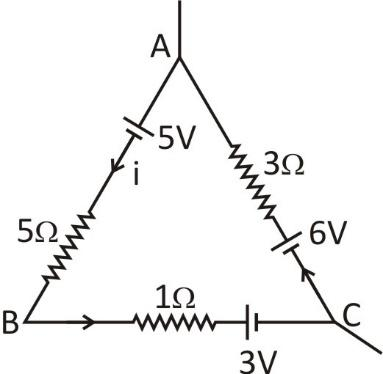
Find ‘i’ for the given loop.
A. $6/5A$
B. $8/9A$
C. $1/2A$
D. $1A$

Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: We can use Kirchhoff’s current law to find the currents flowing around more complex circuits. We hopefully know by now that the algebraic sum of all the currents at a node (junction point) is equal to zero and with this idea in mind, it is a simple case of determining the currents entering a node and those leaving the node.
Complete step by step answer:A cell or battery is drawn with a long line and a shorter line. The long line is the positive side and the short line is the negative side.
Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) is Kirchhoff’s first law that deals with the conservation of charge entering and leaving a junction.
Kirchhoff's Current Law or KCL, states that the “total current or charge entering a junction or node is exactly equal to the charge leaving the node as it has no other place to go except to leave, as no charge is lost within the node“.
We can use Kirchhoff’s current law to find the currents flowing around more complex circuits. We hopefully know by now that the algebraic sum of all the currents at a node (junction point) is equal to zero and with this idea in mind, it is a simple case of determining the currents entering a node and those leaving the node.
Applying Kirchoff's law starting from point A,
$5 - 5i - i - 3 + 6 - 3i = 0$
$\Rightarrow 8 - 9i = 0$
$\Rightarrow 9i = 8$
$\Rightarrow i = 8/9A$
Hence, option (B) is correct.
Note:Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL): “The algebraic sum of all currents entering and exiting a node must equal zero”
Complete step by step answer:A cell or battery is drawn with a long line and a shorter line. The long line is the positive side and the short line is the negative side.
Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) is Kirchhoff’s first law that deals with the conservation of charge entering and leaving a junction.
Kirchhoff's Current Law or KCL, states that the “total current or charge entering a junction or node is exactly equal to the charge leaving the node as it has no other place to go except to leave, as no charge is lost within the node“.
We can use Kirchhoff’s current law to find the currents flowing around more complex circuits. We hopefully know by now that the algebraic sum of all the currents at a node (junction point) is equal to zero and with this idea in mind, it is a simple case of determining the currents entering a node and those leaving the node.
Applying Kirchoff's law starting from point A,
$5 - 5i - i - 3 + 6 - 3i = 0$
$\Rightarrow 8 - 9i = 0$
$\Rightarrow 9i = 8$
$\Rightarrow i = 8/9A$
Hence, option (B) is correct.
Note:Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL): “The algebraic sum of all currents entering and exiting a node must equal zero”
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




