
How do you find an equation in standard form of the parabola passing through the points $\left( 1,1 \right)$, $\left( -1,-3 \right)$, $\left( -3,1 \right)$?
Answer
549k+ views
Hint: In this problem we need to calculate the equation of the parabola which passes through the given points. We have the standard equation of the parabola as $y=a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c$. So, we will substitute the given points in the standard form of the parabola and simplify the equation to get the system of linear equations in three variables $a$, $b$, $c$. Now we will solve the obtained system of linear equations and substitute the values of $a$, $b$, $c$ in the standard form of the parabola to get the required solution.
Complete step by step solution:
Given points, $\left( 1,1 \right)$, $\left( -1,-3 \right)$, $\left( -3,1 \right)$.
We have the standard form of the parabola as $y=a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c$.
Substituting the first point $\left( 1,1 \right)$ in the above equation, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 1=a{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}+b\left( 1 \right)+c \\
& \Rightarrow a+b+c=1....\left( \text{i} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the second point $\left( -1,-3 \right)$ in the equation of the parabola, then we will have
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow -3=a{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}+b\left( -1 \right)+c \\
& \Rightarrow a-b+c=-3....\left( \text{ii} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the third point $\left( -3,1 \right)$ in the equation of the parabola, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 1=a{{\left( -3 \right)}^{2}}+b\left( -3 \right)+c \\
& \Rightarrow 9a-3b+c=1....\left( \text{iii} \right) \\
\end{align}$
We have the three linear systems of equations in terms of $a$, $b$, $c$. To solve these equations, we are going to eliminate the term $c$ from all the equation by subtracting $\left( \text{i} \right)$ from $\left( \text{ii} \right)$ and $\left( \text{iii} \right)$.
Subtracting $\left( \text{i} \right)$ from $\left( \text{ii} \right)$, then we will have
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow a-b+c-\left( a+b+c \right)=-3-1 \\
& \Rightarrow a-b+c-a-b-c=-4 \\
& \Rightarrow -2b=-4 \\
\end{align}$
Dividing the above equation with $-2$ on both sides, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{-2b}{-2}=\dfrac{-4}{-2} \\
& \Rightarrow b=2 \\
\end{align}$
Subtracting equation $\left( \text{i} \right)$ from $\left( \text{iii} \right)$, then we will have
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 9a-3b+c-\left( a+b+c \right)=1-1 \\
& \Rightarrow 9a-3b+c-a-b-c=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 8a-4b=0 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the value of $b=2$ in the above equation, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 8a-4\left( 2 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 8a=8 \\
& \Rightarrow a=1 \\
\end{align}$
Up to now we have the values of $a=1$, $b=2$. To calculate the value of $c$ we can substitute the known values in any one of the equations we have.
Substituting the values $a=1$, $b=2$ in the equation $\left( \text{i} \right)$ and simplifying it, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow a+b+c=1 \\
& \Rightarrow 1+2+c=1 \\
& \Rightarrow c=1-3 \\
& \Rightarrow c=-2 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the values $a=1$, $b=2$ and $c=-2$ in the standard form of the parabola, then we will get the equation of required parabola as
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=\left( 1 \right){{x}^{2}}+\left( 2 \right)x-2 \\
& \therefore y={{x}^{2}}+2x-2 \\
\end{align}$
Hence the equation of the parabola passing through the given points $\left( 1,1 \right)$, $\left( -1,-3 \right)$, $\left( -3,1 \right)$ is $y={{x}^{2}}+2x-2$. The graph of the parabola will be
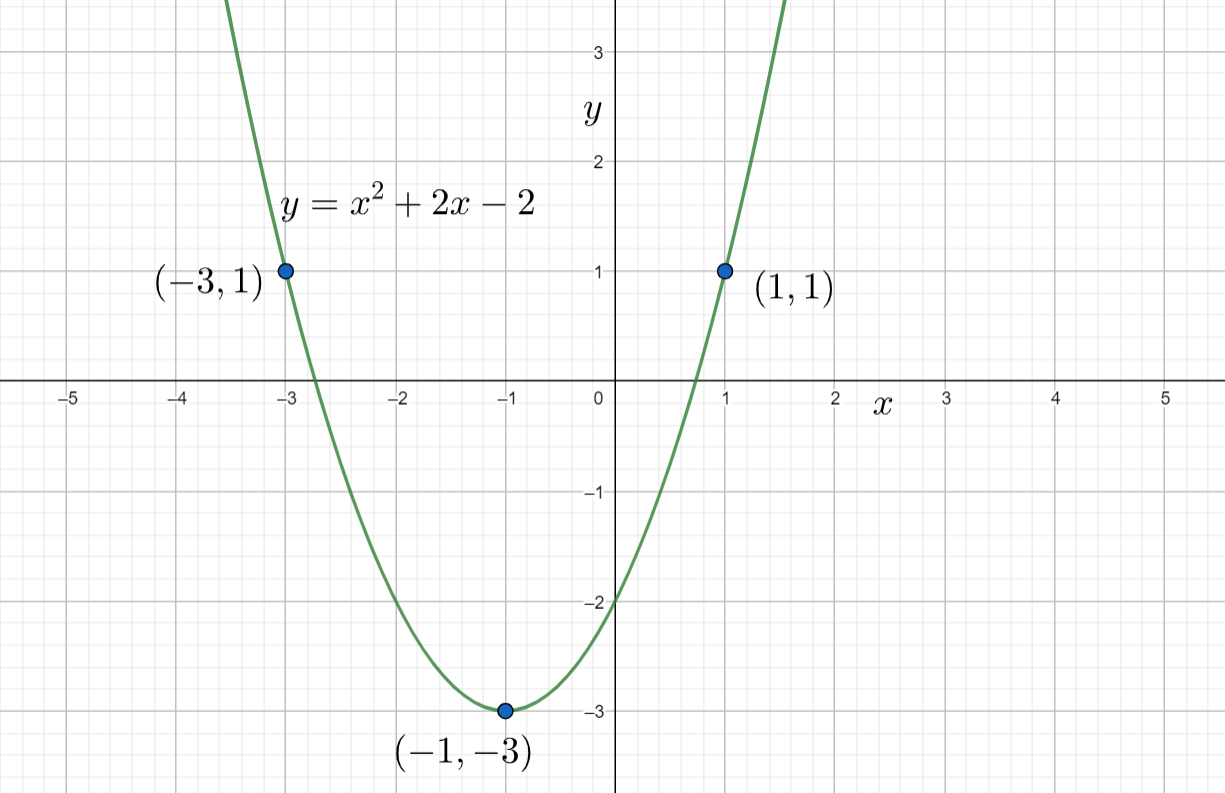
Note:
In this type of problems students may make mistakes at substituting the given points in the standard form of the equation. If the point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ lies on the parabola, then the equation of parabola must be satisfied by the point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ i.e., ${{y}_{1}}=a{{x}_{1}}^{2}+b{{x}_{1}}+c$. Students may write the equation as ${{x}_{1}}=a{{y}_{1}}^{2}+b{{y}_{1}}+c$ in hurry but it not the correct way to solve the problem.
Complete step by step solution:
Given points, $\left( 1,1 \right)$, $\left( -1,-3 \right)$, $\left( -3,1 \right)$.
We have the standard form of the parabola as $y=a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c$.
Substituting the first point $\left( 1,1 \right)$ in the above equation, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 1=a{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}+b\left( 1 \right)+c \\
& \Rightarrow a+b+c=1....\left( \text{i} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the second point $\left( -1,-3 \right)$ in the equation of the parabola, then we will have
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow -3=a{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}+b\left( -1 \right)+c \\
& \Rightarrow a-b+c=-3....\left( \text{ii} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the third point $\left( -3,1 \right)$ in the equation of the parabola, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 1=a{{\left( -3 \right)}^{2}}+b\left( -3 \right)+c \\
& \Rightarrow 9a-3b+c=1....\left( \text{iii} \right) \\
\end{align}$
We have the three linear systems of equations in terms of $a$, $b$, $c$. To solve these equations, we are going to eliminate the term $c$ from all the equation by subtracting $\left( \text{i} \right)$ from $\left( \text{ii} \right)$ and $\left( \text{iii} \right)$.
Subtracting $\left( \text{i} \right)$ from $\left( \text{ii} \right)$, then we will have
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow a-b+c-\left( a+b+c \right)=-3-1 \\
& \Rightarrow a-b+c-a-b-c=-4 \\
& \Rightarrow -2b=-4 \\
\end{align}$
Dividing the above equation with $-2$ on both sides, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{-2b}{-2}=\dfrac{-4}{-2} \\
& \Rightarrow b=2 \\
\end{align}$
Subtracting equation $\left( \text{i} \right)$ from $\left( \text{iii} \right)$, then we will have
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 9a-3b+c-\left( a+b+c \right)=1-1 \\
& \Rightarrow 9a-3b+c-a-b-c=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 8a-4b=0 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the value of $b=2$ in the above equation, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 8a-4\left( 2 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 8a=8 \\
& \Rightarrow a=1 \\
\end{align}$
Up to now we have the values of $a=1$, $b=2$. To calculate the value of $c$ we can substitute the known values in any one of the equations we have.
Substituting the values $a=1$, $b=2$ in the equation $\left( \text{i} \right)$ and simplifying it, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow a+b+c=1 \\
& \Rightarrow 1+2+c=1 \\
& \Rightarrow c=1-3 \\
& \Rightarrow c=-2 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the values $a=1$, $b=2$ and $c=-2$ in the standard form of the parabola, then we will get the equation of required parabola as
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=\left( 1 \right){{x}^{2}}+\left( 2 \right)x-2 \\
& \therefore y={{x}^{2}}+2x-2 \\
\end{align}$
Hence the equation of the parabola passing through the given points $\left( 1,1 \right)$, $\left( -1,-3 \right)$, $\left( -3,1 \right)$ is $y={{x}^{2}}+2x-2$. The graph of the parabola will be

Note:
In this type of problems students may make mistakes at substituting the given points in the standard form of the equation. If the point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ lies on the parabola, then the equation of parabola must be satisfied by the point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ i.e., ${{y}_{1}}=a{{x}_{1}}^{2}+b{{x}_{1}}+c$. Students may write the equation as ${{x}_{1}}=a{{y}_{1}}^{2}+b{{y}_{1}}+c$ in hurry but it not the correct way to solve the problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




