
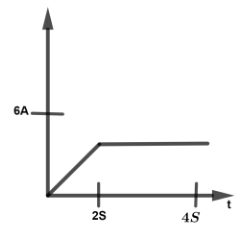
Figure shows the waveform of the current passing through an inductor of resistance $1\Omega $ and inductance $2H$. The energy absorbed by the inductor in the first four seconds is
A. $144J$
B. $98J$
C. $132J$
D. $168J$

Answer
515.4k+ views
Hint:There is a waveform of current passing through an inductor of resistance and inductor, from this we have to find the energy absorbed for the first four seconds. For total energy, it is the sum of kinetic and gravitational potential energy. By using this theory we are going to find the energy observed.
Complete step by step answer:
From the given data there is an inductor of resistance $1\Omega $ and inductance $2H$.By using these values only we are going to calculate the energy. Energy observed by inductor is given as,
${E_L} = \int\limits_0^t {Pdt} $
Whereas power $P = VI = I\left( {L\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}}} \right)$
So the equation is, ${E_L} = \int\limits_0^t {LI\left( {\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}}} \right)dt} $
In the diagram already given the time of the waveform that is from, $0 \leqslant t \leqslant 4\sec $
For $0 \leqslant t \leqslant 4\sec $
${E_L} = 2\int\limits_0^4 {I\left( {\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}}} \right)dt} \\
\Rightarrow {E_L} = 2\int\limits_0^2 {I\left( 3 \right)dt + 2\int\limits_2^4 {I\left( 0 \right)dt} } \\ $
In the above equation, $\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} = 3$ and time is also changed, $0 \leqslant t \leqslant 2$
Therefore for $\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} = 0$ for this the time is, $2 < t < 4$
${E_L} = 6\int\limits_0^2 {Idt} \\
\Rightarrow {E_L} = 6 \\ $
Which is under the area of curve,
${E_L} = 6 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \times 2 \times 6 \\
\Rightarrow {E_L} = 36J \\ $
Now we are discussing about the energy observed by $1\Omega $ resistor is,
${E_R} = \int\limits_0^1 {{I^2}Rdt} $
Here
$I = 3t,0 \leqslant t \leqslant 2 \\
\Rightarrow I = 6A,2 \leqslant t \leqslant 4 \\ $
Therefore the above equation is,
${E_R} = \int\limits_0^2 {{{\left( {3t} \right)}^2} \times 1dt} + \int\limits_2^4 {{{\left( 6 \right)}^2}dt} \\
\Rightarrow {E_R} = 9 \times {\left[ {\dfrac{{{t^3}}}{3}} \right]_0}^2 + 36{\left[ t \right]^4}_2 \\
\Rightarrow {E_R} = 24 + 72 \\
\Rightarrow {E_R} = 96J \\ $
Now to calculate the total energy observed in first four seconds is,
$E = {E_L} + {E_R}$
As already we have calculated the above values, by substituting those values we get the total energy,
$E = 36 + 96 \\
\therefore E = 132\,J \\ $
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:For calculating the total energy first we have calculated the value of energy in inductance and then calculated the energy in resistance later by adding those two energies we have the total energy in the inductor for the first four seconds. Hence we have derived the problem.
Complete step by step answer:
From the given data there is an inductor of resistance $1\Omega $ and inductance $2H$.By using these values only we are going to calculate the energy. Energy observed by inductor is given as,
${E_L} = \int\limits_0^t {Pdt} $
Whereas power $P = VI = I\left( {L\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}}} \right)$
So the equation is, ${E_L} = \int\limits_0^t {LI\left( {\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}}} \right)dt} $
In the diagram already given the time of the waveform that is from, $0 \leqslant t \leqslant 4\sec $
For $0 \leqslant t \leqslant 4\sec $
${E_L} = 2\int\limits_0^4 {I\left( {\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}}} \right)dt} \\
\Rightarrow {E_L} = 2\int\limits_0^2 {I\left( 3 \right)dt + 2\int\limits_2^4 {I\left( 0 \right)dt} } \\ $
In the above equation, $\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} = 3$ and time is also changed, $0 \leqslant t \leqslant 2$
Therefore for $\dfrac{{dI}}{{dt}} = 0$ for this the time is, $2 < t < 4$
${E_L} = 6\int\limits_0^2 {Idt} \\
\Rightarrow {E_L} = 6 \\ $
Which is under the area of curve,
${E_L} = 6 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \times 2 \times 6 \\
\Rightarrow {E_L} = 36J \\ $
Now we are discussing about the energy observed by $1\Omega $ resistor is,
${E_R} = \int\limits_0^1 {{I^2}Rdt} $
Here
$I = 3t,0 \leqslant t \leqslant 2 \\
\Rightarrow I = 6A,2 \leqslant t \leqslant 4 \\ $
Therefore the above equation is,
${E_R} = \int\limits_0^2 {{{\left( {3t} \right)}^2} \times 1dt} + \int\limits_2^4 {{{\left( 6 \right)}^2}dt} \\
\Rightarrow {E_R} = 9 \times {\left[ {\dfrac{{{t^3}}}{3}} \right]_0}^2 + 36{\left[ t \right]^4}_2 \\
\Rightarrow {E_R} = 24 + 72 \\
\Rightarrow {E_R} = 96J \\ $
Now to calculate the total energy observed in first four seconds is,
$E = {E_L} + {E_R}$
As already we have calculated the above values, by substituting those values we get the total energy,
$E = 36 + 96 \\
\therefore E = 132\,J \\ $
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:For calculating the total energy first we have calculated the value of energy in inductance and then calculated the energy in resistance later by adding those two energies we have the total energy in the inductor for the first four seconds. Hence we have derived the problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




