
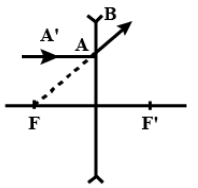
Figure shows ray $AB$ that has passed through a diverging lens. Construct the path of the ray up to the lens if the position of its foci is known.


Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint: A lens is a transmissive optical instrument that uses refraction to concentrate or scatter a light ray. A simple lens is made up of a single transparent piece, while a compound lens is made up of multiple simple lenses arranged around a common axis.
Complete answer:
Divergent lens, negative lens, concave lens, and dispersive lens are all terms for the same thing. When parallel light rays leave the lens, they fan out – and thereby diverge – away from the optical axis. Plano-concave, double concave, or concave-convex lens surfaces are possible. A diverging lens's edge is often thicker than the middle.
In a diverging mirror, parallel light rays appear to form simulated representations of the source from which they originate. A concave lens is one that has at least one inwardly curving surface. It is a diverging mirror, which means that light rays refracted into it are scattered out. The centre of a concave lens is narrower than the edges.Now according to the question, the ray that passes through a diverging lens is denoted by $AB$.The focal length of the lens is denoted by the letter $F$.
When the $AB$ ray is extended backward, it appears to travel around the focal point (F).And where the incident ray is parallel to the principal axis is this feasible. An incident ray parallel to the principal would tend to travel through focus with a diverging prism.
Note: In an optical structure like a camera lens, microscope, or telescopic eye, an optical axis is a line along which there is some degree of rotational symmetry. The optical axis is an imaginary line that, up to first approximation, describes the direction along which light propagates through the device.
Complete answer:
Divergent lens, negative lens, concave lens, and dispersive lens are all terms for the same thing. When parallel light rays leave the lens, they fan out – and thereby diverge – away from the optical axis. Plano-concave, double concave, or concave-convex lens surfaces are possible. A diverging lens's edge is often thicker than the middle.
In a diverging mirror, parallel light rays appear to form simulated representations of the source from which they originate. A concave lens is one that has at least one inwardly curving surface. It is a diverging mirror, which means that light rays refracted into it are scattered out. The centre of a concave lens is narrower than the edges.Now according to the question, the ray that passes through a diverging lens is denoted by $AB$.The focal length of the lens is denoted by the letter $F$.
When the $AB$ ray is extended backward, it appears to travel around the focal point (F).And where the incident ray is parallel to the principal axis is this feasible. An incident ray parallel to the principal would tend to travel through focus with a diverging prism.

Note: In an optical structure like a camera lens, microscope, or telescopic eye, an optical axis is a line along which there is some degree of rotational symmetry. The optical axis is an imaginary line that, up to first approximation, describes the direction along which light propagates through the device.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




